 Picture books are absolutely wonderful for both assessment and treatment purposes! They are terrific as narrative elicitation aids for children of various ages, ranging from pre-K through fourth grade. They are amazing treatment aids for addressing a variety of speech, language, and literacy goals that extend far beyond narrative production. Continue reading Speech, Language, and Literacy Fun with Helen Lester’s Picture Books
Picture books are absolutely wonderful for both assessment and treatment purposes! They are terrific as narrative elicitation aids for children of various ages, ranging from pre-K through fourth grade. They are amazing treatment aids for addressing a variety of speech, language, and literacy goals that extend far beyond narrative production. Continue reading Speech, Language, and Literacy Fun with Helen Lester’s Picture Books
Category: Elementary
Identifying Word Finding Deficits in Narrative Retelling of School-Aged Children
 In the past, I have written several posts on the topic of word finding difficulties (HERE and HERE) as well as narrative assessments (HERE and HERE) of school-aged children. Today I am combining these posts together by offering suggestions on how SLPs can identify word finding difficulties in narrative samples of school-aged children. Continue reading Identifying Word Finding Deficits in Narrative Retelling of School-Aged Children
In the past, I have written several posts on the topic of word finding difficulties (HERE and HERE) as well as narrative assessments (HERE and HERE) of school-aged children. Today I am combining these posts together by offering suggestions on how SLPs can identify word finding difficulties in narrative samples of school-aged children. Continue reading Identifying Word Finding Deficits in Narrative Retelling of School-Aged Children
Analyzing Narratives of School-Aged Children

As mentioned previously, for elicitation purposes, I frequently use the books recommended by the SALT Software website, which include: ‘Frog Where Are You?’ by Mercer Mayer, ‘Pookins Gets Her Way‘ and ‘A Porcupine Named Fluffy‘ by Helen Lester, as well as ‘Dr. DeSoto‘ by William Steig. Continue reading Analyzing Narratives of School-Aged Children
Do Our Therapy Goals Make Sense or How to Create Functional Language Intervention Targets
 In the past several years, I wrote a series of posts on the topic of improving clinical practices in speech-language pathology. Some of these posts were based on my clinical experience as backed by research, while others summarized key point from articles written by prominent colleagues in our field such as Dr. Alan Kamhi, Dr. David DeBonnis, Dr. Andrew Vermiglio, etc.
In the past several years, I wrote a series of posts on the topic of improving clinical practices in speech-language pathology. Some of these posts were based on my clinical experience as backed by research, while others summarized key point from articles written by prominent colleagues in our field such as Dr. Alan Kamhi, Dr. David DeBonnis, Dr. Andrew Vermiglio, etc.
In the past, I have highlighted several articles from the 2014 LSHSS clinical forum entitled: Improving Clinical Practice. Today I would like to explicitly summarize another relevant article written by Dr. Wallach in 2014, entitled “Improving Clinical Practice: A School-Age and School-Based Perspective“, which discusses how to change the “persistence of traditional practices” in order to make our language interventions more functional and meaningful for students with language learning difficulties. Continue reading Do Our Therapy Goals Make Sense or How to Create Functional Language Intervention Targets
Clinical Assessment of Elementary-Aged Students Writing Abilities : Suggestions for SLPs
 Recently I wrote a blog post regarding how SLPs can qualitatively assess writing abilities of adolescent learners. Today due to popular demand, I am offering suggestions regarding how SLPs can assess writing abilities of early-elementary-aged students with suspected learning and literacy deficits. For the purpose of this post, I will focus on assessing writing of second-grade students since by second-grade students are expected to begin producing simple written compositions several sentences in length (CCSS).
Recently I wrote a blog post regarding how SLPs can qualitatively assess writing abilities of adolescent learners. Today due to popular demand, I am offering suggestions regarding how SLPs can assess writing abilities of early-elementary-aged students with suspected learning and literacy deficits. For the purpose of this post, I will focus on assessing writing of second-grade students since by second-grade students are expected to begin producing simple written compositions several sentences in length (CCSS).
So how can we analyze the writing samples of young learners? For starters, it is important to know what the typical writing expectations look like for 2nd-grade students. Here’s is a sampling of typical expectations for second graders as per several sources (e.g., CCSS, Reading Rockets, Time4Writing, etc.)
- With respect to penmanship, students are expected to write legibly.
- With respect to grammar, students are expected to identify and correctly use basic parts of speech such as nouns and verbs.
- With respect to sentence structure students are expected to distinguish between complete and incomplete sentences as well as use correct subject/verb/noun/pronoun agreements and correct verb tenses in simple and compound sentences.
- With respect to punctuation, students are expected to use periods correctly at the end of sentences. They are expected to use commas in sentences with dates and items in a series.
- With respect to capitalization, students are expected to capitalize proper nouns, words at the beginning of sentences, letter salutations, months and days of the week, as well as titles and initials of people.
- With respect to spelling, students are expected to spell CVC (e.g., tap), CVCe (e.g., tape), as well as CCVC words (e.g., trap), high frequency regular and irregular spelled words (e.g., were, said, why, etc), basic inflectional endings (e.g., –ed, -ing, -s, etc), as well as to recognize select orthographic patterns and rules (e.g., when to spell /k/ or /c/ in CVC and CVCe word, how to drop one vowel (e.g., /y/) and replace it with another /i/, etc.)
