 Picture books are absolutely wonderful for both assessment and treatment purposes! They are terrific as narrative elicitation aids for children of various ages, ranging from pre-K through fourth grade. They are amazing treatment aids for addressing a variety of speech, language, and literacy goals that extend far beyond narrative production. Continue reading Speech, Language, and Literacy Fun with Helen Lester’s Picture Books
Picture books are absolutely wonderful for both assessment and treatment purposes! They are terrific as narrative elicitation aids for children of various ages, ranging from pre-K through fourth grade. They are amazing treatment aids for addressing a variety of speech, language, and literacy goals that extend far beyond narrative production. Continue reading Speech, Language, and Literacy Fun with Helen Lester’s Picture Books
Category: Learning Disability
Tips on Reducing ‘Summer Learning Loss’ in Children with Language/Literacy Disorders
 The end of the school year is almost near. Soon many of our clients with language and literacy difficulties will be going on summer vacation and enjoying their time outside of school. However, summer is not all fun and games. For children with learning needs, this is also a time of “learning loss”, or the loss of academic skills and knowledge over the course of the summer break. Students diagnosed with language and learning disabilities are at a particularly significant risk of greater learning loss than typically developing students. Continue reading Tips on Reducing ‘Summer Learning Loss’ in Children with Language/Literacy Disorders
The end of the school year is almost near. Soon many of our clients with language and literacy difficulties will be going on summer vacation and enjoying their time outside of school. However, summer is not all fun and games. For children with learning needs, this is also a time of “learning loss”, or the loss of academic skills and knowledge over the course of the summer break. Students diagnosed with language and learning disabilities are at a particularly significant risk of greater learning loss than typically developing students. Continue reading Tips on Reducing ‘Summer Learning Loss’ in Children with Language/Literacy Disorders
On the Disadvantages of Parents Ceasing to Speak the Birth Language with Bilingual Language Impaired Children
 Despite significant advances in the fields of education and speech pathology, many harmful myths pertaining to multilingualism continue to persist. One particularly infuriating and patently incorrect recommendation to parents is the advice to stop speaking the birth language with their bilingual children with language disorders. Continue reading On the Disadvantages of Parents Ceasing to Speak the Birth Language with Bilingual Language Impaired Children
Despite significant advances in the fields of education and speech pathology, many harmful myths pertaining to multilingualism continue to persist. One particularly infuriating and patently incorrect recommendation to parents is the advice to stop speaking the birth language with their bilingual children with language disorders. Continue reading On the Disadvantages of Parents Ceasing to Speak the Birth Language with Bilingual Language Impaired Children
Help, My Student has a Huge Score Discrepancy Between Tests and I Don’t Know Why?
 Here’s a familiar scenario to many SLPs. You’ve administered several standardized language tests to your student (e.g., CELF-5 & TILLS). You expected to see roughly similar scores across tests. Much to your surprise, you find that while your student attained somewhat average scores on one assessment, s/he had completely bombed the second assessment, and you have no idea why that happened.
Here’s a familiar scenario to many SLPs. You’ve administered several standardized language tests to your student (e.g., CELF-5 & TILLS). You expected to see roughly similar scores across tests. Much to your surprise, you find that while your student attained somewhat average scores on one assessment, s/he had completely bombed the second assessment, and you have no idea why that happened.
So you go on social media and start crowdsourcing for information from a variety of SLPs located in a variety of states and countries in order to figure out what has happened and what you should do about this. Of course, the problem in such situations is that while some responses will be spot on, many will be utterly inappropriate. Luckily, the answer lies much closer than you think, in the actual technical manual of the administered tests.
So what is responsible for such as drastic discrepancy? A few things actually. For starters, unless both tests were co-normed (used the same sample of test takers) be prepared to see disparate scores due to the ability levels of children in the normative groups of each test. Another important factor involved in the score discrepancy is how accurately does the test differentiate disordered children from typical functioning ones.
Let’s compare two actual language tests to learn more. For the purpose of this exercise let us select The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-5 (CELF-5) and the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS). The former is a very familiar entity to numerous SLPs, while the latter is just coming into its own, having been released in the market only several years ago.
Both tests share a number of similarities. Both were created to assess the language abilities of children and adolescents with suspected language disorders. Both assess aspects of language and literacy (albeit not to the same degree nor with the same level of thoroughness). Both can be used for language disorder classification purposes, or can they?
 Actually, my last statement is rather debatable. A careful perusal of the CELF – 5 reveals that its normative sample of 3000 children included a whopping 23% of children with language-related disabilities. In fact, the folks from the Leaders Project did such an excellent and thorough job reviewing its psychometric properties rather than repeating that information, the readers can simply click here to review the limitations of the CELF – 5 straight on the Leaders Project website. Furthermore, even the CELF – 5 developers themselves have stated that: “Based on CELF-5 sensitivity and specificity values, the optimal cut score to achieve the best balance is -1.33 (standard score of 80). Using a standard score of 80 as a cut score yields sensitivity and specificity values of .97. “
Actually, my last statement is rather debatable. A careful perusal of the CELF – 5 reveals that its normative sample of 3000 children included a whopping 23% of children with language-related disabilities. In fact, the folks from the Leaders Project did such an excellent and thorough job reviewing its psychometric properties rather than repeating that information, the readers can simply click here to review the limitations of the CELF – 5 straight on the Leaders Project website. Furthermore, even the CELF – 5 developers themselves have stated that: “Based on CELF-5 sensitivity and specificity values, the optimal cut score to achieve the best balance is -1.33 (standard score of 80). Using a standard score of 80 as a cut score yields sensitivity and specificity values of .97. “
In other words, obtaining a standard score of 80 on the CELF – 5 indicates that a child presents with a language disorder. Of course, as many SLPs already know, the eligibility criteria in the schools requires language scores far below that in order for the student to qualify to receive language therapy services.
In fact, the test’s authors are fully aware of that and acknowledge that in the same document. “Keep in mind that students who have language deficits may not obtain scores that qualify him or her for placement based on the program’s criteria for eligibility. You’ll need to plan how to address the student’s needs within the framework established by your program.”
 But here is another issue – the CELF-5 sensitivity group included only a very small number of: “67 children ranging from 5;0 to 15;11”, whose only requirement was to score 1.5SDs < mean “on any standardized language test”. As the Leaders Project reviewers point out: “This means that the 67 children in the sensitivity group could all have had severe disabilities. They might have multiple disabilities in addition to severe language disorders including severe intellectual disabilities or Autism Spectrum Disorder making it easy for a language disorder test to identify this group as having language disorders with extremely high accuracy. ” (pgs. 7-8)
But here is another issue – the CELF-5 sensitivity group included only a very small number of: “67 children ranging from 5;0 to 15;11”, whose only requirement was to score 1.5SDs < mean “on any standardized language test”. As the Leaders Project reviewers point out: “This means that the 67 children in the sensitivity group could all have had severe disabilities. They might have multiple disabilities in addition to severe language disorders including severe intellectual disabilities or Autism Spectrum Disorder making it easy for a language disorder test to identify this group as having language disorders with extremely high accuracy. ” (pgs. 7-8)
Of course, this begs the question, why would anyone continue to administer any test to students, if its administration A. Does not guarantee disorder identification B. Will not make the student eligible for language therapy despite demonstrated need?
The problem is that even though SLPs are mandated to use a variety of quantitative clinical observations and procedures in order to reliably qualify students for services, standardized tests still carry more value then they should. Consequently, it is important for SLPs to select the right test to make their job easier.
