In my previous post on this topic, I brought up concerns regarding the paucity of useful information in EI SLP reports for children under 3 years of age and made some constructive suggestions of how that could be rectified. In 2013, I had written about another significant concern, which involved neurodevelopmental pediatricians (rather than SLPs), diagnosing Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS), without the adequate level of training and knowledge regarding motor speech disorders. Today, I wanted to combine both topics and delve deeper into another area of EI SLP evaluations, namely, assessments of toddlers with suspected motor speech disorders.
Firstly, it is important to note that CAS is disturbingly overdiagnosed. A cursory review of both parent and professional social media forums quickly reveals that this diagnosis is doled out like candy by both SLPs and medical professionals alike, often without much training and knowledge regarding the disorder in question. The child is under 3, has a limited verbal output coupled with a number of phonological processes, and the next thing you know, s/he is labeled as having Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS). But is this diagnosis truly that straightforward?
Let us begin with the fact that all reputable organizations involved in the dissemination of information on the topic of CAS (e.g., ASHA, CASANA, etc.), strongly discourage the diagnosis of CAS in children under three years of age with limited verbal output, and limited time spent in EBP therapy specifically targeting the remediation of motor speech disorders.
 Assessment of motor speech disorders in young children requires solid knowledge and expertise. That is because CAS has a number of overlapping symptoms with other speech sound disorders (e.g., severe phonological disorder, dysarthria, etc). Furthermore, symptoms which may initially appear as CAS may change during the course of intervention by the time the child is older (e.g., 3 years of age) which is why diagnosing toddlers under 3 years of age is very problematic and the use of “suspected” or “working” diagnosis is recommended (Davis & Velleman, 2000) in order to avoid misdiagnosis. Finally, the diagnosis of CAS is also problematic due to the fact that there are still to this day no valid or reliable standardized assessments sensitive to CAS detection (McCauley & Strand, 2008).
Assessment of motor speech disorders in young children requires solid knowledge and expertise. That is because CAS has a number of overlapping symptoms with other speech sound disorders (e.g., severe phonological disorder, dysarthria, etc). Furthermore, symptoms which may initially appear as CAS may change during the course of intervention by the time the child is older (e.g., 3 years of age) which is why diagnosing toddlers under 3 years of age is very problematic and the use of “suspected” or “working” diagnosis is recommended (Davis & Velleman, 2000) in order to avoid misdiagnosis. Finally, the diagnosis of CAS is also problematic due to the fact that there are still to this day no valid or reliable standardized assessments sensitive to CAS detection (McCauley & Strand, 2008).
In March 2017, Dr. Edythe Strand wrote an excellent article for the ASHA Leader entitled: “Appraising Apraxia“, in which she used a case study of a 3-year-old boy to describe how a differential diagnosis for CAS can be performed. She reviewed CAS characteristics, informal assessment protocols, aspects of diagnosis and treatment, and even included ‘Examples of Diagnostic Statements for CAS’ (which illustrate how clinicians can formulate their impressions regarding the child’s strengths and needs without explicitly labeling the child’s diagnosis as CAS).
Today, I’d like to share what information I tend to include in speech-language reports geared towards the assessing motor speech disorders in children under 3 years of age. I have a specific former client in mind for whom a differential diagnosis was particularly needed. Here’s why.
This particular 30-month client, TQ, (I did mention that I get quite a few clients for assessment around that age), was brought in due to parental concerns over her significantly reduced speech and expressive language abilities characterized by unintelligible “babbling-like” utterances and lack of expressive language. All of TQ’s developmental milestones with the exception of speech and language had been achieved grossly at age expectancy. She began limitedly producing word approximations at ~16 months of age but at 30 months of age, her verbal output was still very restricted. She mainly communicated via gestures, pointing, word approximations, and a handful of signs.
Interestingly, as an infant, she had a restricted lingual frenulum. However, since it did not affect her ability to feed, no surgical intervention was needed. Indeed, TQ presented with an adequate lingual movement for both feeding and speech sound production, so her ankyloglossia (or anterior tongue tie) was definitely not the culprit which caused her to have limited speech production.