 Now let’s apply the above expectations to a writing sample of a 2nd-grade student whose parents are concerned with her writing abilities in addition to other language and learning concerns. This student was provided with a typical second grade writing prompt: “Imagine you are going to the North Pole. How are you going to get there? What would you bring with you? You have 15 minutes to write your story. Please make your story at least 4 sentences long.”
Now let’s apply the above expectations to a writing sample of a 2nd-grade student whose parents are concerned with her writing abilities in addition to other language and learning concerns. This student was provided with a typical second grade writing prompt: “Imagine you are going to the North Pole. How are you going to get there? What would you bring with you? You have 15 minutes to write your story. Please make your story at least 4 sentences long.”
The following is the transcribed story produced by her. “I am going in the north pole. I am going to bring food my mom toy’s stoft (stuffed) animals. I am so icsited (excited). So we are going in a box. We are going to go done (down) the stars (stairs) with the box and wate (wait) intile (until) the male (mail) is hear (here).”
Analysis: The student’s written composition content (thought formulation and elaboration) was judged to be impaired for her grade level. According to the CCSS, 2d grade students are expected to ‘”write narratives in which recount a well-elaborated event or short sequence of events, include details to describe actions, thoughts, and feelings, use temporal words to signal event order, and provide a sense of closure.” However, the above narrative sample by no means satisfies this requirement. The student’s writing was excessively misspelled, as well as lacked organization and clarity of message. While portions of her narrative appropriately addressed the question with respect to whom and what she was going to bring on her travels, her narrative quickly lost coherence by her 4th sentence, when she wrote: “So we are going in a box” with further elaborations regarding what she meant by that sentence. Second-grade students are expected to engage in basic editing and revision of their work. This student only took four minutes to compose the above-written sample and as such had more than adequate amount of time to review the question as well as her response for spelling and punctuation errors as well as for clarity of message, which she did not do. Furthermore, despite being provided with a written prompt which contained the correct capitalization of a place: “North Pole”, the student was not observed to capitalize it in her writing, which indicates ongoing executive function difficulties with the respect to proofreading and attention to details.
Impressions: Clinical assessment of the student’s writing revealed difficulties in the areas of spelling, capitalization, message clarity as well as lack of basic proofreading and editing, which require therapeutic intervention.
 Now let us select a few writing goals for this student.
Now let us select a few writing goals for this student.
Long-Term Goals: Student will improve her writing abilities for academic purposes.
- Short-Term Goals
- Student will label parts of speech (e.g., adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, etc.) in compound sentences.
- Student will use declarative and interrogative sentence types for story composition purposes
- Student will correctly use past, present, and future verb tenses during writing tasks.
- Student will use basic punctuation at the sentence level (e.g., commas, periods, and apostrophes in singular possessives, etc.).
- Student will use basic capitalization at the sentence level (e.g., capitalize proper nouns, words at the beginning of sentences, months and days of the week, etc.).
- Student will proofread her work via reading aloud for clarity
- Student will edit her work for correct grammar, punctuation, and capitalization
Notice the above does not contain any spelling goals. That is because given the complexity of her spelling profile I prefer to tackle her spelling needs in a separate post, which discusses spelling development, assessment, as well as intervention recommendations for students with spelling deficits.
There you have it. A quick and easy qualitative writing assessment for elementary-aged students which can help determine the extent of the student’s writing difficulties as well as establish a few writing remediation targets for intervention purposes.
Using a different type of writing assessment with your students? Please share the details below so we can all benefit from each others knowledge of assessment strategies.
It’s All Due to …Language: How Subtle Symptoms Can Cause Serious Academic Deficits
 Scenario: Len is a 7-2-year-old, 2nd-grade student who struggles with reading and writing in the classroom. He is very bright and has a high average IQ, yet when he is speaking he frequently can’t get his point across to others due to excessive linguistic reformulations and word-finding difficulties. The problem is that Len passed all the typical educational and language testing with flying colors, receiving average scores across the board on various tests including the Woodcock-Johnson Fourth Edition (WJ-IV) and the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-5 (CELF-5). Stranger still is the fact that he aced Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing, Second Edition (CTOPP-2), with flying colors, so he is not even eligible for a “dyslexia” diagnosis. Len is clearly struggling in the classroom with coherently expressing self, telling stories, understanding what he is reading, as well as putting his thoughts on paper. His parents have compiled impressively huge folders containing examples of his struggles. Yet because of his performance on the basic standardized assessment batteries, Len does not qualify for any functional assistance in the school setting, despite being virtually functionally illiterate in second grade.
Scenario: Len is a 7-2-year-old, 2nd-grade student who struggles with reading and writing in the classroom. He is very bright and has a high average IQ, yet when he is speaking he frequently can’t get his point across to others due to excessive linguistic reformulations and word-finding difficulties. The problem is that Len passed all the typical educational and language testing with flying colors, receiving average scores across the board on various tests including the Woodcock-Johnson Fourth Edition (WJ-IV) and the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-5 (CELF-5). Stranger still is the fact that he aced Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing, Second Edition (CTOPP-2), with flying colors, so he is not even eligible for a “dyslexia” diagnosis. Len is clearly struggling in the classroom with coherently expressing self, telling stories, understanding what he is reading, as well as putting his thoughts on paper. His parents have compiled impressively huge folders containing examples of his struggles. Yet because of his performance on the basic standardized assessment batteries, Len does not qualify for any functional assistance in the school setting, despite being virtually functionally illiterate in second grade.