 The TILLS is a far less known assessment than the CELF-5 yet in the few years it has been out on the market it really made its presence felt by being a solid assessment tool due to its valid and reliable psychometric properties. Again, the venerable Dr. Carol Westby had already done such an excellent job reviewing its psychometric properties that I will refer the readers to her review here, rather than repeating this information as it will not add anything new on this topic. The upshot of her review as follows: “The TILLS does not include children and adolescents with language/literacy impairments (LLIs) in the norming sample. Since the 1990s, nearly all language assessments have included children with LLIs in the norming sample. Doing so lowers overall scores, making it more difficult to use the assessment to identify students with LLIs. (pg. 11)”
The TILLS is a far less known assessment than the CELF-5 yet in the few years it has been out on the market it really made its presence felt by being a solid assessment tool due to its valid and reliable psychometric properties. Again, the venerable Dr. Carol Westby had already done such an excellent job reviewing its psychometric properties that I will refer the readers to her review here, rather than repeating this information as it will not add anything new on this topic. The upshot of her review as follows: “The TILLS does not include children and adolescents with language/literacy impairments (LLIs) in the norming sample. Since the 1990s, nearly all language assessments have included children with LLIs in the norming sample. Doing so lowers overall scores, making it more difficult to use the assessment to identify students with LLIs. (pg. 11)”
Now, here many proponents of inclusion of children with language disorders in the normative sample will make a variation of the following claim: “You CANNOT diagnose a language impairment if children with language impairment were not included in the normative sample of that assessment!” Here’s a major problem with such assertion. When a child is referred for a language assessment, we really have no way of knowing if this child has a language impairment until we actually finish testing them. We are in fact attempting to confirm or refute this fact, hopefully via the use of reliable and valid testing. However, if the normative sample includes many children with language and learning difficulties, this significantly affects the accuracy of our identification, since we are interested in comparing this child’s results to typically developing children and not the disordered ones, in order to learn if the child has a disorder in the first place. As per Peña, Spaulding and Plante (2006), “the inclusion of children with disabilities may be at odds with the goal of classification, typically the primary function of the speech pathologist’s assessment. In fact, by including such children in the normative sample, we may be “shooting ourselves in the foot” in terms of testing for the purpose of identifying disorders.”(p. 248)
 Then there’s a variation of this assertion, which I have seen in several Facebook groups: “Children with language disorders score at the low end of normal distribution“. Once again such assertion is incorrect since Spaulding, Plante & Farinella (2006) have actually shown that on average, these kids will score at least 1.28 SDs below the mean, which is not the low average range of normal distribution by any means. As per authors: “Specific data supporting the application of “low score” criteria for the identification of language impairment is not supported by the majority of current commercially available tests. However, alternate sources of data (sensitivity and specificity rates) that support accurate identification are available for a subset of the available tests.” (p. 61)
Then there’s a variation of this assertion, which I have seen in several Facebook groups: “Children with language disorders score at the low end of normal distribution“. Once again such assertion is incorrect since Spaulding, Plante & Farinella (2006) have actually shown that on average, these kids will score at least 1.28 SDs below the mean, which is not the low average range of normal distribution by any means. As per authors: “Specific data supporting the application of “low score” criteria for the identification of language impairment is not supported by the majority of current commercially available tests. However, alternate sources of data (sensitivity and specificity rates) that support accurate identification are available for a subset of the available tests.” (p. 61)
Now, let us get back to your child in question, who performed so differently on both of the administered tests. Given his clinically observed difficulties, you fully expected your testing to confirm it. But you are now more confused than before. Don’t be! Search the technical manual for information on the particular test’s sensitivity and specificity to look up the numbers. Vance and Plante (1994) put forth the following criteria for accurate identification of a disorder (discriminant accuracy): “90% should be considered good discriminant accuracy; 80% to 89% should be considered fair. Below 80%, misidentifications occur at unacceptably high rates” and leading to “serious social consequences” of misidentified children. (p. 21)
Review the sensitivity and specificity of your test/s, take a look at the normative samples, see if anything unusual jumps out at you, which leads you to believe that the administered test may have some issues with assessing what it purports to assess. Then, after supplementing your standardized testing results with good quality clinical data (e.g., narrative samples, dynamic assessment tasks, etc.), consider creating a solidly referenced purchasing pitch to your administration to invest in more valid and reliable standardized tests.
Hope you find this information helpful in your quest to better serve the clients on your caseload. If you are interested in learning more regarding evidence-based assessment practices as well as psychometric properties of various standardized speech-language tests visit the SLPs for Evidence-Based Practice group on Facebook learn more.
References:
- Peña ED, Spaulding TJ, and Plante E. ( 2006) The composition of normative groups and diagnostic decision-making: Shooting ourselves in the foot. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology 15: 247–54.
- Spaulding, T. J., Plante, E., & Farinella, K. A. (2006). Eligibility criteria for language impairment: Is the low end of normal always appropriate? Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 37, 61-72.
- Vance, R., & Plante, E. (1994). Selection of preschool language tests: A data-based approach. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 25, 15-24.
Components of Qualitative Writing Assessments: What Exactly are We Trying to Measure?
Writing! The one assessment area that challenges many SLPs on daily basis! If one polls 10 SLPs on the topic of writing, one will get 10 completely different responses ranging from agreement and rejection to the diverse opinions regarding what should actually be assessed and how exactly it should be accomplished.
Consequently, today I wanted to focus on the basics involved in the assessment of adolescent writing. Why adolescents you may ask? Well, frankly because many SLPs (myself included) are far more likely to assess the writing abilities of adolescents rather than elementary-aged children.
Often, when the students are younger and their literacy abilities are weaker, the SLPs may not get to the assessment of writing abilities due to the students presenting with so many other deficits which require precedence intervention-wise. However, as the students get older and the academic requirements increase exponentially, SLPs may be more frequently asked to assess the students’ writing abilities because difficulties in this area significantly affect them in a variety of classes on a variety of subjects.
So what can we assess when it comes to writing? In the words of Helen Lester’s character ‘Pookins’: “Lots!” There are various types of writing that can be assessed, the most common of which include: expository, persuasive, and fictional. Each of these can be used for assessment purposes in a variety of ways.
To illustrate, if we chose to analyze the student’s written production of fictional narratives then we may broadly choose to analyze the following aspects of the student’s writing: contextual conventions and writing composition.
 The former looks at such writing aspects as the use of correct spelling, punctuation, and capitalization, paragraph formation, etc.
The former looks at such writing aspects as the use of correct spelling, punctuation, and capitalization, paragraph formation, etc.
The latter looks at the nitty-gritty elements involved in plot development. These include effective use of literate vocabulary, plotline twists, character development, use of dialogue, etc.
Perhaps we want to analyze the student’s persuasive writing abilities. After all, high school students are expected to utilize this type of writing frequently for essay writing purposes. Actually, persuasive writing is a complex genre which is particularly difficult for students with language-learning difficulties who struggle to produce essays that are clear, logical, convincing, appropriately sequenced, and take into consideration opposing points of view. It is exactly for that reason that persuasive writing tasks are perfect for assessment purposes.
But what exactly are we looking for analysis wise? What should a typical 15 year old’s persuasive essays contain?
 With respect to syntax, a typical student that age is expected to write complex sentences possessing nominal, adverbial, as well as relative clauses.
With respect to syntax, a typical student that age is expected to write complex sentences possessing nominal, adverbial, as well as relative clauses.
With the respect to semantics, effective persuasive essays require the use of literate vocabulary words of low frequency such as later developing connectors (e.g., first of all, next, for this reason, on the other hand, consequently, finally, in conclusion) as well as metalinguistic and metacognitive verbs (“metaverbs”) that refer to acts of speaking (e.g., assert, concede, predict, argue, imply) and thinking (e.g., hypothesize, remember, doubt, assume, infer).