 Prior to being reevaluated by me, TQ underwent an early intervention assessment at ~26 months of age. She was diagnosed with CAS by an evaluating SLP and was found to be eligible for speech-language services, which she began receiving shortly thereafter. However, Mrs. Q noted that TQ was making very few gains in therapy and her treating SLP was uncertain regarding why her progress in therapy was so limited. Mrs. Q was also rather uncertain that TQ’s diagnosis of CAS was indeed a correct one, which was another reason why she sought a second opinion.
Prior to being reevaluated by me, TQ underwent an early intervention assessment at ~26 months of age. She was diagnosed with CAS by an evaluating SLP and was found to be eligible for speech-language services, which she began receiving shortly thereafter. However, Mrs. Q noted that TQ was making very few gains in therapy and her treating SLP was uncertain regarding why her progress in therapy was so limited. Mrs. Q was also rather uncertain that TQ’s diagnosis of CAS was indeed a correct one, which was another reason why she sought a second opinion.
Assessment of TQ’s social-emotional functioning, play skills, and receptive language (via a combination of Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000), REEL-3, & PLS-5) quickly revealed that she was a very bright little girl who was developing on target in all of the tested areas. Assessment of TQ’s expressive language (via REEL-3, PLS-5 & LUI*), revealed profoundly impaired, expressive language abilities. But due to which cause?
Despite lacking verbal speech, TQ’s communicative frequency (how often she attempted to spontaneously and appropriately initiate interactions with others), as well as her communicative intent (e.g., gaining attention, making requests, indicating protests, etc), were judged to be appropriate for her age. She was highly receptive to language stimulation given tangible reinforcements and as the assessment progressed she was observed to significantly increase the number and variety of vocalizations and word approximations including delayed imitation of words and sounds containing bilabial and alveolar nasal phonemes.
For the purpose of TQ’s speech assessment, I was interested in gaining knowledge regarding the following:
- Automatic vs. volitional control
- Simple vs. complex speech production
- Consistency of productions on repetitions of the same words/word approximations
- Vowel Productions
- Imitation abilities
- Prosody
- Phonetic inventory
- Phonotactic Constraints
- Stimulability
 TQ’s oral peripheral examination yielded no difficulties with oral movements during non-speaking as well as speaking tasks. She was able to blow bubbles, stick out tongue, smile, etc as well as spontaneously vocalize without any difficulties. Her voice quality, pitch, loudness, and resonance during vocalizations and approximated utterances were judged to be appropriate for age and gender. Her prosody and fluency could not be determined due to lack of spontaneously produced continuous verbal output.
TQ’s oral peripheral examination yielded no difficulties with oral movements during non-speaking as well as speaking tasks. She was able to blow bubbles, stick out tongue, smile, etc as well as spontaneously vocalize without any difficulties. Her voice quality, pitch, loudness, and resonance during vocalizations and approximated utterances were judged to be appropriate for age and gender. Her prosody and fluency could not be determined due to lack of spontaneously produced continuous verbal output.
- Phonetic inventory of all the sounds TQ produced during the assessment is as follows:
- Consonants: plosive nasals (/m/) and alveolars (/t/, /d/, n), as well as a glide (/w/)
- Vowels: (/a/, /e/, /i/, /o/)
- TQ’s phonotactic repertoire was primarily comprised of word approximations restricted to specific sounds and consisted of CV (e.g., ne), VCV (e.g., ada), CVC (e.g., nyam), CVCV (e.g., nada), VCVC (e.g., adat), CVCVCV (nadadi), VCVCV(e.g., adada) syllable shapes
- TQ’s speech intelligibility in known and unknown contexts was profoundly reduced to unfamiliar listeners. However, her word approximations were consistent across all productions.