The truth is that Len is quite a familiar figure to many SLPs, who at one time or another have encountered such a student and asked for guidance regarding the appropriate accommodations and services for him on various SLP-geared social media forums. But what makes Len such an enigma, one may inquire? Surely if the child had tangible deficits, wouldn’t standardized testing at least partially reveal them?
Well, it all depends really, on what type of testing was administered to Len in the first place. A few years ago I wrote a post entitled: “What Research Shows About the Functional Relevance of Standardized Language Tests“. What researchers found is that there is a “lack of a correlation between frequency of test use and test accuracy, measured both in terms of sensitivity/specificity and mean difference scores” (Betz et al, 2012, 141). Furthermore, they also found that the most frequently used tests were the comprehensive assessments including the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals and the Preschool Language Scale as well as one-word vocabulary tests such as the Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test”. Most damaging finding was the fact that: “frequently SLPs did not follow up the comprehensive standardized testing with domain-specific assessments (critical thinking, social communication, etc.) but instead used the vocabulary testing as a second measure”.(Betz et al, 2012, 140)
In other words, many SLPs only use the tests at hand rather than the RIGHT tests aimed at identifying the student’s specific deficits. But the problem doesn’t actually stop there. Due to the variation in psychometric properties of various tests, many children with language impairment are overlooked by standardized tests by receiving scores within the average range or not receiving low enough scores to qualify for services.
Thus, “the clinical consequence is that a child who truly has a language impairment has a roughly equal chance of being correctly or incorrectly identified, depending on the test that he or she is given.” Furthermore, “even if a child is diagnosed accurately as language impaired at one point in time, future diagnoses may lead to the false perception that the child has recovered, depending on the test(s) that he or she has been given (Spaulding, Plante & Farinella, 2006, 69).”
There’s of course yet another factor affecting our hypothetical client and that is his relatively young age. This is especially evident with many educational and language testing for children in the 5-7 age group. Because the bar is set so low, concept-wise for these age-groups, many children with moderate language and literacy deficits can pass these tests with flying colors, only to be flagged by them literally two years later and be identified with deficits, far too late in the game. Coupled with the fact that many SLPs do not utilize non-standardized measures to supplement their assessments, Len is in a pretty serious predicament.
But what if there was a do-over? What could we do differently for Len to rectify this situation? For starters, we need to pay careful attention to his deficits profile in order to choose appropriate tests to evaluate his areas of needs. The above can be accomplished via a number of ways. The SLP can interview Len’s teacher and his caregiver/s in order to obtain a summary of his pressing deficits. Depending on the extent of the reported deficits the SLP can also provide them with a referral checklist to mark off the most significant areas of need.
In Len’s case, we already have a pretty good idea regarding what’s going on. We know that he passed basic language and educational testing, so in the words of Dr. Geraldine Wallach, we need to keep “peeling the onion” via the administration of more sensitive tests to tap into Len’s reported areas of deficits which include: word-retrieval, narrative production, as well as reading and writing.
 For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS), which was developed to identify language and literacy disorders, has good psychometric properties, and contains subtests for assessment of relevant skills such as reading fluency, reading comprehension, phonological awareness, spelling, as well as writing in school-age children.
For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS), which was developed to identify language and literacy disorders, has good psychometric properties, and contains subtests for assessment of relevant skills such as reading fluency, reading comprehension, phonological awareness, spelling, as well as writing in school-age children.
 Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the Social Language Development Test Elementary (SLDTE). Here’s why. Research indicates that narrative weaknesses significantly correlate with social communication deficits (Norbury, Gemmell & Paul, 2014). As such, it’s not just children with Autism Spectrum Disorders who present with impaired narrative abilities. Many children with developmental language impairment (DLD) (#devlangdis) can present with significant narrative deficits affecting their social and academic functioning, which means that their social communication abilities need to be tested to confirm/rule out presence of these difficulties.
Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the Social Language Development Test Elementary (SLDTE). Here’s why. Research indicates that narrative weaknesses significantly correlate with social communication deficits (Norbury, Gemmell & Paul, 2014). As such, it’s not just children with Autism Spectrum Disorders who present with impaired narrative abilities. Many children with developmental language impairment (DLD) (#devlangdis) can present with significant narrative deficits affecting their social and academic functioning, which means that their social communication abilities need to be tested to confirm/rule out presence of these difficulties.
However, standardized tests are not enough, since even the best-standardized tests have significant limitations. As such, several non-standardized assessments in the areas of narrative production, reading, and writing, may be recommended for Len to meaningfully supplement his testing.
Let’s begin with an informal narrative assessment which provides detailed information regarding microstructural and macrostructural aspects of storytelling as well as child’s thought processes and socio-emotional functioning. My nonstandardized narrative assessments are based on the book elicitation recommendations from the SALT website. For 2nd graders, I use the book by Helen Lester entitled Pookins Gets Her Way. I first read the story to the child, then cover up the words and ask the child to retell the story based on pictures. I read the story first because: “the model narrative presents the events, plot structure, and words that the narrator is to retell, which allows more reliable scoring than a generated story that can go in many directions” (Allen et al, 2012, p. 207).