With respect to pragmatics, as students mature, their sensitivity to the perspectives of others improves, as a result, their persuasive essays increase in length (i.e., total number of words produced) and they are able to offer a greater number of different reasons to support their own opinions (Nippold, Ward-Lonergan, & Fanning, 2005).
Now let’s apply our knowledge by analyzing a writing sample of a 15-year-old with suspected literacy deficits. Below 10th-grade student was provided with a written prompt first described in the Nippold, et al, 2005 study, entitled: “The Circus Controversy”. “People have different views on animals performing in circuses. For example, some people think it is a great idea because it provides lots of entertainment for the public. Also, it gives parents and children something to do together, and the people who train the animals can make some money. However, other people think having animals in circuses is a bad idea because the animals are often locked in small cages and are not fed well. They also believe it is cruel to force a dog, tiger, or elephant to perform certain tricks that might be dangerous. I am interested in learning what you think about this controversy, and whether or not you think circuses with trained animals should be allowed to perform for the public. I would like you to spend the next 20 minutes writing an essay. Tell me exactly what you think about the controversy. Give me lots of good reasons for your opinion. Please use your best writing style, with correct grammar and spelling. If you aren’t sure how to spell a word, just take a guess.”(Nippold, Ward-Lonergan, & Fanning, 2005)
He produced the following written sample during the allotted 20 minutes.
Analysis: This student was able to generate a short, 3-paragraph, composition containing an introduction and a body without a definitive conclusion. His persuasive essay was judged to be very immature for his grade level due to significant disorganization, limited ability to support his point of view as well as the presence of tangential information in the introduction of his composition, which was significantly compromised by many writing mechanics errors (punctuation, capitalization, as well as spelling) that further impacted the coherence and cohesiveness of his written output.
The student’s introduction began with an inventive dialogue, which was irrelevant to the body of his persuasive essay. He did have three important points relevant to the body of the essay: animal cruelty, danger to the animals, and potential for the animals to harm humans. However, he was unable to adequately develop those points into full paragraphs. The notable absence of proofreading and editing of the composition further contributed to its lack of clarity. The above coupled with a lack of a conclusion was not commensurate grade-level expectations.
 Based on the above-written sample, the student’s persuasive composition content (thought formulation and elaboration) was judged to be significantly immature for his grade level and is commensurate with the abilities of a much younger student. The student’s composition contained several emerging claims that suggested a vague position. However, though the student attempted to back up his opinion and support his position (animals should not be performing in circuses), ultimately he was unable to do so in a coherent and cohesive manner.
Based on the above-written sample, the student’s persuasive composition content (thought formulation and elaboration) was judged to be significantly immature for his grade level and is commensurate with the abilities of a much younger student. The student’s composition contained several emerging claims that suggested a vague position. However, though the student attempted to back up his opinion and support his position (animals should not be performing in circuses), ultimately he was unable to do so in a coherent and cohesive manner.
Now that we know what the student’s written difficulties look like, the following goals will be applicable with respect to his writing remediation:
Long-Term Goals: Student will improve his written abilities for academic purposes.
- Short-Term Goals
- Student will appropriately utilize parts of speech (e.g., adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, etc.) in compound and complex sentences.
- Student will use a variety of sentence types for story composition purposes (e.g., declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences).
- Student will correctly use past, present, and future verb tenses during writing tasks.
- Student will utilize appropriate punctuation at the sentence level (e.g., apostrophes, periods, commas, colons, quotation marks in dialogue, and apostrophes in singular possessives, etc.).
- Student will utilize appropriate capitalization at the sentence level (e.g., capitalize proper nouns, holidays, product names, titles with names, initials, geographic locations, historical periods, special events, etc.).
- Student will use prewriting techniques to generate writing ideas (e.g., list keywords, state key ideas, etc.).
- Student will determine the purpose of his writing and his intended audience in order to establish the tone of his writing as well as outline the main idea of his writing.
- Student will generate a draft in which information is organized in chronological order via use of temporal markers (e.g., “meanwhile,” “immediately”) as well as cohesive ties (e.g., ‘but’, ‘yet’, ‘so’, ‘nor’) and cause/effect transitions (e.g., “therefore,” “as a result”).
- Student will improve coherence and logical organization of his written output via the use of revision strategies (e.g., modify supporting details, use sentence variety, employ literary devices).
- Student will edit his draft for appropriate grammar, spelling, punctuation, and capitalization.
There you have it. A quick and easy qualitative writing assessment which can assist SLPs to determine the extent of the student’s writing difficulties as well as establish writing remediation targets for intervention purposes.
Using a different type of writing assessment with your students? Please share the details below so we can all benefit from each others knowledge of assessment strategies.
References:
- Nippold, M., Ward-Lonergan, J., & Fanning, J. (2005). Persuasive writing in children, adolescents, and adults: a study of syntactic, semantic, and pragmatic development. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 36, 125-138.
It’s All Due to …Language: How Subtle Symptoms Can Cause Serious Academic Deficits
 Scenario: Len is a 7-2-year-old, 2nd-grade student who struggles with reading and writing in the classroom. He is very bright and has a high average IQ, yet when he is speaking he frequently can’t get his point across to others due to excessive linguistic reformulations and word-finding difficulties. The problem is that Len passed all the typical educational and language testing with flying colors, receiving average scores across the board on various tests including the Woodcock-Johnson Fourth Edition (WJ-IV) and the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-5 (CELF-5). Stranger still is the fact that he aced Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing, Second Edition (CTOPP-2), with flying colors, so he is not even eligible for a “dyslexia” diagnosis. Len is clearly struggling in the classroom with coherently expressing self, telling stories, understanding what he is reading, as well as putting his thoughts on paper. His parents have compiled impressively huge folders containing examples of his struggles. Yet because of his performance on the basic standardized assessment batteries, Len does not qualify for any functional assistance in the school setting, despite being virtually functionally illiterate in second grade.
Scenario: Len is a 7-2-year-old, 2nd-grade student who struggles with reading and writing in the classroom. He is very bright and has a high average IQ, yet when he is speaking he frequently can’t get his point across to others due to excessive linguistic reformulations and word-finding difficulties. The problem is that Len passed all the typical educational and language testing with flying colors, receiving average scores across the board on various tests including the Woodcock-Johnson Fourth Edition (WJ-IV) and the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-5 (CELF-5). Stranger still is the fact that he aced Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing, Second Edition (CTOPP-2), with flying colors, so he is not even eligible for a “dyslexia” diagnosis. Len is clearly struggling in the classroom with coherently expressing self, telling stories, understanding what he is reading, as well as putting his thoughts on paper. His parents have compiled impressively huge folders containing examples of his struggles. Yet because of his performance on the basic standardized assessment batteries, Len does not qualify for any functional assistance in the school setting, despite being virtually functionally illiterate in second grade.
The truth is that Len is quite a familiar figure to many SLPs, who at one time or another have encountered such a student and asked for guidance regarding the appropriate accommodations and services for him on various SLP-geared social media forums. But what makes Len such an enigma, one may inquire? Surely if the child had tangible deficits, wouldn’t standardized testing at least partially reveal them?
Well, it all depends really, on what type of testing was administered to Len in the first place. A few years ago I wrote a post entitled: “What Research Shows About the Functional Relevance of Standardized Language Tests“. What researchers found is that there is a “lack of a correlation between frequency of test use and test accuracy, measured both in terms of sensitivity/specificity and mean difference scores” (Betz et al, 2012, 141). Furthermore, they also found that the most frequently used tests were the comprehensive assessments including the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals and the Preschool Language Scale as well as one-word vocabulary tests such as the Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test”. Most damaging finding was the fact that: “frequently SLPs did not follow up the comprehensive standardized testing with domain-specific assessments (critical thinking, social communication, etc.) but instead used the vocabulary testing as a second measure”.(Betz et al, 2012, 140)
In other words, many SLPs only use the tests at hand rather than the RIGHT tests aimed at identifying the student’s specific deficits. But the problem doesn’t actually stop there. Due to the variation in psychometric properties of various tests, many children with language impairment are overlooked by standardized tests by receiving scores within the average range or not receiving low enough scores to qualify for services.