- Due to the above I could not perform an in-depth phonological processes analysis
However, by this time I had already formulated a working hypothesis regarding TQ’s speech production difficulties. Based on her speech sound assessment TQ presented with severe phonological disorder characterized by restricted sound inventory, simplification of sound sequences, as well as patterns of sound use errors (e.g., predominance of alveolar /d/ and nasal /n/ sounds when attempting to produce most word approximations) in speech (Stoel-Gammon, 1987).
TQ’s difficulties were not consistent with the diagnosis Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS) at that time due to the following:
- Adequate and varied production of vowels
- Lack of restricted use of syllables during verbalizations (TQ was observed to make verbalizations up to 3 syllables in length)
- Lack of disruptions in rate, rhythm, and stress of speech
- Frequent and spontaneous use of consistently produced verbalizations
- Lack of verbal groping behaviors when producing word-approximations
- Good control of pitch, loudness and vocal quality during vocalizations
 I felt that the diagnosis of CAS was not applicable because TQ lacked a verbal lexicon and no specific phonological intervention techniques had been trialed with her during the course of her brief therapy (~4 months) to elicit word productions (Davis & Velleman, 2000; Strand, 2003). While her EI speech therapist documented that therapy has primarily focused on ‘oral motor activities to increase TQ’s awareness of her articulators and to increase imitation of oral motor movements’, I knew that until a variety of phonological/motor-speech specific interventions had been trialed over a period of time (at least ~6 months as per Davis & Velleman, 2000) the diagnosis of CAS could not be reliably made.
I felt that the diagnosis of CAS was not applicable because TQ lacked a verbal lexicon and no specific phonological intervention techniques had been trialed with her during the course of her brief therapy (~4 months) to elicit word productions (Davis & Velleman, 2000; Strand, 2003). While her EI speech therapist documented that therapy has primarily focused on ‘oral motor activities to increase TQ’s awareness of her articulators and to increase imitation of oral motor movements’, I knew that until a variety of phonological/motor-speech specific interventions had been trialed over a period of time (at least ~6 months as per Davis & Velleman, 2000) the diagnosis of CAS could not be reliably made.
I still, however, wanted to be cautious as there were a few red flags I had noted which may have potentially indicative of a non-CAS motor speech involvement, due to which I wanted to include some recommendations pertaining to motor speech remediation.
Now it is possible that after 6 months of intensive application of EBP phonological and motor speech approaches TQ would have turned 3 and still presented with highly restricted speech sound inventory and profoundly impaired speech production, making her eligible for the diagnosis of CAS in earnest. However, at the time of my assessment, making such diagnosis in view of all the available evidence would have been both clinically inappropriate and unethical.
So what were my recommendations you may ask? Well, I provisionally diagnosed TQ with a severe phonological disorder and recommended that among a variety of phonologically-based approaches to trial, an EBP approach to the treatment of motor speech disorders be also used with her for a period of 6 months to determine if it would expedite speech gains.
 *For those of you who are interested in the latest EBP treatment for motor speech disorders, current evidence supports the use of the Rapid Syllable Transition Treatment (ReST). ReST is a free EBP treatment developed by the SLPs at the University of Sydney, which uses nonsense words, designed to help children coordinate movements across syllables in long words and phrases as well as helps them learn new speech movements. It is, however, important to note for young children with highly restricted sound inventories, characterized by a lack of syllable production, ReST will not be applicable. For them, the Integral Stimulation/Dynamic Temporal and Tactile Cueing (DTTC) approaches do have some limited empirical support.
*For those of you who are interested in the latest EBP treatment for motor speech disorders, current evidence supports the use of the Rapid Syllable Transition Treatment (ReST). ReST is a free EBP treatment developed by the SLPs at the University of Sydney, which uses nonsense words, designed to help children coordinate movements across syllables in long words and phrases as well as helps them learn new speech movements. It is, however, important to note for young children with highly restricted sound inventories, characterized by a lack of syllable production, ReST will not be applicable. For them, the Integral Stimulation/Dynamic Temporal and Tactile Cueing (DTTC) approaches do have some limited empirical support.