As the child is retelling his story I digitally record him using the Voice Memos application on my iPhone, for a later transcription and thorough analysis. During storytelling, I only use the prompts: ‘What else can you tell me?’ and ‘Can you tell me more?’ to elicit additional information. I try not to prompt the child excessively since I am interested in cataloging all of his narrative-based deficits. After I transcribe the sample, I analyze it and make sure that I include the transcription and a detailed write-up in the body of my report, so parents and professionals can see and understand the nature of the child’s errors/weaknesses.
 Now we are ready to move on to a brief nonstandardized reading assessment. For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: Reading for Comprehension, which contains books for grades 1-8. After I confirm with either the parent or the child’s teacher that the selected passage is reflective of the complexity of work presented in the classroom for his grade level, I ask the child to read the text. As the child is reading, I calculate the correct number of words he reads per minute as well as what type of errors the child is exhibiting during reading. Then I ask the child to state the main idea of the text, summarize its key points as well as define select text embedded vocabulary words and answer a few, verbally presented reading comprehension questions. After that, I provide the child with accompanying 5 multiple choice question worksheet and ask the child to complete it. I analyze my results in order to determine whether I have accurately captured the child’s reading profile.
Now we are ready to move on to a brief nonstandardized reading assessment. For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: Reading for Comprehension, which contains books for grades 1-8. After I confirm with either the parent or the child’s teacher that the selected passage is reflective of the complexity of work presented in the classroom for his grade level, I ask the child to read the text. As the child is reading, I calculate the correct number of words he reads per minute as well as what type of errors the child is exhibiting during reading. Then I ask the child to state the main idea of the text, summarize its key points as well as define select text embedded vocabulary words and answer a few, verbally presented reading comprehension questions. After that, I provide the child with accompanying 5 multiple choice question worksheet and ask the child to complete it. I analyze my results in order to determine whether I have accurately captured the child’s reading profile.
Finally, if any additional information is needed, I administer a nonstandardized writing assessment, which I base on the Common Core State Standards for 2nd grade. For this task, I provide a student with a writing prompt common for second grade and give him a period of 15-20 minutes to generate a writing sample. I then analyze the writing sample with respect to contextual conventions (punctuation, capitalization, grammar, and syntax) as well as story composition (overall coherence and cohesion of the written sample).
The above relatively short assessment battery (2 standardized tests and 3 informal assessment tasks) which takes approximately 2-2.5 hours to administer, allows me to create a comprehensive profile of the child’s language and literacy strengths and needs. It also allows me to generate targeted goals in order to begin effective and meaningful remediation of the child’s deficits.
Children like Len will, unfortunately, remain unidentified unless they are administered more sensitive tasks to better understand their subtle pattern of deficits. Consequently, to ensure that they do not fall through the cracks of our educational system due to misguided overreliance on a limited number of standardized assessments, it is very important that professionals select the right assessments, rather than the assessments at hand, in order to accurately determine the child’s areas of needs.
References:
- Allen, M, Ukrainetz, T & Carswell, A (2012) The narrative language performance of three types of at-risk first-grade readers. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 43(2), 205-221.
- Betz et al. (2013) Factors Influencing the Selection of Standardized Tests for the Diagnosis of Specific Language Impairment. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 44, 133-146.
- Hasbrouck, J. & Tindal, G. A. (2006). Oral reading fluency norms: A valuable assessment tool for reading teachers. The Reading Teacher. 59(7), 636-644.).
- Norbury, C. F., Gemmell, T., & Paul, R. (2014). Pragmatics abilities in narrative production: a cross-disorder comparison. Journal of child language, 41(03), 485-510.
- Peña, E.D., Spaulding, T.J., & Plante, E. (2006). The Composition of Normative Groups and Diagnostic Decision Making: Shooting Ourselves in the Foot. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 15, 247-254.
- Spaulding, Plante & Farinella (2006) Eligibility Criteria for Language Impairment: Is the Low End of Normal Always Appropriate? Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 37, 61-72.
- Spaulding, Szulga, & Figueria (2012) Using Norm-Referenced Tests to Determine Severity of Language Impairment in Children: Disconnect Between U.S. Policy Makers and Test Developers. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research. 43, 176-190.
Making Our Interventions Count or What’s Research Got To Do With It?
 Two years ago I wrote a blog post entitled: “What’s Memes Got To Do With It?” which summarized key points of Dr. Alan G. Kamhi’s 2004 article: “A Meme’s Eye View of Speech-Language Pathology“. It delved into answering the following question: “Why do some terms, labels, ideas, and constructs [in our field] prevail whereas others fail to gain acceptance?”.
Two years ago I wrote a blog post entitled: “What’s Memes Got To Do With It?” which summarized key points of Dr. Alan G. Kamhi’s 2004 article: “A Meme’s Eye View of Speech-Language Pathology“. It delved into answering the following question: “Why do some terms, labels, ideas, and constructs [in our field] prevail whereas others fail to gain acceptance?”.
Today I would like to reference another article by Dr. Kamhi written in 2014, entitled “Improving Clinical Practices for Children With Language and Learning Disorders“.
This article was written to address the gaps between research and clinical practice with respect to the implementation of EBP for intervention purposes.
Dr. Kamhi begins the article by posing 10 True or False questions for his readers:
- Learning is easier than generalization.
- Instruction that is constant and predictable is more effective than instruction that varies the conditions of learning and practice.
- Focused stimulation (massed practice) is a more effective teaching strategy than varied stimulation (distributed practice).
- The more feedback, the better.
- Repeated reading of passages is the best way to learn text information.