Thus, “the clinical consequence is that a child who truly has a language impairment has a roughly equal chance of being correctly or incorrectly identified, depending on the test that he or she is given.” Furthermore, “even if a child is diagnosed accurately as language impaired at one point in time, future diagnoses may lead to the false perception that the child has recovered, depending on the test(s) that he or she has been given (Spaulding, Plante & Farinella, 2006, 69).”
There’s of course yet another factor affecting our hypothetical client and that is his relatively young age. This is especially evident with many educational and language testing for children in the 5-7 age group. Because the bar is set so low, concept-wise for these age-groups, many children with moderate language and literacy deficits can pass these tests with flying colors, only to be flagged by them literally two years later and be identified with deficits, far too late in the game. Coupled with the fact that many SLPs do not utilize non-standardized measures to supplement their assessments, Len is in a pretty serious predicament.
But what if there was a do-over? What could we do differently for Len to rectify this situation? For starters, we need to pay careful attention to his deficits profile in order to choose appropriate tests to evaluate his areas of needs. The above can be accomplished via a number of ways. The SLP can interview Len’s teacher and his caregiver/s in order to obtain a summary of his pressing deficits. Depending on the extent of the reported deficits the SLP can also provide them with a referral checklist to mark off the most significant areas of need.
In Len’s case, we already have a pretty good idea regarding what’s going on. We know that he passed basic language and educational testing, so in the words of Dr. Geraldine Wallach, we need to keep “peeling the onion” via the administration of more sensitive tests to tap into Len’s reported areas of deficits which include: word-retrieval, narrative production, as well as reading and writing.
 For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS), which was developed to identify language and literacy disorders, has good psychometric properties, and contains subtests for assessment of relevant skills such as reading fluency, reading comprehension, phonological awareness, spelling, as well as writing in school-age children.
For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS), which was developed to identify language and literacy disorders, has good psychometric properties, and contains subtests for assessment of relevant skills such as reading fluency, reading comprehension, phonological awareness, spelling, as well as writing in school-age children.
 Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the Social Language Development Test Elementary (SLDTE). Here’s why. Research indicates that narrative weaknesses significantly correlate with social communication deficits (Norbury, Gemmell & Paul, 2014). As such, it’s not just children with Autism Spectrum Disorders who present with impaired narrative abilities. Many children with developmental language impairment (DLD) (#devlangdis) can present with significant narrative deficits affecting their social and academic functioning, which means that their social communication abilities need to be tested to confirm/rule out presence of these difficulties.
Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the Social Language Development Test Elementary (SLDTE). Here’s why. Research indicates that narrative weaknesses significantly correlate with social communication deficits (Norbury, Gemmell & Paul, 2014). As such, it’s not just children with Autism Spectrum Disorders who present with impaired narrative abilities. Many children with developmental language impairment (DLD) (#devlangdis) can present with significant narrative deficits affecting their social and academic functioning, which means that their social communication abilities need to be tested to confirm/rule out presence of these difficulties.
However, standardized tests are not enough, since even the best-standardized tests have significant limitations. As such, several non-standardized assessments in the areas of narrative production, reading, and writing, may be recommended for Len to meaningfully supplement his testing.
Let’s begin with an informal narrative assessment which provides detailed information regarding microstructural and macrostructural aspects of storytelling as well as child’s thought processes and socio-emotional functioning. My nonstandardized narrative assessments are based on the book elicitation recommendations from the SALT website. For 2nd graders, I use the book by Helen Lester entitled Pookins Gets Her Way. I first read the story to the child, then cover up the words and ask the child to retell the story based on pictures. I read the story first because: “the model narrative presents the events, plot structure, and words that the narrator is to retell, which allows more reliable scoring than a generated story that can go in many directions” (Allen et al, 2012, p. 207).
As the child is retelling his story I digitally record him using the Voice Memos application on my iPhone, for a later transcription and thorough analysis. During storytelling, I only use the prompts: ‘What else can you tell me?’ and ‘Can you tell me more?’ to elicit additional information. I try not to prompt the child excessively since I am interested in cataloging all of his narrative-based deficits. After I transcribe the sample, I analyze it and make sure that I include the transcription and a detailed write-up in the body of my report, so parents and professionals can see and understand the nature of the child’s errors/weaknesses.
 Now we are ready to move on to a brief nonstandardized reading assessment. For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: Reading for Comprehension, which contains books for grades 1-8. After I confirm with either the parent or the child’s teacher that the selected passage is reflective of the complexity of work presented in the classroom for his grade level, I ask the child to read the text. As the child is reading, I calculate the correct number of words he reads per minute as well as what type of errors the child is exhibiting during reading. Then I ask the child to state the main idea of the text, summarize its key points as well as define select text embedded vocabulary words and answer a few, verbally presented reading comprehension questions. After that, I provide the child with accompanying 5 multiple choice question worksheet and ask the child to complete it. I analyze my results in order to determine whether I have accurately captured the child’s reading profile.
Now we are ready to move on to a brief nonstandardized reading assessment. For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: Reading for Comprehension, which contains books for grades 1-8. After I confirm with either the parent or the child’s teacher that the selected passage is reflective of the complexity of work presented in the classroom for his grade level, I ask the child to read the text. As the child is reading, I calculate the correct number of words he reads per minute as well as what type of errors the child is exhibiting during reading. Then I ask the child to state the main idea of the text, summarize its key points as well as define select text embedded vocabulary words and answer a few, verbally presented reading comprehension questions. After that, I provide the child with accompanying 5 multiple choice question worksheet and ask the child to complete it. I analyze my results in order to determine whether I have accurately captured the child’s reading profile.
Finally, if any additional information is needed, I administer a nonstandardized writing assessment, which I base on the Common Core State Standards for 2nd grade. For this task, I provide a student with a writing prompt common for second grade and give him a period of 15-20 minutes to generate a writing sample. I then analyze the writing sample with respect to contextual conventions (punctuation, capitalization, grammar, and syntax) as well as story composition (overall coherence and cohesion of the written sample).
The above relatively short assessment battery (2 standardized tests and 3 informal assessment tasks) which takes approximately 2-2.5 hours to administer, allows me to create a comprehensive profile of the child’s language and literacy strengths and needs. It also allows me to generate targeted goals in order to begin effective and meaningful remediation of the child’s deficits.
Children like Len will, unfortunately, remain unidentified unless they are administered more sensitive tasks to better understand their subtle pattern of deficits. Consequently, to ensure that they do not fall through the cracks of our educational system due to misguided overreliance on a limited number of standardized assessments, it is very important that professionals select the right assessments, rather than the assessments at hand, in order to accurately determine the child’s areas of needs.
References:
- Allen, M, Ukrainetz, T & Carswell, A (2012) The narrative language performance of three types of at-risk first-grade readers. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 43(2), 205-221.
- Betz et al. (2013) Factors Influencing the Selection of Standardized Tests for the Diagnosis of Specific Language Impairment. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 44, 133-146.
- Hasbrouck, J. & Tindal, G. A. (2006). Oral reading fluency norms: A valuable assessment tool for reading teachers. The Reading Teacher. 59(7), 636-644.).