I also made sure to make a note in my report regarding the inappropriate use of non-speech oral motor exercises (NSOMEs) in therapy, indicating that there is NO research to support the use of NSOMEs to stimulate speech production (Lof, 2010).
In addition to the trialing of phonological and motor based approaches I also emphasized the need to establish consistent lexicon via development of functional words needed in daily communication and listed a number of examples across several categories. I made recommendations regarding select approaches and treatment techniques to trial in therapy, as well as suggestions for expansion of sounds and structures. Finally, I made suggestions for long and short term therapy goals for a period of 6 months to trial with TQ in therapy and provided relevant references to support the claims I’ve made in my report.
You may be interested in knowing that nowadays TQ is doing quite well, and at this juncture, she is still, ineligible for the diagnosis CAS (although she needs careful ongoing monitoring with respect to the development of reading difficulties when she is older).
 Now I know that some clinicians will be quick to ask me: “What’s the harm in overdiagnosing CAS if the child’s speech production will still be treated via the application of motor speech production principles?” Well, aside from the fact that it’s obviously unethical and can result in terrifying the parents into obtaining all sorts of questionable and even downright harmful bunk treatments for their children, the treatment may only be limitedly appropriate, and may not result in the best possible outcomes for a particular child. To illustrate, TQ never presented with CAS and as such, while she may have initially limitedly benefited from the application of motor speech principles to address her speech production, shortly thereafter, the application of the principles of the dynamic systems theory is what brought about significant changes in her phonological repertoire.
Now I know that some clinicians will be quick to ask me: “What’s the harm in overdiagnosing CAS if the child’s speech production will still be treated via the application of motor speech production principles?” Well, aside from the fact that it’s obviously unethical and can result in terrifying the parents into obtaining all sorts of questionable and even downright harmful bunk treatments for their children, the treatment may only be limitedly appropriate, and may not result in the best possible outcomes for a particular child. To illustrate, TQ never presented with CAS and as such, while she may have initially limitedly benefited from the application of motor speech principles to address her speech production, shortly thereafter, the application of the principles of the dynamic systems theory is what brought about significant changes in her phonological repertoire.
That is why the correct diagnosis is so important for young children under 3 years of age. But before it can be made, extensive (reputable and evidence supported) training and education are needed by evaluating SLPs on the assessment and treatment of motor speech disorders in young children.
References:
- Davis, B & Velleman, S (2000). Differential diagnosis and treatment of developmental apraxia of speech in infants and toddlers”. The Transdisciplinary Journal. 10 (3): 177 – 192.
- Lof, G., & Watson, M. (2010). Five reasons why nonspeech oral-motor exercises do not work. Perspectives on School-Based Issues, 11.109-117.
- McCauley RJ, Strand EA. (2008). A Review of Standardized Tests of Nonverbal Oral and Speech Motor Performance in Children. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 17,81-91.
- McCauley R.J., Strand E., Lof, G.L., Schooling T. & Frymark, T. (2009). Evidence-Based Systematic Review: Effects of Nonspeech Oral Motor Exercises on Speech, American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 18, 343-360.
- Murray, E., McCabe, P. & Ballard, K.J. (2015). A Randomized Control Trial of Treatments for Childhood Apraxia of Speech. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research 58 (3) 669-686.
- Stoel-Gammon, C. (1987). Phonological skills of 2-year-olds. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 18, 323-329.
- Strand, E (2003). Childhood apraxia of speech: suggested diagnostic markers for the young child. In Shriberg, L & Campbell, T (Eds) Proceedings of the 2002 childhood apraxia of speech research symposium. Carlsbad, CA: Hendrix Foundation.
- Strand, E, McCauley, R, Weigand, S, Stoeckel, R & Baas, B (2013) A Motor Speech Assessment for Children with Severe Speech Disorders: Reliability and Validity Evidence. Journal of Speech Language and Hearing Research, vol 56; 505-520.