- More therapy is always better.
- The most effective language and literacy interventions target processing limitations rather than knowledge deficits.
- Telegraphic utterances (e.g., push ball, mommy sock) should not be provided as input for children with limited language.
- Appropriate language goals include increasing levels of mean length of utterance (MLU) and targeting Brown’s (1973) 14 grammatical morphemes.
- Sequencing is an important skill for narrative competence.
Guess what? Only statement 8 of the above quiz is True! Every other statement from the above is FALSE!
Now, let’s talk about why that is!
 First up is the concept of learning vs. generalization. Here Dr. Kamhi discusses that some clinicians still possess an “outdated behavioral view of learning” in our field, which is not theoretically and clinically useful. He explains that when we are talking about generalization – what children truly have a difficulty with is “transferring narrow limited rules to new situations“. “Children with language and learning problems will have difficulty acquiring broad-based rules and modifying these rules once acquired, and they also will be more vulnerable to performance demands on speech production and comprehension (Kamhi, 1988)” (93). After all, it is not “reasonable to expect children to use language targets consistently after a brief period of intervention” and while we hope that “language intervention [is] designed to lead children with language disorders to acquire broad-based language rules” it is a hugely difficult task to undertake and execute.
First up is the concept of learning vs. generalization. Here Dr. Kamhi discusses that some clinicians still possess an “outdated behavioral view of learning” in our field, which is not theoretically and clinically useful. He explains that when we are talking about generalization – what children truly have a difficulty with is “transferring narrow limited rules to new situations“. “Children with language and learning problems will have difficulty acquiring broad-based rules and modifying these rules once acquired, and they also will be more vulnerable to performance demands on speech production and comprehension (Kamhi, 1988)” (93). After all, it is not “reasonable to expect children to use language targets consistently after a brief period of intervention” and while we hope that “language intervention [is] designed to lead children with language disorders to acquire broad-based language rules” it is a hugely difficult task to undertake and execute.
Next, Dr. Kamhi addresses the issue of instructional factors, specifically the importance of “varying conditions of instruction and practice“. Here, he addresses the fact that while contextualized instruction is highly beneficial to learners unless we inject variability and modify various aspects of instruction including context, composition, duration, etc., we ran the risk of limiting our students’ long-term outcomes.
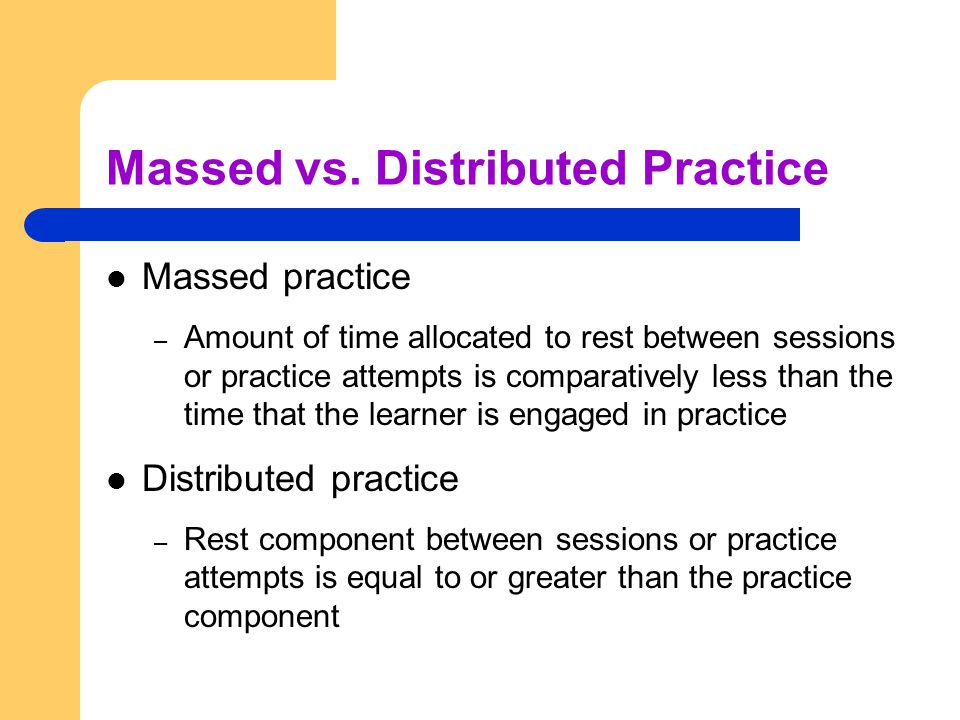 After that, Dr. Kamhi addresses the concept of distributed practice (spacing of intervention) and how important it is for teaching children with language disorders. He points out that a number of recent studies have found that “spacing and distribution of teaching episodes have more of an impact on treatment outcomes than treatment intensity” (94).
After that, Dr. Kamhi addresses the concept of distributed practice (spacing of intervention) and how important it is for teaching children with language disorders. He points out that a number of recent studies have found that “spacing and distribution of teaching episodes have more of an impact on treatment outcomes than treatment intensity” (94).
He also advocates reducing evaluative feedback to learners to “enhance long-term retention and generalization of motor skills“. While he cites research from studies pertaining to speech production, he adds that language learning could also benefit from this practice as it would reduce conversational disruptions and tunning out on the part of the student.
From there he addresses the limitations of repetition for specific tasks (e.g., text rereading). He emphasizes how important it is for students to recall and retrieve text rather than repeatedly reread it (even without correction), as the latter results in a lack of comprehension/retention of read information.
After that, he discusses treatment intensity. Here he emphasizes the fact that higher dose of instruction will not necessarily result in better therapy outcomes due to the research on the effects of “learning plateaus and threshold effects in language and literacy” (95). We have seen research on this with respect to joint book reading, vocabulary words exposure, etc. As such, at a certain point in time increased intensity may actually result in decreased treatment benefits.
 His next point against processing interventions is very near and dear to my heart. Those of you familiar with my blog know that I have devoted a substantial number of posts pertaining to the lack of validity of CAPD diagnosis (as a standalone entity) and urged clinicians to provide language based vs. specific auditory interventions which lack treatment utility. Here, Dr. Kamhi makes a great point that: “Interventions that target processing skills are particularly appealing because they offer the promise of improving language and learning deficits without having to directly target the specific knowledge and skills required to be a proficient speaker, listener, reader, and writer.” (95) The problem is that we have numerous studies on the topic of improvement of isolated skills (e.g., auditory skills, working memory, slow processing, etc.) which clearly indicate lack of effectiveness of these interventions. As such, “practitioners should be highly skeptical of interventions that promise quick fixes for language and learning disabilities” (96).
His next point against processing interventions is very near and dear to my heart. Those of you familiar with my blog know that I have devoted a substantial number of posts pertaining to the lack of validity of CAPD diagnosis (as a standalone entity) and urged clinicians to provide language based vs. specific auditory interventions which lack treatment utility. Here, Dr. Kamhi makes a great point that: “Interventions that target processing skills are particularly appealing because they offer the promise of improving language and learning deficits without having to directly target the specific knowledge and skills required to be a proficient speaker, listener, reader, and writer.” (95) The problem is that we have numerous studies on the topic of improvement of isolated skills (e.g., auditory skills, working memory, slow processing, etc.) which clearly indicate lack of effectiveness of these interventions. As such, “practitioners should be highly skeptical of interventions that promise quick fixes for language and learning disabilities” (96).
Now let us move on to language and particularly the models we provide to our clients to encourage greater verbal output. Research indicates that when clinicians are attempting to expand children’s utterances, they need to provide well-formed language models. Studies show that children select strong input when its surrounded by weaker input (the surrounding weaker syllables make stronger syllables stand out). As such, clinicians should expand upon/comment on what clients are saying with grammatically complete models vs. telegraphic productions.
 From there lets us take a look at Dr. Kamhi’s recommendations for grammar and syntax. Grammatical development goes much further than addressing Brown’s morphemes in therapy and calling it a day. As such, it is important to understand that children with developmental language disorders (DLD) (#DevLang) do not have difficulty acquiring all morphemes. Rather studies have shown that they have difficulty learning grammatical morphemes that reflect tense and agreement (e.g., third-person singular, past tense, auxiliaries, copulas, etc.). As such, use of measures developed by Hadley & Holt, 2006; Hadley & Short, 2005 (e.g., Tense Marker Total & Productivity Score) can yield helpful information regarding which grammatical structures to target in therapy.
From there lets us take a look at Dr. Kamhi’s recommendations for grammar and syntax. Grammatical development goes much further than addressing Brown’s morphemes in therapy and calling it a day. As such, it is important to understand that children with developmental language disorders (DLD) (#DevLang) do not have difficulty acquiring all morphemes. Rather studies have shown that they have difficulty learning grammatical morphemes that reflect tense and agreement (e.g., third-person singular, past tense, auxiliaries, copulas, etc.). As such, use of measures developed by Hadley & Holt, 2006; Hadley & Short, 2005 (e.g., Tense Marker Total & Productivity Score) can yield helpful information regarding which grammatical structures to target in therapy.
With respect to syntax, Dr. Kamhi notes that many clinicians erroneously believe that complex syntax should be targeted when children are much older. The Common Core State Standards do not help this cause further, since according to the CCSS complex syntax should be targeted 2-3 grades, which is far too late. Typically developing children begin developing complex syntax around 2 years of age and begin readily producing it around 3 years of age. As such, clinicians should begin targeting complex syntax in preschool years and not wait until the children have mastered all morphemes and clauses (97)
Finally, Dr. Kamhi wraps up his article by offering suggestions regarding prioritizing intervention goals. Here, he explains that goal prioritization is affected by
- clinician experience and competencies
- the degree of collaboration with other professionals
- type of service delivery model
- client/student factors
He provides a hypothetical case scenario in which the teaching responsibilities are divvied up between three professionals, with SLP in charge of targeting narrative discourse. Here, he explains that targeting narratives does not involve targeting sequencing abilities. “The ability to understand and recall events in a story or script depends on conceptual understanding of the topic and attentional/memory abilities, not sequencing ability.” He emphasizes that sequencing is not a distinct cognitive process that requires isolated treatment. Yet many SLPs “continue to believe that sequencing is a distinct processing skill that needs to be assessed and treated.” (99)
 Dr. Kamhi supports the above point by providing an example of two passages. One, which describes a random order of events, and another which follows a logical order of events. He then points out that the randomly ordered story relies exclusively on attention and memory in terms of “sequencing”, while the second story reduces demands on memory due to its logical flow of events. As such, he points out that retelling deficits seemingly related to sequencing, tend to be actually due to “limitations in attention, working memory, and/or conceptual knowledge“. Hence, instead of targeting sequencing abilities in therapy, SLPs should instead use contextualized language intervention to target aspects of narrative development (macro and microstructural elements).
Dr. Kamhi supports the above point by providing an example of two passages. One, which describes a random order of events, and another which follows a logical order of events. He then points out that the randomly ordered story relies exclusively on attention and memory in terms of “sequencing”, while the second story reduces demands on memory due to its logical flow of events. As such, he points out that retelling deficits seemingly related to sequencing, tend to be actually due to “limitations in attention, working memory, and/or conceptual knowledge“. Hence, instead of targeting sequencing abilities in therapy, SLPs should instead use contextualized language intervention to target aspects of narrative development (macro and microstructural elements).
Furthermore, here it is also important to note that the “sequencing fallacy” affects more than just narratives. It is very prevalent in the intervention process in the form of the ubiquitous “following directions” goal/s. Many clinicians readily create this goal for their clients due to their belief that it will result in functional therapeutic language gains. However, when one really begins to deconstruct this goal, one will realize that it involves a number of discrete abilities including: memory, attention, concept knowledge, inferencing, etc. Consequently, targeting the above goal will not result in any functional gains for the students (their memory abilities will not magically improve as a result of it). Instead, targeting specific language and conceptual goals (e.g., answering questions, producing complex sentences, etc.) and increasing the students’ overall listening comprehension and verbal expression will result in improvements in the areas of attention, memory, and processing, including their ability to follow complex directions.
 There you have it! Ten practical suggestions from Dr. Kamhi ready for immediate implementation! And for more information, I highly recommend reading the other articles in the same clinical forum, all of which possess highly practical and relevant ideas for therapeutic implementation. They include:
There you have it! Ten practical suggestions from Dr. Kamhi ready for immediate implementation! And for more information, I highly recommend reading the other articles in the same clinical forum, all of which possess highly practical and relevant ideas for therapeutic implementation. They include:
- Clinical Scientists Improving Clinical Practices: In Thoughts and Actions
- Approaching Early Grammatical Intervention From a Sentence-Focused Framework
- What Works in Therapy: Further Thoughts on Improving Clinical Practice for Children With Language Disorders
- Improving Clinical Practice: A School-Age and School-Based Perspective
- Improving Clinical Services: Be Aware of Fuzzy Connections Between Principles and Strategies
- One Size Does Not Fit All: Improving Clinical Practice in Older Children and Adolescents With Language and Learning Disorders
- Language Intervention at the Middle School: Complex Talk Reflects Complex Thought
- Using Our Knowledge of Typical Language Development
References:
Kamhi, A. (2014). Improving clinical practices for children with language and learning disorders. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 45(2), 92-103
Helpful Social Media Resources:
New Products for the 2017 Academic School Year for SLPs
September is quickly approaching and school-based speech language pathologists (SLPs) are preparing to go back to work. Many of them are looking to update their arsenal of speech and language materials for the upcoming academic school year.
With that in mind, I wanted to update my readers regarding all the new products I have recently created with a focus on assessment and treatment in speech language pathology. Continue reading New Products for the 2017 Academic School Year for SLPs
The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
 As SLPs we routinely administer a variety of testing batteries in order to assess our students’ speech-language abilities. Grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and sentence formulation get frequent and thorough attention. But how about narrative production? Does it get its fair share of attention when the clinicians are looking to determine the extent of the child’s language deficits? I was so curious about what the clinicians across the country were doing that in 2013, I created a survey and posted a link to it in several SLP-related FB groups. I wanted to find out how many SLPs were performing narrative assessments, in which settings, and with which populations. From those who were performing these assessments, I wanted to know what type of assessments were they using and how they were recording and documenting their findings. Since the purpose of this survey was non-research based (I wasn’t planning on submitting a research manuscript with my findings), I only analyzed the first 100 responses (the rest were very similar in nature) which came my way, in order to get the general flavor of current trends among clinicians, when it came to narrative assessments. Here’s a brief overview of my [limited] findings. Continue reading The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
As SLPs we routinely administer a variety of testing batteries in order to assess our students’ speech-language abilities. Grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and sentence formulation get frequent and thorough attention. But how about narrative production? Does it get its fair share of attention when the clinicians are looking to determine the extent of the child’s language deficits? I was so curious about what the clinicians across the country were doing that in 2013, I created a survey and posted a link to it in several SLP-related FB groups. I wanted to find out how many SLPs were performing narrative assessments, in which settings, and with which populations. From those who were performing these assessments, I wanted to know what type of assessments were they using and how they were recording and documenting their findings. Since the purpose of this survey was non-research based (I wasn’t planning on submitting a research manuscript with my findings), I only analyzed the first 100 responses (the rest were very similar in nature) which came my way, in order to get the general flavor of current trends among clinicians, when it came to narrative assessments. Here’s a brief overview of my [limited] findings. Continue reading The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
Phonological Awareness Screening App Review: ProPA
 Summer is in full swing and for many SLPs that means a welcome break from work. However, for me, it’s business as usual, since my program is year around, and we have just started our extended school year program.
Summer is in full swing and for many SLPs that means a welcome break from work. However, for me, it’s business as usual, since my program is year around, and we have just started our extended school year program.
Of course, even my program is a bit light on activities during the summer. There are lots of field trips, creative and imaginative play, as well as less focus on academics as compared to during the school year. However, I’m also highly cognizant of summer learning loss, which is the phenomena characterized by the loss of academic skills and knowledge over the course of summer holidays.

According to Cooper et al, 1996, while generally, typical students lose about one month of learning, there is actually a significant degree of variability of loss based on SES. According to Cooper’s study, low-income students lose approximately two months of achievement. Furthermore, ethnic minorities, twice-exceptional students (2xE), as well as students with language disorders tend to be disproportionately affected (Graham et al, 2011; Kim & Guryan, 2010; Kim, 2004). Finally, it is important to note that according to research, summer loss is particularly prominent in the area of literacy (Graham et al, 2011).
So this summer I have been busy screening the phonological awareness abilities (PA) of an influx of new students (our program enrolls quite a few students during the ESY), as well as rescreening PA abilities of students already on my caseload, who have been receiving services in this area for the past few months.
Why do I intensively focus on phonological awareness (PA)? Because PA is a precursor to emergent reading. It helps children to manipulate sounds in words (see Age of Aquisition of PA Skills). Children need to attain PA mastery (along with a host of a few literacy-related skills) in order to become good readers.
When children exhibit poor PA skills for their age it is a red flag for reading disabilities. Thus it is very important to assess the child’s PA abilities in order to determine their proficiency in this area.
While there are a number of comprehensive tests available in this area, for the purposes of my screening I prefer to use the ProPA app by Smarty Ears.

The Profile of Phonological Awareness (Pro-PA) is an informal phonological awareness screening. According to the developers on average it takes approximately 10 to 20 minutes to administer based on the child’s age and skill levels. In my particular setting (outpatient school based in a psychiatric hospital) it takes approximately 30 minutes to administer to students on the individual basis. It is by no means a comprehensive tool such as the CTOPP-2 or the PAT-2, as there are not enough trials, complexity or PA categories to qualify for a full-blown informal assessment. However, it is a highly useful measure for a quick determination of the students’ strengths and weaknesses with respect to their phonological awareness abilities. Given its current retail price of $29.99 on iTunes, it is a relatively affordable phonological awareness screening option, as the app allows its users to store data, and generates a two-page report at the completion of the screening.
The Pro-PA assesses six different skill areas:
- Rhyming
- Identification
- Production
- Blending
- Syllables
- Sounds
- Sound Isolation
- Initial
- Final
- Medial
- Segmentation
- Words in sentences
- Syllables in words
- Sounds in words
- Words with consonant clusters
- Deletion
- Syllables
- Sounds
- Words with consonant clusters
- Substitution
- Sounds in initial position of words
- Sounds in final position of words
 After the completion of the screening, the app generates a two-page report which describes the students’ abilities as:
After the completion of the screening, the app generates a two-page report which describes the students’ abilities as:
- Achieved (80%+ accuracy)
- Not achieved (0-50% accuracy)
- Emerging (~50-79% accuracy)
The above is perfect for quickly tracking progress or for generating phonological awareness goals to target the students’ phonological awareness weaknesses. While the report can certainly be provided as an attachment to parents and teachers, I usually tend to summarize its findings in my own reports for the purpose of brevity. Below is one example of what that looks like:
 The Profile of Phonological Awareness (Pro-PA), an informal phonological awareness screening was administered to “Justine” in May 2017 to further determine the extent of her phonological awareness strengths and weaknesses.
The Profile of Phonological Awareness (Pro-PA), an informal phonological awareness screening was administered to “Justine” in May 2017 to further determine the extent of her phonological awareness strengths and weaknesses.
On the Pro-PA, “Justine” evidenced strengths (80-100% accuracy) in the areas of rhyme identification, initial and final sound isolation in words, syllable segmentation, as well as substitution of sounds in initial position in words.
She also evidenced emerging abilities (~60-66% accuracy) in the areas of syllable and sound blending in words, as well as sound segmentation in CVC words,
However, Pro-PA assessment also revealed weaknesses (inability to perform) in the areas of: rhyme production, isolation of medial sounds in words, segmentation of words, segmentation of sounds in words with consonant blends,deletion of first sounds, consonant clusters, as well as substitution of sounds in final position in words. Continuation of therapeutic intervention is recommended in order to improve “Justine’s” abilities in these phonological awareness areas.
Now you know how I quickly screen and rescreen my students’ phonological awareness abilities, I’d love to hear from you! What screening instruments are you using (free or paid) to assess your students’ phonological awareness abilities? Do you feel that they are more or less comprehensive/convenient than ProPA?
References:
- Cooper, H., Nye, B., Charlton, K., Lindsay, J., & Greathouse, S. (1996). “The effects of summer vacation on achievement test scores: A narrative and meta analytic review.” Review of Educational Research, 66, 227–268.
- Graham, A., McNamara, J. K., & Van Lankveld, J. (2011). Closing the summer learning gap for vulnerable learners: An exploratory study of a summer literacy programme for kindergarten children at-risk for reading difficulties. Early Child Development and Care, 181, 575–585.
- Kim, J. S. (2004). Summer reading and the ethnic achievement gap. Journal of Education for Students Placed
at Risk, 9, 169–188. - Kim, J.,S. & Guryan, J. (2010). The efficacy of a voluntary summer book reading intervention for low-income Latino children from language minority families. Journal of
Educational Psychology, 102(1), 20-31