- Norbury, C. F., Gemmell, T., & Paul, R. (2014). Pragmatics abilities in narrative production: a cross-disorder comparison. Journal of child language, 41(03), 485-510.
- Peña, E.D., Spaulding, T.J., & Plante, E. (2006). The Composition of Normative Groups and Diagnostic Decision Making: Shooting Ourselves in the Foot. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 15, 247-254.
- Spaulding, Plante & Farinella (2006) Eligibility Criteria for Language Impairment: Is the Low End of Normal Always Appropriate? Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 37, 61-72.
- Spaulding, Szulga, & Figueria (2012) Using Norm-Referenced Tests to Determine Severity of Language Impairment in Children: Disconnect Between U.S. Policy Makers and Test Developers. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research. 43, 176-190.
Making Our Interventions Count or What’s Research Got To Do With It?
 Two years ago I wrote a blog post entitled: “What’s Memes Got To Do With It?” which summarized key points of Dr. Alan G. Kamhi’s 2004 article: “A Meme’s Eye View of Speech-Language Pathology“. It delved into answering the following question: “Why do some terms, labels, ideas, and constructs [in our field] prevail whereas others fail to gain acceptance?”.
Two years ago I wrote a blog post entitled: “What’s Memes Got To Do With It?” which summarized key points of Dr. Alan G. Kamhi’s 2004 article: “A Meme’s Eye View of Speech-Language Pathology“. It delved into answering the following question: “Why do some terms, labels, ideas, and constructs [in our field] prevail whereas others fail to gain acceptance?”.
Today I would like to reference another article by Dr. Kamhi written in 2014, entitled “Improving Clinical Practices for Children With Language and Learning Disorders“.
This article was written to address the gaps between research and clinical practice with respect to the implementation of EBP for intervention purposes.
Dr. Kamhi begins the article by posing 10 True or False questions for his readers:
- Learning is easier than generalization.
- Instruction that is constant and predictable is more effective than instruction that varies the conditions of learning and practice.
- Focused stimulation (massed practice) is a more effective teaching strategy than varied stimulation (distributed practice).
- The more feedback, the better.
- Repeated reading of passages is the best way to learn text information.
- More therapy is always better.
- The most effective language and literacy interventions target processing limitations rather than knowledge deficits.
- Telegraphic utterances (e.g., push ball, mommy sock) should not be provided as input for children with limited language.
- Appropriate language goals include increasing levels of mean length of utterance (MLU) and targeting Brown’s (1973) 14 grammatical morphemes.
- Sequencing is an important skill for narrative competence.
Guess what? Only statement 8 of the above quiz is True! Every other statement from the above is FALSE!
Now, let’s talk about why that is!
 First up is the concept of learning vs. generalization. Here Dr. Kamhi discusses that some clinicians still possess an “outdated behavioral view of learning” in our field, which is not theoretically and clinically useful. He explains that when we are talking about generalization – what children truly have a difficulty with is “transferring narrow limited rules to new situations“. “Children with language and learning problems will have difficulty acquiring broad-based rules and modifying these rules once acquired, and they also will be more vulnerable to performance demands on speech production and comprehension (Kamhi, 1988)” (93). After all, it is not “reasonable to expect children to use language targets consistently after a brief period of intervention” and while we hope that “language intervention [is] designed to lead children with language disorders to acquire broad-based language rules” it is a hugely difficult task to undertake and execute.
First up is the concept of learning vs. generalization. Here Dr. Kamhi discusses that some clinicians still possess an “outdated behavioral view of learning” in our field, which is not theoretically and clinically useful. He explains that when we are talking about generalization – what children truly have a difficulty with is “transferring narrow limited rules to new situations“. “Children with language and learning problems will have difficulty acquiring broad-based rules and modifying these rules once acquired, and they also will be more vulnerable to performance demands on speech production and comprehension (Kamhi, 1988)” (93). After all, it is not “reasonable to expect children to use language targets consistently after a brief period of intervention” and while we hope that “language intervention [is] designed to lead children with language disorders to acquire broad-based language rules” it is a hugely difficult task to undertake and execute.
Next, Dr. Kamhi addresses the issue of instructional factors, specifically the importance of “varying conditions of instruction and practice“. Here, he addresses the fact that while contextualized instruction is highly beneficial to learners unless we inject variability and modify various aspects of instruction including context, composition, duration, etc., we ran the risk of limiting our students’ long-term outcomes.
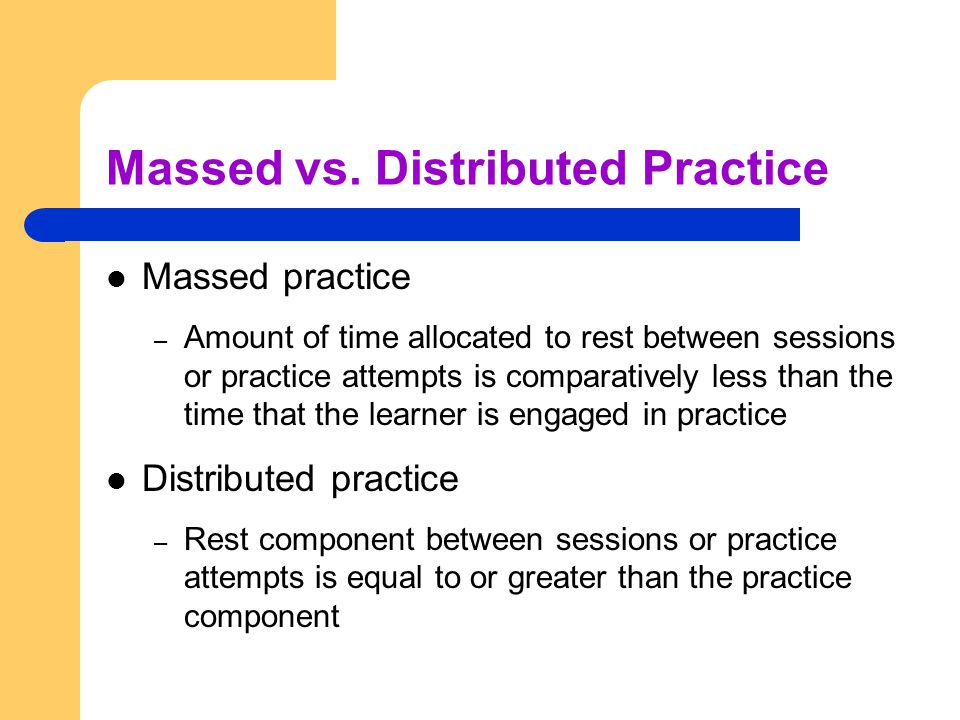 After that, Dr. Kamhi addresses the concept of distributed practice (spacing of intervention) and how important it is for teaching children with language disorders. He points out that a number of recent studies have found that “spacing and distribution of teaching episodes have more of an impact on treatment outcomes than treatment intensity” (94).
After that, Dr. Kamhi addresses the concept of distributed practice (spacing of intervention) and how important it is for teaching children with language disorders. He points out that a number of recent studies have found that “spacing and distribution of teaching episodes have more of an impact on treatment outcomes than treatment intensity” (94).
He also advocates reducing evaluative feedback to learners to “enhance long-term retention and generalization of motor skills“. While he cites research from studies pertaining to speech production, he adds that language learning could also benefit from this practice as it would reduce conversational disruptions and tunning out on the part of the student.
From there he addresses the limitations of repetition for specific tasks (e.g., text rereading). He emphasizes how important it is for students to recall and retrieve text rather than repeatedly reread it (even without correction), as the latter results in a lack of comprehension/retention of read information.
After that, he discusses treatment intensity. Here he emphasizes the fact that higher dose of instruction will not necessarily result in better therapy outcomes due to the research on the effects of “learning plateaus and threshold effects in language and literacy” (95). We have seen research on this with respect to joint book reading, vocabulary words exposure, etc. As such, at a certain point in time increased intensity may actually result in decreased treatment benefits.
 His next point against processing interventions is very near and dear to my heart. Those of you familiar with my blog know that I have devoted a substantial number of posts pertaining to the lack of validity of CAPD diagnosis (as a standalone entity) and urged clinicians to provide language based vs. specific auditory interventions which lack treatment utility. Here, Dr. Kamhi makes a great point that: “Interventions that target processing skills are particularly appealing because they offer the promise of improving language and learning deficits without having to directly target the specific knowledge and skills required to be a proficient speaker, listener, reader, and writer.” (95) The problem is that we have numerous studies on the topic of improvement of isolated skills (e.g., auditory skills, working memory, slow processing, etc.) which clearly indicate lack of effectiveness of these interventions. As such, “practitioners should be highly skeptical of interventions that promise quick fixes for language and learning disabilities” (96).
His next point against processing interventions is very near and dear to my heart. Those of you familiar with my blog know that I have devoted a substantial number of posts pertaining to the lack of validity of CAPD diagnosis (as a standalone entity) and urged clinicians to provide language based vs. specific auditory interventions which lack treatment utility. Here, Dr. Kamhi makes a great point that: “Interventions that target processing skills are particularly appealing because they offer the promise of improving language and learning deficits without having to directly target the specific knowledge and skills required to be a proficient speaker, listener, reader, and writer.” (95) The problem is that we have numerous studies on the topic of improvement of isolated skills (e.g., auditory skills, working memory, slow processing, etc.) which clearly indicate lack of effectiveness of these interventions. As such, “practitioners should be highly skeptical of interventions that promise quick fixes for language and learning disabilities” (96).
Now let us move on to language and particularly the models we provide to our clients to encourage greater verbal output. Research indicates that when clinicians are attempting to expand children’s utterances, they need to provide well-formed language models. Studies show that children select strong input when its surrounded by weaker input (the surrounding weaker syllables make stronger syllables stand out). As such, clinicians should expand upon/comment on what clients are saying with grammatically complete models vs. telegraphic productions.
 From there lets us take a look at Dr. Kamhi’s recommendations for grammar and syntax. Grammatical development goes much further than addressing Brown’s morphemes in therapy and calling it a day. As such, it is important to understand that children with developmental language disorders (DLD) (#DevLang) do not have difficulty acquiring all morphemes. Rather studies have shown that they have difficulty learning grammatical morphemes that reflect tense and agreement (e.g., third-person singular, past tense, auxiliaries, copulas, etc.). As such, use of measures developed by Hadley & Holt, 2006; Hadley & Short, 2005 (e.g., Tense Marker Total & Productivity Score) can yield helpful information regarding which grammatical structures to target in therapy.
From there lets us take a look at Dr. Kamhi’s recommendations for grammar and syntax. Grammatical development goes much further than addressing Brown’s morphemes in therapy and calling it a day. As such, it is important to understand that children with developmental language disorders (DLD) (#DevLang) do not have difficulty acquiring all morphemes. Rather studies have shown that they have difficulty learning grammatical morphemes that reflect tense and agreement (e.g., third-person singular, past tense, auxiliaries, copulas, etc.). As such, use of measures developed by Hadley & Holt, 2006; Hadley & Short, 2005 (e.g., Tense Marker Total & Productivity Score) can yield helpful information regarding which grammatical structures to target in therapy.
With respect to syntax, Dr. Kamhi notes that many clinicians erroneously believe that complex syntax should be targeted when children are much older. The Common Core State Standards do not help this cause further, since according to the CCSS complex syntax should be targeted 2-3 grades, which is far too late. Typically developing children begin developing complex syntax around 2 years of age and begin readily producing it around 3 years of age. As such, clinicians should begin targeting complex syntax in preschool years and not wait until the children have mastered all morphemes and clauses (97)
Finally, Dr. Kamhi wraps up his article by offering suggestions regarding prioritizing intervention goals. Here, he explains that goal prioritization is affected by
- clinician experience and competencies
- the degree of collaboration with other professionals
- type of service delivery model
- client/student factors
He provides a hypothetical case scenario in which the teaching responsibilities are divvied up between three professionals, with SLP in charge of targeting narrative discourse. Here, he explains that targeting narratives does not involve targeting sequencing abilities. “The ability to understand and recall events in a story or script depends on conceptual understanding of the topic and attentional/memory abilities, not sequencing ability.” He emphasizes that sequencing is not a distinct cognitive process that requires isolated treatment. Yet many SLPs “continue to believe that sequencing is a distinct processing skill that needs to be assessed and treated.” (99)
 Dr. Kamhi supports the above point by providing an example of two passages. One, which describes a random order of events, and another which follows a logical order of events. He then points out that the randomly ordered story relies exclusively on attention and memory in terms of “sequencing”, while the second story reduces demands on memory due to its logical flow of events. As such, he points out that retelling deficits seemingly related to sequencing, tend to be actually due to “limitations in attention, working memory, and/or conceptual knowledge“. Hence, instead of targeting sequencing abilities in therapy, SLPs should instead use contextualized language intervention to target aspects of narrative development (macro and microstructural elements).
Dr. Kamhi supports the above point by providing an example of two passages. One, which describes a random order of events, and another which follows a logical order of events. He then points out that the randomly ordered story relies exclusively on attention and memory in terms of “sequencing”, while the second story reduces demands on memory due to its logical flow of events. As such, he points out that retelling deficits seemingly related to sequencing, tend to be actually due to “limitations in attention, working memory, and/or conceptual knowledge“. Hence, instead of targeting sequencing abilities in therapy, SLPs should instead use contextualized language intervention to target aspects of narrative development (macro and microstructural elements).
Furthermore, here it is also important to note that the “sequencing fallacy” affects more than just narratives. It is very prevalent in the intervention process in the form of the ubiquitous “following directions” goal/s. Many clinicians readily create this goal for their clients due to their belief that it will result in functional therapeutic language gains. However, when one really begins to deconstruct this goal, one will realize that it involves a number of discrete abilities including: memory, attention, concept knowledge, inferencing, etc. Consequently, targeting the above goal will not result in any functional gains for the students (their memory abilities will not magically improve as a result of it). Instead, targeting specific language and conceptual goals (e.g., answering questions, producing complex sentences, etc.) and increasing the students’ overall listening comprehension and verbal expression will result in improvements in the areas of attention, memory, and processing, including their ability to follow complex directions.
 There you have it! Ten practical suggestions from Dr. Kamhi ready for immediate implementation! And for more information, I highly recommend reading the other articles in the same clinical forum, all of which possess highly practical and relevant ideas for therapeutic implementation. They include:
There you have it! Ten practical suggestions from Dr. Kamhi ready for immediate implementation! And for more information, I highly recommend reading the other articles in the same clinical forum, all of which possess highly practical and relevant ideas for therapeutic implementation. They include:
- Clinical Scientists Improving Clinical Practices: In Thoughts and Actions
- Approaching Early Grammatical Intervention From a Sentence-Focused Framework
- What Works in Therapy: Further Thoughts on Improving Clinical Practice for Children With Language Disorders
- Improving Clinical Practice: A School-Age and School-Based Perspective
- Improving Clinical Services: Be Aware of Fuzzy Connections Between Principles and Strategies
- One Size Does Not Fit All: Improving Clinical Practice in Older Children and Adolescents With Language and Learning Disorders
- Language Intervention at the Middle School: Complex Talk Reflects Complex Thought
- Using Our Knowledge of Typical Language Development
References:
Kamhi, A. (2014). Improving clinical practices for children with language and learning disorders. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 45(2), 92-103
Helpful Social Media Resources:
Back to School SLP Efficiency Bundles™
 September is practically here and many speech language pathologists (SLPs) are looking to efficiently prepare for assessing and treating a variety of clients on their caseloads.
September is practically here and many speech language pathologists (SLPs) are looking to efficiently prepare for assessing and treating a variety of clients on their caseloads.
With that in mind, a few years ago I created SLP Efficiency Bundles™, which are materials highly useful for SLPs working with pediatric clients. These materials are organized by areas of focus for efficient and effective screening, assessment, and treatment of speech and language disorders.
A. General Assessment and Treatment Start-Up Bundle contains 5 downloads for general speech language assessment and treatment planning and includes:
- Speech Language Assessment Checklist for a Preschool Child
- Speech Language Assessment Checklist for a School-Aged Child
- Creating a Functional Therapy Plan: Therapy Goals & SOAP Note Documentation
- Selecting Clinical Materials for Pediatric Therapy
- Types and Levels of Cues and Prompts in Speech Language Therapy
B. The Checklists Bundle contains 7 checklists relevant to screening and assessment in speech language pathology
- Speech Language Assessment Checklist for a Preschool Child 3:00-6:11 years of age
- Speech Language Assessment Checklist for a School-Aged Child 7:00-11:11 years of age
- Speech Language Assessment Checklist for Adolescents 12-18 years of age
- Language Processing Deficits (LPD) Checklist for School Aged Children 7:00-11:11 years of age
- Language Processing Deficits (LPD) Checklist for Preschool Children 3:00-6:11 years of age
- Social Pragmatic Deficits Checklist for School Aged Children 7:00-11:11 years of age
- Social Pragmatic Deficits Checklist for Preschool Children 3:00-6:11 years of age
C. Social Pragmatic Assessment and Treatment Bundle contains 6 downloads for social pragmatic assessment and treatment planning (from 18 months through school age) and includes:
- Recognizing the Warning Signs of Social Emotional Difficulties in Language Impaired Toddlers and Preschoolers
- Behavior Management Strategies for Speech Language Pathologists
- Social Pragmatic Deficits Checklist for School Aged Children
- Social Pragmatic Deficits Checklist for Preschool Children
- Assessing Social Pragmatic Skills of School Aged Children
- Treatment of Social Pragmatic Deficits in School Aged Children
D. Multicultural Assessment and Treatment Bundle contains 2 downloads relevant to assessment and treatment of bilingual/multicultural children
- Language Difference vs. Language Disorder: Assessment & Intervention Strategies for SLPs Working with Bilingual Children
- Impact of Cultural and Linguistic Variables On Speech-Language Services
E. Narrative Assessment Bundle contains 3 downloads relevant to narrative assessment
- Narrative Assessments of Preschool and School Aged Children
- Understanding Complex Sentences
- Vocabulary Development: Working with Disadvantaged Populations
F. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Assessment and Treatment Bundle contains 3 downloads relevant to FASD assessment and treatment
- Orofacial Observations of At-Risk Children
- Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: An Overview of Deficits
- Speech Language Assessment and Treatment of Children With Alcohol Related Disorders
G. Psychiatric Disorders Bundle contains 7 downloads relevant to language assessment and treatment in psychiatrically impaired children
- Recognizing the Warning Signs of Social Emotional Difficulties in Language Impaired Toddlers and Preschoolers
- Social Pragmatic Deficits Checklist for School Aged Children
- Social Pragmatic Deficits Checklist for Preschool Children
- Assessing Social Skills in Children with Psychiatric Disturbances
- Improving Social Skills of Children with Psychiatric Disturbances
- Behavior Management Strategies for Speech Language Pathologists
- Differential Diagnosis Of ADHD In Speech Language Pathology
You can find these bundles on SALE in my online store by clicking on the individual bundle links above. You can also purchase these products individually in my online store by clicking HERE.

Adolescent Assessments in Action: Clinical Reading Evaluation
 In the past several years, due to an influx of adolescent students with language and learning difficulties on my caseload, I have begun to research in depth aspects of adolescent language development, assessment, and intervention.
In the past several years, due to an influx of adolescent students with language and learning difficulties on my caseload, I have begun to research in depth aspects of adolescent language development, assessment, and intervention.
While a number of standardized assessments are available to test various components of adolescent language from syntax and semantics to problem-solving and social communication, etc., in my experience with this age group, frequently, clinical assessments (vs. the standardized tests), do a far better job of teasing out language difficulties in adolescents.
Today I wanted to write about the importance of performing a clinical reading assessment as part of select* adolescent language and literacy evaluations.
There are a number of standardized tests on the market, which presently assess reading. However, not all of them by far are as functional as many clinicians would like them to be. To illustrate, one popular reading assessment is the Gray Oral Reading Tests-5 (GORT-5). It assesses the student’s rate, accuracy, fluency, and comprehension abilities. While it’s a useful test to possess in one’s assessment toolbox, it is not without its limitations. In my experience assessing adolescent students with literacy deficits, many can pass this test with average scores, yet still present with pervasive reading comprehension difficulties in the school setting. As such, as part of the assessment process, I like to administer clinical reading assessments to students who pass the standardized reading tests (e.g., GORT-5), in order to ensure that the student does not possess any reading deficits at the grade text level.
So how do I clinically assess the reading abilities of struggling adolescent learners?
First, I select a one-page long grade level/below grade-level text (for very impaired readers). I ask the student to read the text, and I time the first minute of their reading in order to analyze their oral reading fluency or words correctly read per minute (wcpm).
 For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: Content Reading for Geography, Social Studies, & Science. Texts for grades 5 – 7 of the series are perfect for assessment of struggling adolescent readers. In some cases using a below grade level text allows me to starkly illustrate the extent of the student’s reading difficulties. Below is an example of one of such a clinical reading assessments in action.
For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: Content Reading for Geography, Social Studies, & Science. Texts for grades 5 – 7 of the series are perfect for assessment of struggling adolescent readers. In some cases using a below grade level text allows me to starkly illustrate the extent of the student’s reading difficulties. Below is an example of one of such a clinical reading assessments in action.
CLINICAL READING ASSESSMENT: 8th Grade Male
A clinical reading assessment was administered to TS, a 15-5-year-old male, on a supplementary basis in order to further analyze his reading abilities. Given the fact that TS was reported to present with grade-level reading difficulties, the examiner provided TS a 7th-grade text by Continental Press. TS was asked to read aloud the 7 paragraph long text, and then answer factual and inferential questions, summarize the presented information, define select context embedded vocabulary words as well as draw conclusions based on the presented text. (Please note that in order to protect the client’s privacy some portions of the below assessment questions and responses were changed to be deliberately vague).
 Reading Fluency: TS’s reading fluency (automaticity, prosody, accuracy and speed, expression, intonation, and phrasing) during the reading task was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody.
Reading Fluency: TS’s reading fluency (automaticity, prosody, accuracy and speed, expression, intonation, and phrasing) during the reading task was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody.
With respect to specific errors, TS was observed to occasionally add word fillers to text (e.g., and, a, etc.), change morphological endings of select words (e.g., read /elasticity/ as /elastic/, etc.) as well as substitute similar looking words (e.g., from/for; those/these, etc.) during reading. He occasionally placed stress on the first vs. second syllable in disyllabic words, which resulted in distorted word productions (e.g., products, residual, upward, etc.), as well as inserted extra words into text (e.g., read: “until pressure inside the earth starts to build again” as “until pressure inside the earth starts to build up again”). He also began reading a number of his sentences with false starts (e.g., started reading the word “drinking” as ‘drunk’, etc.) and as a result was observed to make a number of self-corrections during reading.
During reading, TS demonstrated adequate tracking movements for text scanning as well as use of context to aid his decoding. For example, TS was observed to read the phonetic spelling of select unfamiliar words in parenthesis (e.g., equilibrium) and then read them correctly in subsequent sentences. However, he exhibited limited use of metalinguistic strategies and did not always self-correct misread words; dispute the fact that they did not always make sense in the context of the read sentences.
TS’s oral reading rate during today’s reading was judged to be reduced for his age/grade levels. An average 8th grader is expected to have an oral reading rate between 145 and 160 words per minute. In contrast, TS was only able to read 114 words per minute. However, it is important to note that recent research on reading fluency has indicated that as early as by 4th grade reading faster than 90 wcpm will not generate increases in comprehension for struggling readers. Consequently, TS’s current reading rate of off 114 words per minute was judged to be adequate for reading purposes. Furthermore, given the fact that TS’s reading comprehension is already compromised at this rate (see below for further details) rather than making a recommendation to increase his reading rate further, it is instead recommended that intervention focuses on slowing TS’s rate via relevant strategies as well as improving his reading comprehension abilities. Strategies should focus on increasing his opportunities to learn domain knowledge via use of informational texts; purposeful selection of texts to promote knowledge acquisition and gain of expertise in different domains; teaching morphemic as well as semantic feature analyses (to expand upon already robust vocabulary), increasing discourse and critical thinking with respect to informational text, as well as use of graphic organizers to teach text structure and conceptual frameworks.
Verbal Text Summary: TS’s text summary following his reading was very abbreviated, simplified, and confusing. When asked: “What was this text about?” Rather than stating the main idea, TS nonspecifically provided several vague details and was unable to elaborate further. When asked: “Do you think you can summarize this story for me from beginning to the end?” TS produced the two disjointed statements, which did not adequately address the presented question When asked: “What is the main idea of this text.” TS vaguely responded: “Science,” which was the broad topic rather than the main idea of the story.
 Text Vocabulary Comprehension:
Text Vocabulary Comprehension:
After that, TS was asked a number of questions regarding story vocabulary. The first word presented to him was “equilibrium”. When asked: “What does ‘equilibrium’ mean?” TS first incorrectly responded: “temperature”. Then when prompted: “Anything else?” TS correctly replied: “balance.” He was then asked to provide some examples of how nature leans towards equilibrium from the story. TS nonspecifically produced: “Ah, gravity.” When asked to explain how gravity contributes to the process of equilibrium TS again nonspecifically replied: “gravity is part of the planet”, and could not elaborate further. TS was then asked to define another word from the text provided to him in a sentence: “Scientists believe that this is residual heat remaining from the beginnings of the solar system.” What is the meaning of the word: “residual?” TS correctly identified: “remaining.” Then the examiner asked him to define the term found in the last paragraph of the text: “What is thermal equilibrium?” TS nonspecifically responded: “a balance of temperature”, and was unable to elaborate further.
Reading Comprehension (with/out text access):
TS was also asked to respond to a number of factual text questions without the benefit of visual support. However, he presented with significant difficulty recalling text details. TS was asked: When asked, “Why did this story mention ____? What did they have to do with ____?” TS responded nonspecifically, “______.” When prompted to tell more, TS produced a rambling response which did not adequately address the presented question. When asked: “Why did the text talk about bungee jumpers? How are they connected to it?” TS stated, “I am ah, not sure really.”
Finally, TS was provided with a brief worksheet which accompanied the text and asked to complete it given the benefit of written support. While TS’s performance on this task was better, he still achieved only 66% accuracy and was only able to answer 4 out of 6 questions correctly. On this task, TS presented with difficulty identifying the main idea of the third paragraph, even after being provided with multiple choice answers. He also presented with difficulty correctly responding to the question pertaining to the meaning of the last paragraph.
 Impressions: Clinical below grade-level reading comprehension assessment reading revealed that TS presents with a number of reading related difficulties. TS’s reading fluency was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody. TS’s understanding as well as his verbal summary of the presented text was immature for his age and was characterized by impaired gestalt processing of information resulting in an ineffective and confusing summarization. While TS’s text-based vocabulary knowledge was deemed to be grossly adequate for his age, his reading comprehension abilities were judged to be impaired for his age. Therapeutic intervention is strongly recommended to improve TS’s reading abilities. (See Impressions and Recommendations sections for further details).
Impressions: Clinical below grade-level reading comprehension assessment reading revealed that TS presents with a number of reading related difficulties. TS’s reading fluency was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody. TS’s understanding as well as his verbal summary of the presented text was immature for his age and was characterized by impaired gestalt processing of information resulting in an ineffective and confusing summarization. While TS’s text-based vocabulary knowledge was deemed to be grossly adequate for his age, his reading comprehension abilities were judged to be impaired for his age. Therapeutic intervention is strongly recommended to improve TS’s reading abilities. (See Impressions and Recommendations sections for further details).
There you have it! This is just one of many different types of informal reading assessments, which I occasionally conduct with adolescents who attain average scores on reading fluency and reading comprehension tests such as the GORT-5 or the Test of Reading Comprehension -4 (TORC-4), but still present with pervasive reading difficulties working with grade level text.
You can find more information on the topic of adolescent assessments (including other comprehensive informal write-up examples) in this recently developed product entitled: Assessment of Adolescents with Language and Literacy Impairments in Speech Language Pathology currently available in my online store.
What about you? What type of informal tasks and materials are you using to assess your adolescent students’ reading abilities and why do you like using them?
Helpful Smart Speech Therapy Adolescent Assessment Resources:
- Assessment of Adolescents with Language and Literacy Impairments in Speech Language Pathology
- Comprehensive Literacy Checklist For School-Aged Children
- Speech Language Assessment Checklist for Adolescents
The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
 As SLPs we routinely administer a variety of testing batteries in order to assess our students’ speech-language abilities. Grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and sentence formulation get frequent and thorough attention. But how about narrative production? Does it get its fair share of attention when the clinicians are looking to determine the extent of the child’s language deficits? I was so curious about what the clinicians across the country were doing that in 2013, I created a survey and posted a link to it in several SLP-related FB groups. I wanted to find out how many SLPs were performing narrative assessments, in which settings, and with which populations. From those who were performing these assessments, I wanted to know what type of assessments were they using and how they were recording and documenting their findings. Since the purpose of this survey was non-research based (I wasn’t planning on submitting a research manuscript with my findings), I only analyzed the first 100 responses (the rest were very similar in nature) which came my way, in order to get the general flavor of current trends among clinicians, when it came to narrative assessments. Here’s a brief overview of my [limited] findings. Continue reading The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
As SLPs we routinely administer a variety of testing batteries in order to assess our students’ speech-language abilities. Grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and sentence formulation get frequent and thorough attention. But how about narrative production? Does it get its fair share of attention when the clinicians are looking to determine the extent of the child’s language deficits? I was so curious about what the clinicians across the country were doing that in 2013, I created a survey and posted a link to it in several SLP-related FB groups. I wanted to find out how many SLPs were performing narrative assessments, in which settings, and with which populations. From those who were performing these assessments, I wanted to know what type of assessments were they using and how they were recording and documenting their findings. Since the purpose of this survey was non-research based (I wasn’t planning on submitting a research manuscript with my findings), I only analyzed the first 100 responses (the rest were very similar in nature) which came my way, in order to get the general flavor of current trends among clinicians, when it came to narrative assessments. Here’s a brief overview of my [limited] findings. Continue reading The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