 Recently I wrote a blog post regarding how SLPs can qualitatively assess writing abilities of adolescent learners. Today due to popular demand, I am offering suggestions regarding how SLPs can assess writing abilities of early-elementary-aged students with suspected learning and literacy deficits. For the purpose of this post, I will focus on assessing writing of second-grade students since by second-grade students are expected to begin producing simple written compositions several sentences in length (CCSS).
Recently I wrote a blog post regarding how SLPs can qualitatively assess writing abilities of adolescent learners. Today due to popular demand, I am offering suggestions regarding how SLPs can assess writing abilities of early-elementary-aged students with suspected learning and literacy deficits. For the purpose of this post, I will focus on assessing writing of second-grade students since by second-grade students are expected to begin producing simple written compositions several sentences in length (CCSS). Now let’s apply the above expectations to a writing sample of a 2nd-grade student whose parents are concerned with her writing abilities in addition to other language and learning concerns. This student was provided with a typical second grade writing prompt: “Imagine you are going to the North Pole. How are you going to get there? What would you bring with you? You have 15 minutes to write your story. Please make your story at least 4 sentences long.”
Now let’s apply the above expectations to a writing sample of a 2nd-grade student whose parents are concerned with her writing abilities in addition to other language and learning concerns. This student was provided with a typical second grade writing prompt: “Imagine you are going to the North Pole. How are you going to get there? What would you bring with you? You have 15 minutes to write your story. Please make your story at least 4 sentences long.” Now let us select a few writing goals for this student.
Now let us select a few writing goals for this student. The former looks at such writing aspects as the use of correct spelling, punctuation, and capitalization, paragraph formation, etc.
The former looks at such writing aspects as the use of correct spelling, punctuation, and capitalization, paragraph formation, etc. With respect to syntax, a typical student that age is expected to write complex sentences possessing nominal, adverbial, as well as relative clauses.
With respect to syntax, a typical student that age is expected to write complex sentences possessing nominal, adverbial, as well as relative clauses.
 Based on the above-written sample, the student’s persuasive composition content (thought formulation and elaboration) was judged to be significantly immature for his grade level and is commensurate with the abilities of a much younger student. The student’s composition contained several emerging claims that suggested a vague position. However, though the student attempted to back up his opinion and support his position (animals should not be performing in circuses), ultimately he was unable to do so in a coherent and cohesive manner.
Based on the above-written sample, the student’s persuasive composition content (thought formulation and elaboration) was judged to be significantly immature for his grade level and is commensurate with the abilities of a much younger student. The student’s composition contained several emerging claims that suggested a vague position. However, though the student attempted to back up his opinion and support his position (animals should not be performing in circuses), ultimately he was unable to do so in a coherent and cohesive manner.
 For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the
For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the  Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the
Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the 
 Today I am writing my last installment in the five-part early intervention assessment series. My
Today I am writing my last installment in the five-part early intervention assessment series. My 
 Spoon Stripping and Mouth Closure: During the yogurt presentation, AK’s spoon stripping abilities and mouth closure were deemed good (adequate) when fed by a caregiver and fair when AK fed self (incomplete food stripping from the spoon was observed due to only partial mouth closure). According to parental report, AK’s spoon stripping abilities have improved in recent months. Ms. K was observed to present spoon upwardly in AK’s mouth and hold it still until AK placed her lips firmly around the spoon and initiated spoon stripping. Since this strategy is working adequately for all parties in question no further recommendations regarding spoon feeding are necessary at this time. Skill monitoring is recommended on an ongoing basis for further refinement.
Spoon Stripping and Mouth Closure: During the yogurt presentation, AK’s spoon stripping abilities and mouth closure were deemed good (adequate) when fed by a caregiver and fair when AK fed self (incomplete food stripping from the spoon was observed due to only partial mouth closure). According to parental report, AK’s spoon stripping abilities have improved in recent months. Ms. K was observed to present spoon upwardly in AK’s mouth and hold it still until AK placed her lips firmly around the spoon and initiated spoon stripping. Since this strategy is working adequately for all parties in question no further recommendations regarding spoon feeding are necessary at this time. Skill monitoring is recommended on an ongoing basis for further refinement.  Cup and Straw Drinking: AK was also observed to drink 40 mls of water from a cup given parental assistance. Minor anterior spillage was intermittently noted during liquid intake. It is recommended that the parents modify cup presentation by providing AK with a plastic cup with two handles on each side, which would improve her ability to grasp and maintain hold on cup while drinking.
Cup and Straw Drinking: AK was also observed to drink 40 mls of water from a cup given parental assistance. Minor anterior spillage was intermittently noted during liquid intake. It is recommended that the parents modify cup presentation by providing AK with a plastic cup with two handles on each side, which would improve her ability to grasp and maintain hold on cup while drinking. In the past several years, due to an influx of adolescent students with language and learning difficulties on my caseload, I have begun to research in depth aspects of adolescent
In the past several years, due to an influx of adolescent students with language and learning difficulties on my caseload, I have begun to research in depth aspects of adolescent  For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled:
For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: 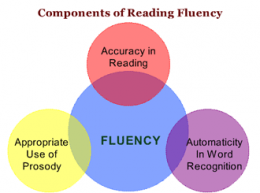 Reading Fluency: TS’s reading fluency (automaticity, prosody, accuracy and speed, expression, intonation, and phrasing) during the reading task was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody.
Reading Fluency: TS’s reading fluency (automaticity, prosody, accuracy and speed, expression, intonation, and phrasing) during the reading task was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody. Text Vocabulary Comprehension:
Text Vocabulary Comprehension: Impressions: Clinical below grade-level reading comprehension assessment reading revealed that TS presents with a number of reading related difficulties. TS’s reading fluency was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody. TS’s understanding as well as his verbal summary of the presented text was immature for his age and was characterized by impaired gestalt processing of information resulting in an ineffective and confusing summarization. While TS’s text-based vocabulary knowledge was deemed to be grossly adequate for his age, his reading comprehension abilities were judged to be impaired for his age. Therapeutic intervention is strongly recommended to improve TS’s reading abilities. (See Impressions and Recommendations sections for further details).
Impressions: Clinical below grade-level reading comprehension assessment reading revealed that TS presents with a number of reading related difficulties. TS’s reading fluency was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody. TS’s understanding as well as his verbal summary of the presented text was immature for his age and was characterized by impaired gestalt processing of information resulting in an ineffective and confusing summarization. While TS’s text-based vocabulary knowledge was deemed to be grossly adequate for his age, his reading comprehension abilities were judged to be impaired for his age. Therapeutic intervention is strongly recommended to improve TS’s reading abilities. (See Impressions and Recommendations sections for further details). To date, I have written 3 posts on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first post offered suggestions on what information to include in
To date, I have written 3 posts on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first post offered suggestions on what information to include in 




 If I happen to know that a child is highly verbal, I may actually include a
If I happen to know that a child is highly verbal, I may actually include a  To illustrate, below is a narrative sample from a typically developing 2-year-old child based on the Mercer Mayer’s classic wordless picture book: “Frog Where Are You?”
To illustrate, below is a narrative sample from a typically developing 2-year-old child based on the Mercer Mayer’s classic wordless picture book: “Frog Where Are You?” Of course, a play assessment for this age group is a must. Since, in my first post,
Of course, a play assessment for this age group is a must. Since, in my first post,  For toddlers 18+months of age, I like using the Language Use Inventory (LUI)
For toddlers 18+months of age, I like using the Language Use Inventory (LUI)  In addition to the LUI, I recently discovered the
In addition to the LUI, I recently discovered the 




 In this post, I am continuing my series of articles on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first installment in this series offered suggestions regarding what information to include in
In this post, I am continuing my series of articles on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first installment in this series offered suggestions regarding what information to include in  As mentioned in my previous post on
As mentioned in my previous post on  Developmental Milestones expected of a 16-18 months old toddler:
Developmental Milestones expected of a 16-18 months old toddler:  Play Skills/Routines:
Play Skills/Routines: Materials to use with the child to promote language and play:
Materials to use with the child to promote language and play:  Core vocabulary categories for listening and speaking:
Core vocabulary categories for listening and speaking: Prior to being reevaluated by me, TQ underwent an early intervention assessment at ~26 months of age. She was diagnosed with CAS by an evaluating SLP and was found to be eligible for speech-language services, which she began receiving shortly thereafter. However, Mrs. Q noted that TQ was making very few gains in therapy and her treating SLP was uncertain regarding why her progress in therapy was so limited. Mrs. Q was also rather uncertain that TQ’s diagnosis of CAS was indeed a correct one, which was another reason why she sought a second opinion.
Prior to being reevaluated by me, TQ underwent an early intervention assessment at ~26 months of age. She was diagnosed with CAS by an evaluating SLP and was found to be eligible for speech-language services, which she began receiving shortly thereafter. However, Mrs. Q noted that TQ was making very few gains in therapy and her treating SLP was uncertain regarding why her progress in therapy was so limited. Mrs. Q was also rather uncertain that TQ’s diagnosis of CAS was indeed a correct one, which was another reason why she sought a second opinion. TQ’s oral peripheral examination yielded no difficulties with oral movements during non-speaking as well as speaking tasks. She was able to blow bubbles, stick out tongue, smile, etc as well as spontaneously vocalize without any difficulties. Her voice quality, pitch, loudness, and resonance during vocalizations and approximated utterances were judged to be appropriate for age and gender. Her prosody and fluency could not be determined due to lack of spontaneously produced continuous verbal output.
TQ’s oral peripheral examination yielded no difficulties with oral movements during non-speaking as well as speaking tasks. She was able to blow bubbles, stick out tongue, smile, etc as well as spontaneously vocalize without any difficulties. Her voice quality, pitch, loudness, and resonance during vocalizations and approximated utterances were judged to be appropriate for age and gender. Her prosody and fluency could not be determined due to lack of spontaneously produced continuous verbal output. I felt that the diagnosis of CAS was not applicable because TQ lacked a verbal lexicon and no specific phonological intervention techniques had been trialed with her during the course of her brief therapy (~4 months) to elicit word productions (Davis & Velleman, 2000; Strand, 2003). While her EI speech therapist documented that therapy has primarily focused on ‘oral motor activities to increase TQ’s awareness of her articulators and to increase imitation of oral motor movements’, I knew that until a variety of phonological/motor-speech specific interventions had been trialed over a period of time (at least ~6 months as per Davis & Velleman, 2000) the diagnosis of CAS could not be reliably made.
I felt that the diagnosis of CAS was not applicable because TQ lacked a verbal lexicon and no specific phonological intervention techniques had been trialed with her during the course of her brief therapy (~4 months) to elicit word productions (Davis & Velleman, 2000; Strand, 2003). While her EI speech therapist documented that therapy has primarily focused on ‘oral motor activities to increase TQ’s awareness of her articulators and to increase imitation of oral motor movements’, I knew that until a variety of phonological/motor-speech specific interventions had been trialed over a period of time (at least ~6 months as per Davis & Velleman, 2000) the diagnosis of CAS could not be reliably made. *For those of you who are interested in the latest EBP treatment for motor speech disorders, current evidence supports the use of the
*For those of you who are interested in the latest EBP treatment for motor speech disorders, current evidence supports the use of the  Now I know that some clinicians will be quick to ask me: “What’s the harm in overdiagnosing CAS if the child’s speech production will still be treated via the application of motor speech production principles?” Well, aside from the fact that it’s obviously unethical and can result in terrifying the parents into obtaining all sorts of
Now I know that some clinicians will be quick to ask me: “What’s the harm in overdiagnosing CAS if the child’s speech production will still be treated via the application of motor speech production principles?” Well, aside from the fact that it’s obviously unethical and can result in terrifying the parents into obtaining all sorts of  Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age.
Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age. Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age.
Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age. At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to
At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to  Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers.
Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers.