As SLPs we routinely administer a variety of testing batteries in order to assess our students’ speech-language abilities. Grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and sentence formulation get frequent and thorough attention. But how about narrative production? Does it get its fair share of attention when the clinicians are looking to determine the extent of the child’s language deficits? I was so curious about what the clinicians across the country were doing that in 2013, I created a survey and posted a link to it in several SLP-related FB groups. I wanted to find out how many SLPs were performing narrative assessments, in which settings, and with which populations. From those who were performing these assessments, I wanted to know what type of assessments were they using and how they were recording and documenting their findings. Since the purpose of this survey was non-research based (I wasn’t planning on submitting a research manuscript with my findings), I only analyzed the first 100 responses (the rest were very similar in nature) which came my way, in order to get the general flavor of current trends among clinicians, when it came to narrative assessments. Here’s a brief overview of my [limited] findings. Continue reading The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
As SLPs we routinely administer a variety of testing batteries in order to assess our students’ speech-language abilities. Grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and sentence formulation get frequent and thorough attention. But how about narrative production? Does it get its fair share of attention when the clinicians are looking to determine the extent of the child’s language deficits? I was so curious about what the clinicians across the country were doing that in 2013, I created a survey and posted a link to it in several SLP-related FB groups. I wanted to find out how many SLPs were performing narrative assessments, in which settings, and with which populations. From those who were performing these assessments, I wanted to know what type of assessments were they using and how they were recording and documenting their findings. Since the purpose of this survey was non-research based (I wasn’t planning on submitting a research manuscript with my findings), I only analyzed the first 100 responses (the rest were very similar in nature) which came my way, in order to get the general flavor of current trends among clinicians, when it came to narrative assessments. Here’s a brief overview of my [limited] findings. Continue reading The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
Category: Middle School
Improving Executive Function Skills of Language Impaired Students with Hedbanz
 Those of you who have previously read my blog know that I rarely use children’s games to address language goals. However, over the summer I have been working on improving executive function abilities (EFs) of some of the language impaired students on my caseload. As such, I found select children’s games to be highly beneficial for improving language-based executive function abilities.
Those of you who have previously read my blog know that I rarely use children’s games to address language goals. However, over the summer I have been working on improving executive function abilities (EFs) of some of the language impaired students on my caseload. As such, I found select children’s games to be highly beneficial for improving language-based executive function abilities.
For those of you who are only vaguely familiar with this concept, executive functions are higher level cognitive processes involved in the inhibition of thought, action, and emotion, which located in the prefrontal cortex of the frontal lobe of the brain. The development of executive functions begins in early infancy; but it can be easily disrupted by a number of adverse environmental and organic experiences (e.g., psychosocial deprivation, trauma). Furthermore, research in this area indicates that the children with language impairments present with executive function weaknesses which require remediation.
EF components include working memory, inhibitory control, planning, and set-shifting.
- Working memory
- Ability to store and manipulate information in mind over brief periods of time
- Inhibitory control
- Suppressing responses that are not relevant to the task
- Set-shifting
- Ability to shift behavior in response to changes in tasks or environment
Simply put, EFs contribute to the child’s ability to sustain attention, ignore distractions, and succeed in academic settings. By now some of you must be wondering: “So what does Hedbanz have to do with any of it?”
Well, Hedbanz is a quick-paced multiplayer (2-6 people) game of “What Am I?” for children ages 7 and up. Players get 3 chips and wear a “picture card” in their headband. They need to ask questions in rapid succession to figure out what they are. “Am I fruit?” “Am I a dessert?” “Am I sports equipment?” When they figure it out, they get rid of a chip. The first player to get rid of all three chips wins.
The game sounds deceptively simple. Yet if any SLPs or parents have ever played that game with their language impaired students/children as they would be quick to note how extraordinarily difficult it is for the children to figure out what their card is. Interestingly, in my clinical experience, I’ve noticed that it’s not just moderately language impaired children who present with difficulty playing this game. Even my bright, average intelligence teens, who have passed vocabulary and semantic flexibility testing (such as the WORD Test 2-Adolescent or the Vocabulary Awareness subtest of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy ) significantly struggle with their language organization when playing this game.
So what makes Hedbanz so challenging for language impaired students? Primarily, it’s the involvement and coordination of the multiple executive functions during the game. In order to play Hedbanz effectively and effortlessly, the following EF involvement is needed:
- Task Initiation
- Students with executive function impairments will often “freeze up” and as a result may have difficulty initiating the asking of questions in the game because many will not know what kind of questions to ask, even after extensive explanations and elaborations by the therapist.
- Organization
- Students with executive function impairments will present with difficulty organizing their questions by meaningful categories and as a result will frequently lose their track of thought in the game.
- Working Memory
- This executive function requires the student to keep key information in mind as well as keep track of whatever questions they have already asked.
- Flexible Thinking
- This executive function requires the student to consider a situation from multiple angles in order to figure out the quickest and most effective way of arriving at a solution. During the game, students may present with difficulty flexibly generating enough organizational categories in order to be effective participants.
- Impulse Control
- Many students with difficulties in this area may blurt out an inappropriate category or in an appropriate question without thinking it through first.
- They may also present with difficulty set-shifting. To illustrate, one of my 13-year-old students with ASD, kept repeating the same question when it was his turn, despite the fact that he was informed by myself as well as other players of the answer previously.
- Many students with difficulties in this area may blurt out an inappropriate category or in an appropriate question without thinking it through first.
- Emotional Control
- This executive function will help students with keeping their emotions in check when the game becomes too frustrating. Many students of difficulties in this area will begin reacting behaviorally when things don’t go their way and they are unable to figure out what their card is quickly enough. As a result, they may have difficulty mentally regrouping and reorganizing their questions when something goes wrong in the game.
- Self-Monitoring
- This executive function allows the students to figure out how well or how poorly they are doing in the game. Students with poor insight into own abilities may present with difficulty understanding that they are doing poorly and may require explicit instruction in order to change their question types.
- Planning and Prioritizing
- Students with poor abilities in this area will present with difficulty prioritizing their questions during the game.
Consequently, all of the above executive functions can be addressed via language-based goals. However, before I cover that, I’d like to review some of my session procedures first.
Typically, long before game initiation, I use the cards from the game to prep the students by teaching them how to categorize and classify presented information so they effectively and efficiently play the game.
 Rather than using the “tip cards”, I explain to the students how to categorize information effectively.
Rather than using the “tip cards”, I explain to the students how to categorize information effectively.
This, in turn, becomes a great opportunity for teaching students relevant vocabulary words, which can be extended far beyond playing the game.
I begin the session by explaining to the students that pretty much everything can be roughly divided into two categories animate (living) or inanimate (nonliving) things. I explain that humans, animals, as well as plants belong to the category of living things, while everything else belongs to the category of inanimate objects. I further divide the category of inanimate things into naturally existing and man-made items. I explain to the students that the naturally existing category includes bodies of water, landmarks, as well as things in space (moon, stars, sky, sun, etc.). In contrast, things constructed in factories or made by people would be example of man-made objects (e.g., building, aircraft, etc.)
When I’m confident that the students understand my general explanations, we move on to discuss further refinement of these broad categories. If a student determines that their card belongs to the category of living things, we discuss how from there the student can further determine whether they are an animal, a plant, or a human. If a student determined that their card belongs to the animal category, we discuss how we can narrow down the options of figuring out what animal is depicted on their card by asking questions regarding their habitat (“Am I a jungle animal?”), and classification (“Am I a reptile?”). From there, discussion of attributes prominently comes into play. We discuss shapes, sizes, colors, accessories, etc., until the student is able to confidently figure out which animal is depicted on their card.
In contrast, if the student’s card belongs to the inanimate category of man-made objects, we further subcategorize the information by the object’s location (“Am I found outside or inside?”; “Am I found in ___ room of the house?”, etc.), utility (“Can I be used for ___?”), as well as attributes (e.g., size, shape, color, etc.)
Thus, in addition to improving the students’ semantic flexibility skills (production of definitions, synonyms, attributes, etc.) the game teaches the students to organize and compartmentalize information in order to effectively and efficiently arrive at a conclusion in the most time expedient fashion.
Now, we are ready to discuss what type of EF language-based goals, SLPs can target by simply playing this game.
1. Initiation: Student will initiate questioning during an activity in __ number of instances per 30-minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
2. Planning: Given a specific routine, student will verbally state the order of steps needed to complete it with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
3. Working Memory: Student will repeat clinician provided verbal instructions pertaining to the presented activity, prior to its initiation, with 80% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
4. Flexible Thinking: Following a training by the clinician, student will generate at least __ questions needed for task completion (e.g., winning the game) with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
5. Organization: Student will use predetermined written/visual cues during an activity to assist self with organization of information (e.g., questions to ask) with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
6. Impulse Control: During the presented activity the student will curb blurting out inappropriate responses (by silently counting to 3 prior to providing his response) in __ number of instances per 30 minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
7. Emotional Control: When upset, student will verbalize his/her frustration (vs. behavioral activing out) in __ number of instances per 30 minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
8. Self-Monitoring: Following the completion of an activity (e.g., game) student will provide insight into own strengths and weaknesses during the activity (recap) by verbally naming the instances in which s/he did well, and instances in which s/he struggled with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
There you have it. This one simple game doesn’t just target a plethora of typical expressive language goals. It can effectively target and improve language-based executive function goals as well. Considering the fact that it sells for approximately $12 on Amazon.com, that’s a pretty useful therapy material to have in one’s clinical tool repertoire. For fancier versions, clinicians can use “Jeepers Peepers” photo card sets sold by Super Duper Inc. Strapped for cash, due to highly limited budget? You can find plenty of free materials online if you simply input “Hedbanz cards” in your search query on Google. So have a little fun in therapy, while your students learn something valuable in the process and play Hedbanz today!
Related Smart Speech Therapy Resources:
A Focus on Literacy
 In recent months, I have been focusing more and more on speaking engagements as well as the development of products with an explicit focus on assessment and intervention of literacy in speech-language pathology. Today I’d like to introduce 4 of my recently developed products pertinent to assessment and treatment of literacy in speech-language pathology.
In recent months, I have been focusing more and more on speaking engagements as well as the development of products with an explicit focus on assessment and intervention of literacy in speech-language pathology. Today I’d like to introduce 4 of my recently developed products pertinent to assessment and treatment of literacy in speech-language pathology.
 First up is the Comprehensive Assessment and Treatment of Literacy Disorders in Speech-Language Pathology
First up is the Comprehensive Assessment and Treatment of Literacy Disorders in Speech-Language Pathology
which describes how speech-language pathologists can effectively assess and treat children with literacy disorders, (reading, spelling, and writing deficits including dyslexia) from preschool through adolescence. It explains the impact of language disorders on literacy development, lists formal and informal assessment instruments and procedures, as well as describes the importance of assessing higher order language skills for literacy purposes. It reviews components of effective reading instruction including phonological awareness, orthographic knowledge, vocabulary awareness, morphological awareness, as well as reading fluency and comprehension. Finally, it provides recommendations on how components of effective reading instruction can be cohesively integrated into speech-language therapy sessions in order to improve literacy abilities of children with language disorders and learning disabilities.
 Next up is a product entitled From Wordless Picture Books to Reading Instruction: Effective Strategies for SLPs Working with Intellectually Impaired Students. This product discusses how to address the development of critical thinking skills through a variety of picture books utilizing the framework outlined in Bloom’s Taxonomy: Cognitive Domain which encompasses the categories of knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation in children with intellectual impairments. It shares a number of similarities with the above product as it also reviews components of effective reading instruction for children with language and intellectual disabilities as well as provides recommendations on how to integrate reading instruction effectively into speech-language therapy sessions.
Next up is a product entitled From Wordless Picture Books to Reading Instruction: Effective Strategies for SLPs Working with Intellectually Impaired Students. This product discusses how to address the development of critical thinking skills through a variety of picture books utilizing the framework outlined in Bloom’s Taxonomy: Cognitive Domain which encompasses the categories of knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation in children with intellectual impairments. It shares a number of similarities with the above product as it also reviews components of effective reading instruction for children with language and intellectual disabilities as well as provides recommendations on how to integrate reading instruction effectively into speech-language therapy sessions.
 The product Improving Critical Thinking Skills via Picture Books in Children with Language Disorders is also available for sale on its own with a focus on only teaching critical thinking skills via the use of picture books.
The product Improving Critical Thinking Skills via Picture Books in Children with Language Disorders is also available for sale on its own with a focus on only teaching critical thinking skills via the use of picture books.
 Finally, my last product Best Practices in Bilingual Literacy Assessments and Interventions focuses on how bilingual speech-language pathologists (SLPs) can effectively assess and intervene with simultaneously bilingual and multicultural children (with stronger academic English language skills) diagnosed with linguistically-based literacy impairments. Topics include components of effective literacy assessments for simultaneously bilingual children (with stronger English abilities), best instructional literacy practices, translanguaging support strategies, critical questions relevant to the provision of effective interventions, as well as use of accommodations, modifications and compensatory strategies for improvement of bilingual students’ performance in social and academic settings.
Finally, my last product Best Practices in Bilingual Literacy Assessments and Interventions focuses on how bilingual speech-language pathologists (SLPs) can effectively assess and intervene with simultaneously bilingual and multicultural children (with stronger academic English language skills) diagnosed with linguistically-based literacy impairments. Topics include components of effective literacy assessments for simultaneously bilingual children (with stronger English abilities), best instructional literacy practices, translanguaging support strategies, critical questions relevant to the provision of effective interventions, as well as use of accommodations, modifications and compensatory strategies for improvement of bilingual students’ performance in social and academic settings.
You can find these and other products in my online store (HERE).
Helpful Smart Speech Therapy Resources:
- Dynamic Assessment of Bilingual and Multicultural Learners in Speech-Language Pathology
- Differential Assessment and Treatment of Processing Disorders in Speech-Language Pathology
- Practical Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing and Treating Bilingual Children
- The Checklists Bundle
- General Assessment and Treatment Start Up Bundle
- Multicultural Assessment Bundle
- Narrative Assessment and Treatment Bundle
- Social Pragmatic Assessment and Treatment Bundle
- Psychiatric Disorders Bundle
New Product Giveaway: Comprehensive Literacy Checklist For School-Aged Children
 I wanted to start the new year right by giving away a few copies of a new checklist I recently created entitled: “Comprehensive Literacy Checklist For School-Aged Children“.
I wanted to start the new year right by giving away a few copies of a new checklist I recently created entitled: “Comprehensive Literacy Checklist For School-Aged Children“.
It was created to assist Speech Language Pathologists (SLPs) in the decision-making process of how to identify deficit areas and select assessment instruments to prioritize a literacy assessment for school aged children.
The goal is to eliminate administration of unnecessary or irrelevant tests and focus on the administration of instruments directly targeting the specific areas of difficulty that the student presents with.
*For the purpose of this product, the term “literacy checklist” rather than “dyslexia checklist” is used throughout this document to refer to any deficits in the areas of reading, writing, and spelling that the child may present with in order to identify any possible difficulties the child may present with, in the areas of literacy as well as language.
This checklist can be used for multiple purposes.
1. To identify areas of deficits the child presents with for targeted assessment purposes
2. To highlight areas of strengths (rather than deficits only) the child presents with pre or post intervention
3. To highlight residual deficits for intervention purpose in children already receiving therapy services without further reassessment
Checklist Contents:
- Page 1 Title
- Page 2 Directions
- Pages 3-9 Checklist
- Page 10 Select Tests of Reading, Spelling, and Writing for School-Aged Children
- Pages 11-12 Helpful Smart Speech Therapy Materials
Checklist Areas:
- AT RISK FAMILY HISTORY
- AT RISK DEVELOPMENTAL HISTORY
- BEHAVIORAL MANIFESTATIONS
- LEARNING DEFICITS
- Memory for Sequences
- Vocabulary Knowledge
- Narrative Production
- Phonological Awareness
- Phonics
- Morphological Awareness
- Reading Fluency
- Reading Comprehension
- Spelling
- Writing Conventions
- Writing Composition
- Handwriting
You can find this product in my online store HERE.
Would you like to check it out in action? I’ll be giving away two copies of the checklist in a Rafflecopter Giveaway to two winners. So enter today to win your own copy!
Comprehensive Assessment of Adolescents with Suspected Language and Literacy Disorders
 When many of us think of such labels as “language disorder” or “learning disability”, very infrequently do adolescents (students 13-18 years of age) come to mind. Even today, much of the research in the field of pediatric speech pathology involves preschool and school-aged children under 12 years of age.
When many of us think of such labels as “language disorder” or “learning disability”, very infrequently do adolescents (students 13-18 years of age) come to mind. Even today, much of the research in the field of pediatric speech pathology involves preschool and school-aged children under 12 years of age.
The prevalence and incidence of language disorders in adolescents is very difficult to estimate due to which some authors even referred to them as a Neglected Group with Significant Problems having an “invisible disability“.
Far fewer speech language therapists work with middle-schoolers vs. preschoolers and elementary aged kids, while the numbers of SLPs working with high-school aged students is frequently in single digits in some districts while being completely absent in others. In fact, I am frequently told (and often see it firsthand) that some administrators try to cut costs by attempting to dictate a discontinuation of speech-language services on the grounds that adolescents “are far too old for services” or can “no longer benefit from services”.
But of course the above is blatantly false. Undetected language deficits don’t resolve with age! They simply exacerbate and turn into learning disabilities. Similarly, lack of necessary and appropriate service provision to children with diagnosed language impairments at the middle-school and high-school levels will strongly affect their academic functioning and hinder their future vocational outcomes.
A cursory look at the Speech Pathology Related Facebook Groups as well as ASHA forums reveals numerous SLPs in a continual search for best methods of assessment and treatment of older students (~12-18 years of age).
Consequently, today I wanted to dedicate this post to a review of standardized assessments options available for students 12-18 years of age with suspected language and literacy deficits.
Most comprehensive standardized assessments, “typically focus on semantics, syntax, morphology, and phonology, as these are the performance areas in which specific skill development can be most objectively measured” (Hill & Coufal, 2005, p 35). Very few of them actually incorporate aspects of literacy into its subtests in a meaningful way. Yet by the time students reach adolescence literacy begins to play an incredibly critical role not just in all the aspects of academics but also social communication.
So when it comes to comprehensive general language testing I highly recommended that SLPs select standardized measures with a focus on not language but also literacy. Presently of all the comprehensive assessment tools I highly prefer the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS) for students up to 18 years of age, (see a comprehensive review HERE), which covers such literacy areas as phonological awareness, reading fluency, reading comprehension, writing and spelling in addition to traditional language areas as as vocabulary awareness, following directions, story recall, etc. However, while comprehensive tests have numerous uses, their sole administration will not constitute an adequate assessment.
So what areas should be assessed during language and literacy testing? Below are a few suggestions of standardized testing measures (and informal procedures) aimed at exploring the student abilities in particular areas pertaining to language and literacy.
TESTS OF LANGUAGE
- Listening Comprehension (for stories not just sentences)
- The Listening Comprehension Test-Adolescent (up to 18 years of age)
- Can be supplemented with informal listening comprehension assessment by giving the students grade level passages
- The Listening Comprehension Test-Adolescent (up to 18 years of age)
- Comprehension of Ambiguous and Figurative Language (e.g., idioms, ambiguous expressions, etc.)
- Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals -5 Metalinguistics (up to 22 years of age)
- Semantic Flexibility (e.g., generation of definitions, synonyms, antonyms, multiple meaning words, etc.)
- WORD Test 2 Adolescent (up to 18 years of age)
- Can be supplemented with informal narrative assessment to determine if the student coherently and cohesively summarize expository or narrative texts
- WORD Test 2 Adolescent (up to 18 years of age)
- Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
- TOPS-2 Adolescent Test of Problem Solving-2 (up to 18 years of age)
- Social Communication
- Social Language Development Test Adolescent (up to 18 years of age)
- Clinical Assessment of Pragmatics (CAPs)
- Can be supplemented with informal assessment of social communication Informal Social Thinking Dynamic Assessment Protocol®)
- Executive Function
- Informal use of Situational Awareness STOP Observation Tool (Ward & Jacobsen, 2014)
- Phonological Awareness
- Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing-2 (CTOPP-2) (up to 25 years of age)
- Word Fluency
- Rapid Automatized Naming/Rapid Alternating Stimulus RAN/RAS (up to 18 years of age)
- Reading Fluency
- GORT-5: Gray Oral Reading Tests−Fifth Edition (up to 24 years of age)
- The Test of Silent Word Reading Fluency (TOSWRF-2) (up to 25 years of age)
- Test of Silent Contextual Reading Fluency (TOSCRF-2) (up to 25 years of age)
- Reading Comprehension
- Spelling
- Writing
- TOWL-4: Test of Written Language–Fourth Edition (up to 18 years of age)
- Can be informally supplemented with the use of Grade Rubrics addressing Persuasive/Expository Texts
- TOWL-4: Test of Written Language–Fourth Edition (up to 18 years of age)
It is understandable how given the sheer amount of assessment choices some clinicians may feel overwhelmed and be unsure regarding the starting point of an adolescent evaluation. Consequently, the use the checklist prior to the initiation of assessment may be highly useful in order to identify potential language weaknesses/deficits the students might experience. It will also allow clinicians to prioritize the hierarchy of testing instruments to use during the assessment.
While clinicians are encouraged to develop such checklists for their personal use, those who lack time and opportunity can locate a number of already available checklists on the market.
For example, the comprehensive 6-page Speech Language Assessment Checklist for Adolescents (below) can be given to caregivers, classroom teachers, and even older students in order to check off the most pressing difficulties the student is experiencing in an academic setting.
It is important for several individuals to fill out this checklist to ensure consistency of deficits, prior to determining whether an assessment is warranted in the first place and if so, which assessment areas need to be targeted.
Checklist Categories:
- Receptive Language

- Memory, Attention and Cognition
- Expressive Language
- Vocabulary
- Discourse
- Speech
- Voice
- Prosody
- Resonance
- Reading
- Writing
- Problem Solving
- Pragmatic Language Skills
- Social Emotional Development
- Executive Functioning
Based on the checklist administration SLPs can reliably pinpoint the student’s areas of deficits without needless administration of unrelated/unnecessary testing instruments. For example, if a student presents with deficits in the areas of problem solving and social pragmatic functioning the administration of a general language test such as the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals® – Fifth Edition (CELF-5) would NOT be functional (especially if the previous administration of educational testing did not reveal any red flags). In contrast, the administration of such tests as Test Of Problem Solving 2 Adolescent and Social Language Development Test Adolescent would be better reflective of the student’s deficits in the above areas. (Checklist HERE; checklist sample HERE).
It is very important to understand that students presenting with language and literacy deficits will not outgrow these deficits on their own. While there may be “a time period when the students with early language disorders seem to catch up with their typically developing peers” (e.g., illusory recovery) by undergoing a “spurt” in language learning”(Sun & Wallach, 2014). These spurts are typically followed by a “post-spurt plateau”. This is because due to the ongoing challenges and an increase in academic demands “many children with early language disorders fail to “outgrow” these difficulties or catch up with their typically developing peers”(Sun & Wallach, 2014). As such many adolescents “may not show academic or language-related learning difficulties until linguistic and cognitive demands of the task increase and exceed their limited abilities” (Sun & Wallach, 2014). Consequently, SLPs must consider the “underlying deficits that may be masked by early oral language development” and “evaluate a child’s language abilities in all modalities, including pre-literacy, literacy, and metalinguistic skills” (Sun & Wallach, 2014).
References:
- Hill, J. W., & Coufal, K. L. (2005). Emotional/behavioral disorders: A retrospective examination of social skills, linguistics, and student outcomes. Communication Disorders Quarterly, 27(1), 33–46.
- Sun, L & Wallach G (2014) Language Disorders Are Learning Disabilities: Challenges on the Divergent and Diverse Paths to Language Learning Disability. Topics in Language Disorders, Vol. 34; (1), pp 25–38.
Helpful Smart Speech Therapy Resources
- Assessment of Adolescents with Language and Literacy Impairments in Speech Language Pathology
- Assessment and Treatment Bundles
- Social Communication Materials
- Multicultural Materials
Review of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS)
 The Test of Integrated Language & Literacy Skills (TILLS) is an assessment of oral and written language abilities in students 6–18 years of age. Published in the Fall 2015, it is unique in the way that it is aimed to thoroughly assess skills such as reading fluency, reading comprehension, phonological awareness, spelling, as well as writing in school age children. As I have been using this test since the time it was published, I wanted to take an opportunity today to share just a few of my impressions of this assessment.
The Test of Integrated Language & Literacy Skills (TILLS) is an assessment of oral and written language abilities in students 6–18 years of age. Published in the Fall 2015, it is unique in the way that it is aimed to thoroughly assess skills such as reading fluency, reading comprehension, phonological awareness, spelling, as well as writing in school age children. As I have been using this test since the time it was published, I wanted to take an opportunity today to share just a few of my impressions of this assessment.
First, a little background on why I chose to purchase this test so shortly after I had purchased the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals – 5 (CELF-5). Soon after I started using the CELF-5 I noticed that it tended to considerably overinflate my students’ scores on a variety of its subtests. In fact, I noticed that unless a student had a fairly severe degree of impairment, the majority of his/her scores came out either low/slightly below average (click for more info on why this was happening HERE, HERE, or HERE). Consequently, I was excited to hear regarding TILLS development, almost simultaneously through ASHA as well as SPELL-Links ListServe. I was particularly happy because I knew some of this test’s developers (e.g., Dr. Elena Plante, Dr. Nickola Nelson) have published solid research in the areas of psychometrics and literacy respectively.
According to the TILLS developers it has been standardized for 3 purposes:
- to identify language and literacy disorders
- to document patterns of relative strengths and weaknesses
- to track changes in language and literacy skills over time
The testing subtests can be administered in isolation (with the exception of a few) or in its entirety. The administration of all the 15 subtests may take approximately an hour and a half, while the administration of the core subtests typically takes ~45 mins).
Please note that there are 5 subtests that should not be administered to students 6;0-6;5 years of age because many typically developing students are still mastering the required skills.
- Subtest 5 – Nonword Spelling
- Subtest 7 – Reading Comprehension
- Subtest 10 – Nonword Reading
- Subtest 11 – Reading Fluency
- Subtest 12 – Written Expression
However, if needed, there are several tests of early reading and writing abilities which are available for assessment of children under 6:5 years of age with suspected literacy deficits (e.g., TERA-3: Test of Early Reading Ability–Third Edition; Test of Early Written Language, Third Edition-TEWL-3, etc.).
Let’s move on to take a deeper look at its subtests. Please note that for the purposes of this review all images came directly from and are the property of Brookes Publishing Co (clicking on each of the below images will take you directly to their source).
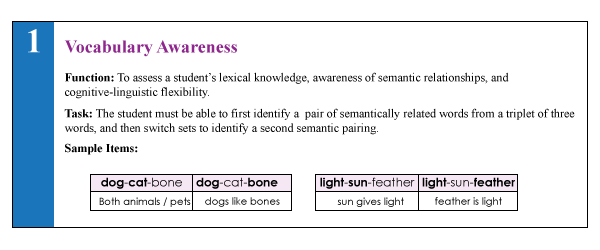 1. Vocabulary Awareness (VA) (description above) requires students to display considerable linguistic and cognitive flexibility in order to earn an average score. It works great in teasing out students with weak vocabulary knowledge and use, as well as students who are unable to quickly and effectively analyze words for deeper meaning and come up with effective definitions of all possible word associations. Be mindful of the fact that even though the words are presented to the students in written format in the stimulus book, the examiner is still expected to read all the words to the students. Consequently, students with good vocabulary knowledge and strong oral language abilities can still pass this subtest despite the presence of significant reading weaknesses. Recommendation: I suggest informally checking the student’s word reading abilities by asking them to read of all the words, before reading all the word choices to them. This way you can informally document any word misreadings made by the student even in the presence of an average subtest score.
1. Vocabulary Awareness (VA) (description above) requires students to display considerable linguistic and cognitive flexibility in order to earn an average score. It works great in teasing out students with weak vocabulary knowledge and use, as well as students who are unable to quickly and effectively analyze words for deeper meaning and come up with effective definitions of all possible word associations. Be mindful of the fact that even though the words are presented to the students in written format in the stimulus book, the examiner is still expected to read all the words to the students. Consequently, students with good vocabulary knowledge and strong oral language abilities can still pass this subtest despite the presence of significant reading weaknesses. Recommendation: I suggest informally checking the student’s word reading abilities by asking them to read of all the words, before reading all the word choices to them. This way you can informally document any word misreadings made by the student even in the presence of an average subtest score.
2. The Phonemic Awareness (PA) subtest (description above) requires students to isolate and delete initial sounds in words of increasing complexity. While this subtest does not require sound isolation and deletion in various word positions, similar to tests such as the CTOPP-2: Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing–Second Edition or the The Phonological Awareness Test 2 (PAT 2), it is still a highly useful and reliable measure of phonemic awareness (as one of many precursors to reading fluency success). This is especially because after the initial directions are given, the student is expected to remember to isolate the initial sounds in words without any prompting from the examiner. Thus, this task also indirectly tests the students’ executive function abilities in addition to their phonemic awareness skills.
3. The Story Retelling (SR) subtest (description above) requires students to do just that retell a story. Be mindful of the fact that the presented stories have reduced complexity. Thus, unless the students possess significant retelling deficits, the above subtest may not capture their true retelling abilities. Recommendation: Consider supplementing this subtest with informal narrative measures. For younger children (kindergarten and first grade) I recommend using wordless picture books to perform a dynamic assessment of their retelling abilities following a clinician’s narrative model (e.g., HERE). For early elementary aged children (grades 2 and up), I recommend using picture books, which are first read to and then retold by the students with the benefit of pictorial but not written support. Finally, for upper elementary aged children (grades 4 and up), it may be helpful for the students to retell a book or a movie seen recently (or liked significantly) by them without the benefit of visual support all together (e.g., HERE).
4. The Nonword Repetition (NR) subtest (description above) requires students to repeat nonsense words of increasing length and complexity. Weaknesses in the area of nonword repetition have consistently been associated with language impairments and learning disabilities due to the task’s heavy reliance on phonological segmentation as well as phonological and lexical knowledge (Leclercq, Maillart, Majerus, 2013). Thus, both monolingual and simultaneously bilingual children with language and literacy impairments will be observed to present with patterns of segment substitutions (subtle substitutions of sounds and syllables in presented nonsense words) as well as segment deletions of nonword sequences more than 2-3 or 3-4 syllables in length (depending on the child’s age).
5. The Nonword Spelling (NS) subtest (description above) requires the students to spell nonwords from the Nonword Repetition (NR) subtest. Consequently, the Nonword Repetition (NR) subtest needs to be administered prior to the administration of this subtest in the same assessment session. In contrast to the real-word spelling tasks, students cannot memorize the spelling of the presented words, which are still bound by orthographic and phonotactic constraints of the English language. While this is a highly useful subtest, is important to note that simultaneously bilingual children may present with decreased scores due to vowel errors. Consequently, it is important to analyze subtest results in order to determine whether dialectal differences rather than a presence of an actual disorder is responsible for the error patterns.
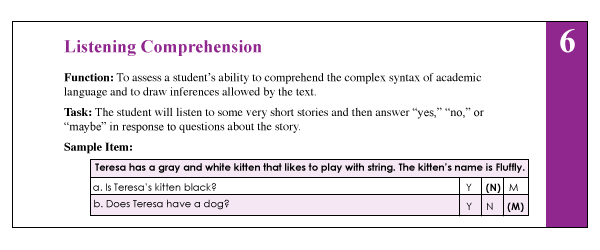
6. The Listening Comprehension (LC) subtest (description above) requires the students to listen to short stories and then definitively answer story questions via available answer choices, which include: “Yes”, “No’, and “Maybe”. This subtest also indirectly measures the students’ metalinguistic awareness skills as they are needed to detect when the text does not provide sufficient information to answer a particular question definitively (e.g., “Maybe” response may be called for). Be mindful of the fact that because the students are not expected to provide sentential responses to questions it may be important to supplement subtest administration with another listening comprehension assessment. Tests such as the Listening Comprehension Test-2 (LCT-2), the Listening Comprehension Test-Adolescent (LCT-A), or the Executive Function Test-Elementary (EFT-E) may be useful if language processing and listening comprehension deficits are suspected or reported by parents or teachers. This is particularly important to do with students who may be ‘good guessers’ but who are also reported to present with word-finding difficulties at sentence and discourse levels.
7. The Reading Comprehension (RC) subtest (description above) requires the students to read short story and answer story questions in “Yes”, “No’, and “Maybe” format. This subtest is not stand alone and must be administered immediately following the administration the Listening Comprehension subtest. The student is asked to read the first story out loud in order to determine whether s/he can proceed with taking this subtest or discontinue due to being an emergent reader. The criterion for administration of the subtest is making 7 errors during the reading of the first story and its accompanying questions. Unfortunately, in my clinical experience this subtest is not always accurate at identifying children with reading-based deficits.
While I find it terrific for students with severe-profound reading deficits and/or below average IQ, a number of my students with average IQ and moderately impaired reading skills managed to pass it via a combination of guessing and luck despite being observed to misread aloud between 40-60% of the presented words. Be mindful of the fact that typically such students may have up to 5-6 errors during the reading of the first story. Thus, according to administration guidelines these students will be allowed to proceed and take this subtest. They will then continue to make text misreadings during each story presentation (you will know that by asking them to read each story aloud vs. silently). However, because the response mode is in definitive (“Yes”, “No’, and “Maybe”) vs. open ended question format, a number of these students will earn average scores by being successful guessers. Recommendation: I highly recommend supplementing the administration of this subtest with grade level (or below grade level) texts (see HERE and/or HERE), to assess the student’s reading comprehension informally.
I present a full one page text to the students and ask them to read it to me in its entirety. I audio/video record the student’s reading for further analysis (see Reading Fluency section below). After the completion of the story I ask the student questions with a focus on main idea comprehension and vocabulary definitions. I also ask questions pertaining to story details. Depending on the student’s age I may ask them abstract/ factual text questions with and without text access. Overall, I find that informal administration of grade level (or even below grade-level) texts coupled with the administration of standardized reading tests provides me with a significantly better understanding of the student’s reading comprehension abilities rather than administration of standardized reading tests alone.
8. The Following Directions (FD) subtest (description above) measures the student’s ability to execute directions of increasing length and complexity. It measures the student’s short-term, immediate and working memory, as well as their language comprehension. What is interesting about the administration of this subtest is that the graphic symbols (e.g., objects, shapes, letter and numbers etc.) the student is asked to modify remain covered as the instructions are given (to prevent visual rehearsal). After being presented with the oral instruction the students are expected to move the card covering the stimuli and then to executive the visual-spatial, directional, sequential, and logical if–then the instructions by marking them on the response form. The fact that the visual stimuli remains covered until the last moment increases the demands on the student’s memory and comprehension. The subtest was created to simulate teacher’s use of procedural language (giving directions) in classroom setting (as per developers).
9. The Delayed Story Retelling (DSR) subtest (description above) needs to be administered to the students during the same session as the Story Retelling (SR) subtest, approximately 20 minutes after the SR subtest administration. Despite the relatively short passage of time between both subtests, it is considered to be a measure of long-term memory as related to narrative retelling of reduced complexity. Here, the examiner can compare student’s performance to determine whether the student did better or worse on either of these measures (e.g., recalled more information after a period of time passed vs. immediately after being read the story). However, as mentioned previously, some students may recall this previously presented story fairly accurately and as a result may obtain an average score despite a history of teacher/parent reported long-term memory limitations. Consequently, it may be important for the examiner to supplement the administration of this subtest with a recall of a movie/book recently seen/read by the student (a few days ago) in order to compare both performances and note any weaknesses/limitations.
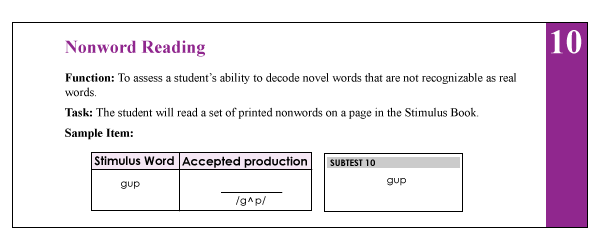
10. The Nonword Reading (NR) subtest (description above) requires students to decode nonsense words of increasing length and complexity. What I love about this subtest is that the students are unable to effectively guess words (as many tend to routinely do when presented with real words). Consequently, the presentation of this subtest will tease out which students have good letter/sound correspondence abilities as well as solid orthographic, morphological and phonological awareness skills and which ones only memorized sight words and are now having difficulty decoding unfamiliar words as a result. 
11. The Reading Fluency (RF) subtest (description above) requires students to efficiently read facts which make up simple stories fluently and correctly. Here are the key to attaining an average score is accuracy and automaticity. In contrast to the previous subtest, the words are now presented in meaningful simple syntactic contexts.
It is important to note that the Reading Fluency subtest of the TILLS has a negatively skewed distribution. As per authors, “a large number of typically developing students do extremely well on this subtest and a much smaller number of students do quite poorly.”
Thus, “the mean is to the left of the mode” (see publisher’s image below). This is why a student could earn an average standard score (near the mean) and a low percentile rank when true percentiles are used rather than NCE percentiles (Normal Curve Equivalent). 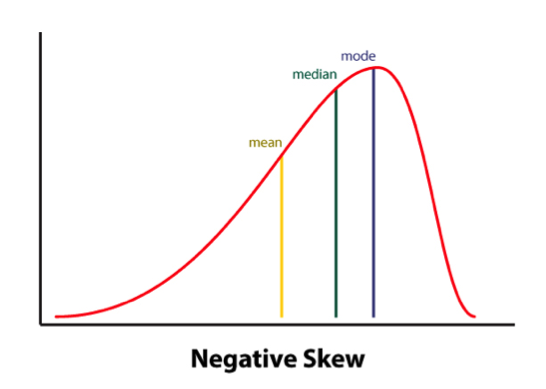
Consequently under certain conditions (See HERE) the percentile rank (vs. the NCE percentile) will be a more accurate representation of the student’s ability on this subtest.
Indeed, due to the reduced complexity of the presented words some students (especially younger elementary aged) may obtain average scores and still present with serious reading fluency deficits.
I frequently see that in students with average IQ and go to long-term memory, who by second and third grades have managed to memorize an admirable number of sight words due to which their deficits in the areas of reading appeared to be minimized. Recommendation: If you suspect that your student belongs to the above category I highly recommend supplementing this subtest with an informal measure of reading fluency. This can be done by presenting to the student a grade level text (I find science and social studies texts particularly useful for this purpose) and asking them to read several paragraphs from it (see HERE and/or HERE).
As the students are reading I calculate their reading fluency by counting the number of words they read per minute. I find it very useful as it allows me to better understand their reading profile (e.g, fast/inaccurate reader, slow/inaccurate reader, slow accurate reader, fast/accurate reader). As the student is reading I note their pauses, misreadings, word-attack skills and the like. Then, I write a summary comparing the students reading fluency on both standardized and informal assessment measures in order to document students strengths and limitations.
12. The Written Expression (WE) subtest (description above) needs to be administered to the students immediately after the administration of the Reading Fluency (RF) subtest because the student is expected to integrate a series of facts presented in the RF subtest into their writing sample. There are 4 stories in total for the 4 different age groups.
The examiner needs to show the student a different story which integrates simple facts into a coherent narrative. After the examiner reads that simple story to the students s/he is expected to tell the students that the story is okay, but “sounds kind of “choppy.” They then need to show the student an example of how they could put the facts together in a way that sounds more interesting and less choppy by combining sentences (see below). Finally, the examiner will ask the students to rewrite the story presented to them in a similar manner (e.g, “less choppy and more interesting.”)
After the student finishes his/her story, the examiner will analyze it and generate the following scores: a discourse score, a sentence score, and a word score. Detailed instructions as well as the Examiner’s Practice Workbook are provided to assist with scoring as it takes a bit of training as well as trial and error to complete it, especially if the examiners are not familiar with certain procedures (e.g., calculating T-units).
Full disclosure: Because the above subtest is still essentially sentence combining, I have only used this subtest a handful of times with my students. Typically when I’ve used it in the past, most of my students fell in two categories: those who failed it completely by either copying text word for word, failing to generate any written output etc. or those who passed it with flying colors but still presented with notable written output deficits. Consequently, I’ve replaced Written Expression subtest administration with the administration of written standardized tests, which I supplement with an informal grade level expository, persuasive, or narrative writing samples.
Having said that many clinicians may not have the access to other standardized written assessments, or lack the time to administer entire standardized written measures (which may frequently take between 60 to 90 minutes of administration time). Consequently, in the absence of other standardized writing assessments, this subtest can be effectively used to gauge the student’s basic writing abilities, and if needed effectively supplemented by informal writing measures (mentioned above).
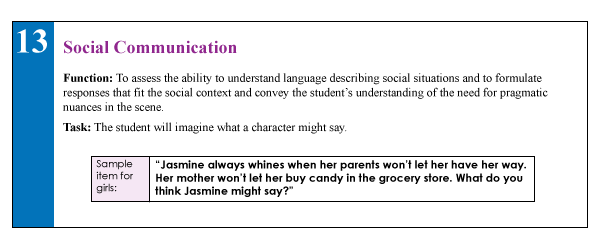
13. The Social Communication (SC) subtest (description above) assesses the students’ ability to understand vocabulary associated with communicative intentions in social situations. It requires students to comprehend how people with certain characteristics might respond in social situations by formulating responses which fit the social contexts of those situations. Essentially students become actors who need to act out particular scenes while viewing select words presented to them.
Full disclosure: Similar to my infrequent administration of the Written Expression subtest, I have also administered this subtest very infrequently to students. Here is why.
I am an SLP who works full-time in a psychiatric hospital with children diagnosed with significant psychiatric impairments and concomitant language and literacy deficits. As a result, a significant portion of my job involves comprehensive social communication assessments to catalog my students’ significant deficits in this area. Yet, past administration of this subtest showed me that number of my students can pass this subtest quite easily despite presenting with notable and easily evidenced social communication deficits. Consequently, I prefer the administration of comprehensive social communication testing when working with children in my hospital based program or in my private practice, where I perform independent comprehensive evaluations of language and literacy (IEEs).
Again, as I’ve previously mentioned many clinicians may not have the access to other standardized social communication assessments, or lack the time to administer entire standardized written measures. Consequently, in the absence of other social communication assessments, this subtest can be used to get a baseline of the student’s basic social communication abilities, and then be supplemented with informal social communication measures such as the Informal Social Thinking Dynamic Assessment Protocol (ISTDAP) or observational social pragmatic checklists.
14. The Digit Span Forward (DSF) subtest (description above) is a relatively isolated measure of short term and verbal working memory ( it minimizes demands on other aspects of language such as syntax or vocabulary).
15. The Digit Span Backward (DSB) subtest (description above) assesses the student’s working memory and requires the student to mentally manipulate the presented stimuli in reverse order. It allows examiner to observe the strategies (e.g. verbal rehearsal, visual imagery, etc.) the students are using to aid themselves in the process. Please note that the Digit Span Forward subtest must be administered immediately before the administration of this subtest.
SLPs who have used tests such as the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals – 5 (CELF-5) or the Test of Auditory Processing Skills – Third Edition (TAPS-3) should be highly familiar with both subtests as they are fairly standard measures of certain aspects of memory across the board.
To continue, in addition to the presence of subtests which assess the students literacy abilities, the TILLS also possesses a number of interesting features.
For starters, the TILLS Easy Score, which allows the examiners to use their scoring online. It is incredibly easy and effective. After clicking on the link and filling out the preliminary demographic information, all the examiner needs to do is to plug in this subtest raw scores, the system does the rest. After the raw scores are plugged in, the system will generate a PDF document with all the data which includes (but is not limited to) standard scores, percentile ranks, as well as a variety of composite and core scores. The examiner can then save the PDF on their device (laptop, PC, tablet etc.) for further analysis.
The there is the quadrant model. According to the TILLS sampler (HERE) “it allows the examiners to assess and compare students’ language-literacy skills at the sound/word level and the sentence/ discourse level across the four oral and written modalities—listening, speaking, reading, and writing” and then create “meaningful pro files of oral and written language skills that will help you understand the strengths and needs of individual students and communicate about them in a meaningful way with teachers, parents, and students. (pg. 21)”
Then there is the Student Language Scale (SLS) which is a one page checklist parents, teachers (and even students) can fill out to informally identify language and literacy based strengths and weaknesses. It allows for meaningful input from multiple sources regarding the students performance (as per IDEA 2004) and can be used not just with TILLS but with other tests or in even isolation (as per developers).
Furthermore according to the developers, because the normative sample included several special needs populations, the TILLS can be used with students diagnosed with ASD, deaf or hard of hearing (see caveat), as well as intellectual disabilities (as long as they are functioning age 6 and above developmentally).
According to the developers the TILLS is aligned with Common Core Standards and can be administered as frequently as two times a year for progress monitoring (min of 6 mos post 1st administration).
With respect to bilingualism examiners can use it with caution with simultaneous English learners but not with sequential English learners (see further explanations HERE). Translations of TILLS are definitely not allowed as they will undermine test validity and reliability.
So there you have it these are just some of my very few impressions regarding this test. Now to some of you may notice that I spend a significant amount of time pointing out some of the tests limitations. However, it is very important to note that we have research that indicates that there is no such thing as a “perfect standardized test” (see HERE for more information). All standardized tests have their limitations.
Having said that, I think that TILLS is a PHENOMENAL addition to the standardized testing market, as it TRULY appears to assess not just language but also literacy abilities of the students on our caseloads.
That’s all from me; however, before signing off I’d like to provide you with more resources and information, which can be reviewed in reference to TILLS. For starters, take a look at Brookes Publishing TILLS resources. These include (but are not limited to) TILLS FAQ, TILLS Easy-Score, TILLS Correction Document, as well as 3 FREE TILLS Webinars. There’s also a Facebook Page dedicated exclusively to TILLS updates (HERE).
But that’s not all. Dr. Nelson and her colleagues have been tirelessly lecturing about the TILLS for a number of years, and many of their past lectures and presentations are available on the ASHA website as well as on the web (e.g., HERE, HERE, HERE, etc). Take a look at them as they contain far more in-depth information regarding the development and implementation of this groundbreaking assessment.
To access TILLS fully-editable template, click HERE
Disclaimer: I did not receive a complimentary copy of this assessment for review nor have I received any encouragement or compensation from either Brookes Publishing or any of the TILLS developers to write it. All images of this test are direct property of Brookes Publishing (when clicked on all the images direct the user to the Brookes Publishing website) and were used in this post for illustrative purposes only.
References:
Leclercq A, Maillart C, Majerus S. (2013) Nonword repetition problems in children with SLI: A deficit in accessing long-term linguistic representations? Topics in Language Disorders. 33 (3) 238-254.
Related Posts:
- Components of Comprehensive Dyslexia Testing: Part I- Introduction and Language Testing
- Part II: Components of Comprehensive Dyslexia Testing – Phonological Awareness and Word Fluency Assessment
- Part III: Components of Comprehensive Dyslexia Testing – Reading Fluency and Reading Comprehension
- Part IV: Components of Comprehensive Dyslexia Testing – Writing and Spelling
- Special Education Disputes and Comprehensive Language Testing: What Parents, Attorneys, and Advocates Need to Know
- Why (C) APD Diagnosis is NOT Valid!
- What Are Speech Pathologists To Do If the (C)APD Diagnosis is NOT Valid?
- What do Auditory Memory Deficits Indicate in the Presence of Average General Language Scores?
- Why Are My Child’s Test Scores Dropping?
- Comprehensive Assessment of Adolescents with Suspected Language and Literacy Disorders
What Research Shows About the Functional Relevance of Standardized Language Tests
 As an SLP who routinely conducts speech and language assessments in several settings (e.g., school and private practice), I understand the utility of and the need for standardized speech, language, and literacy tests. However, as an SLP who works with children with dramatically varying degree of cognition, abilities, and skill-sets, I also highly value supplementing these standardized tests with functional and dynamic assessments, interactions, and observations.
As an SLP who routinely conducts speech and language assessments in several settings (e.g., school and private practice), I understand the utility of and the need for standardized speech, language, and literacy tests. However, as an SLP who works with children with dramatically varying degree of cognition, abilities, and skill-sets, I also highly value supplementing these standardized tests with functional and dynamic assessments, interactions, and observations.
 Since a significant value is placed on standardized testing by both schools and insurance companies for the purposes of service provision and reimbursement, I wanted to summarize in today’s post the findings of recent articles on this topic. Since my primary interest lies in assessing and treating school-age children, for the purposes of today’s post all of the reviewed articles came directly from the Language Speech and Hearing Services in Schools (LSHSS) journal.
Since a significant value is placed on standardized testing by both schools and insurance companies for the purposes of service provision and reimbursement, I wanted to summarize in today’s post the findings of recent articles on this topic. Since my primary interest lies in assessing and treating school-age children, for the purposes of today’s post all of the reviewed articles came directly from the Language Speech and Hearing Services in Schools (LSHSS) journal.
We’ve all been there. We’ve all had situations in which students scored on the low end of normal, or had a few subtest scores in the below average range, which equaled an average total score. We’ve all poured over eligibility requirements trying to figure out whether the student should receive therapy services given the stringent standardized testing criteria in some states/districts.
Of course, as it turns out, the answer is never simple. In 2006, Spaulding, Plante & Farinella set out to examine the assumption: “that children with language impairment will receive low scores on standardized tests, and therefore [those] low scores will accurately identify these children” (61). So they analyzed the data from 43 commercially available child language tests to identify whether evidence exists to support their use in identifying language impairment in children.
 Turns out it did not! Turns out due to the variation in psychometric properties of various tests (see article for specific details), many children with language impairment are overlooked by standardized tests by receiving scores within the average range or not receiving low enough scores to qualify for services. Thus, “the clinical consequence is that a child who truly has a language impairment has a roughly equal chance of being correctly or incorrectly identified, depending on the test that he or she is given.” Furthermore, “even if a child is diagnosed accurately as language impaired at one point in time, future diagnoses may lead to the false perception that the child has recovered, depending on the test(s) that he or she has been given (69).”
Turns out it did not! Turns out due to the variation in psychometric properties of various tests (see article for specific details), many children with language impairment are overlooked by standardized tests by receiving scores within the average range or not receiving low enough scores to qualify for services. Thus, “the clinical consequence is that a child who truly has a language impairment has a roughly equal chance of being correctly or incorrectly identified, depending on the test that he or she is given.” Furthermore, “even if a child is diagnosed accurately as language impaired at one point in time, future diagnoses may lead to the false perception that the child has recovered, depending on the test(s) that he or she has been given (69).”
Consequently, they created a decision tree (see below) with recommendations for clinicians using standardized testing. They recommend using alternate sources of data (sensitivity and specificity rates) to support accurate identification (available for a small subset of select tests).

The idea behind it is: “if sensitivity and specificity data are strong, and these data were derived from subjects who are comparable to the child tested, then the clinician can be relatively confident in relying on the test score data to aid his or her diagnostic decision. However, if the data are weak, then more caution is warranted and other sources of information on the child’s status might have primacy in making a diagnosis (70).”
Fast forward 6 years, and a number of newly revised tests later, in 2012, Spaulding and colleagues set out to “identify various U.S. state education departments’ criteria for determining the severity of language impairment in children, with particular focus on the use of norm-referenced tests” as well as to “determine if norm-referenced tests of child language were developed for the purpose of identifying the severity of children’s language impairment” (176).
They obtained published procedures for severity determinations from available U.S. state education departments, which specified the use of norm-referenced tests, and reviewed the manuals for 45 norm-referenced tests of child language to determine if each test was designed to identify the degree of a child’s language impairment.
What they found out was “the degree of use and cutoff-point criteria for severity determination varied across states. No cutoff-point criteria aligned with the severity cutoff points described within the test manuals. Furthermore, tests that included severity information lacked empirical data on how the severity categories were derived (176).”
 Thus they urged SLPs to exercise caution in determining the severity of children’s language impairment via norm-referenced test performance “given the inconsistency in guidelines and lack of empirical data within test manuals to support this use (176)”.
Thus they urged SLPs to exercise caution in determining the severity of children’s language impairment via norm-referenced test performance “given the inconsistency in guidelines and lack of empirical data within test manuals to support this use (176)”.
Following the publication of this article, Ireland, Hall-Mills & Millikin issued a response to the Spaulding and colleagues article. They pointed out that the “severity of language impairment is only one piece of information considered by a team for the determination of eligibility for special education and related services”. They noted that they left out a host of federal and state guideline requirements and “did not provide an analysis of the regulations governing special education evaluation and criteria for determining eligibility (320).” They pointed out that “IDEA prohibits the use of ‘any single measure or assessment as the sole criterion’ for determination of disability and requires that IEP teams ‘draw upon information from a variety of sources.”
They listed a variety of examples from several different state departments of education (FL, NC, VA, etc.), which mandate the use of functional assessments, dynamic assessments criterion-referenced assessments, etc. for their determination of language therapy eligibility.
 But are the SLPs from across the country appropriately using the federal and state guidelines in order to determine eligibility? While one should certainly hope so, it does not always seem to be the case. To illustrate, in 2012, Betz & colleagues asked 364 SLPs to complete a survey “regarding how frequently they used specific standardized tests when diagnosing suspected specific language impairment (SLI) (133).”
But are the SLPs from across the country appropriately using the federal and state guidelines in order to determine eligibility? While one should certainly hope so, it does not always seem to be the case. To illustrate, in 2012, Betz & colleagues asked 364 SLPs to complete a survey “regarding how frequently they used specific standardized tests when diagnosing suspected specific language impairment (SLI) (133).”
Their purpose was to determine “whether the quality of standardized tests, as measured by the test’s psychometric properties, is related to how frequently the tests are used in clinical practice” (133).
What they found out was that the most frequently used tests were the comprehensive assessments including the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals and the Preschool Language Scale as well as one word vocabulary tests such as the Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test. Furthermore, the date of publication seemed to be the only factor which affected the frequency of test selection.
They also found out that frequently SLPs did not follow up the comprehensive standardized testing with domain specific assessments (critical thinking, social communication, etc.) but instead used the vocabulary testing as a second measure. They were understandably puzzled by that finding. “The emphasis placed on vocabulary measures is intriguing because although vocabulary is often a weakness in children with SLI (e.g., Stothard et al., 1998), the research to date does not show vocabulary to be more impaired than other language domains in children with SLI (140).“
According to the authors, “perhaps the most discouraging finding of this study was the lack of a correlation between frequency of test use and test accuracy, measured both in terms of sensitivity/specificity and mean difference scores (141).”
If since the time (2012) SLPs have not significantly change their practices, the above is certainly disheartening, as it implies that rather than being true diagnosticians, SLPs are using whatever is at hand that has been purchased by their department to indiscriminately assess students with suspected speech language disorders. If that is truly the case, it certainly places into question the Ireland, Hall-Mills & Millikin’s response to Spaulding and colleagues. In other words, though SLPs are aware that they need to comply with state and federal regulations when it comes to unbiased and targeted assessments of children with suspected language disorders, they may not actually be using appropriate standardized testing much less supplementary informal assessments (e.g., dynamic, narrative, language sampling) in order to administer well-rounded assessments.
 So where do we go from here? Well, it’s quite simple really! We already know what the problem is. Based on the above articles we know that:
So where do we go from here? Well, it’s quite simple really! We already know what the problem is. Based on the above articles we know that:
- Standardized tests possess significant limitations
- They are not used with optimal effectiveness by many SLPs
- They may not be frequently supplemented by relevant and targeted informal assessment measures in order to improve the accuracy of disorder determination and subsequent therapy eligibility
Now that we have identified a problem, we need to develop and consistently implement effective practices to ameliorate it. These include researching psychometric properties of tests to review sample size, sensitivity and specificity, etc, use domain specific assessments to supplement administration of comprehensive testing, as well as supplement standardized testing with a plethora of functional assessments.
SLPs can review testing manuals and consult with colleagues when they feel that the standardized testing is underidentifying students with language impairments (e.g., HERE and HERE). They can utilize referral checklists (e.g., HERE) in order to pinpoint the students’ most significant difficulties. Finally, they can develop and consistently implement informal assessment practices (e.g., HERE and HERE) during testing in order to gain a better grasp on their students’ TRUE linguistic functioning.
Stay tuned for the second portion of this post entitled: “What Research Shows About the Functional Relevance of Standardized Speech Tests?” to find out the best practices in the assessment of speech sound disorders in children.
References:
- Spaulding, Plante & Farinella (2006) Eligibility Criteria for Language Impairment: Is the Low End of Normal Always Appropriate?
- Spaulding, Szulga, & Figueria (2012) Using Norm-Referenced Tests to Determine Severity of Language Impairment in Children: Disconnect Between U.S. Policy Makers and Test Developers
- Ireland, Hall-Mills & Millikin (2012) Appropriate Implementation of Severity Ratings, Regulations, and State Guidance: A Response to “Using Norm-Referenced Tests to Determine Severity of Language Impairment in Children: Disconnect Between U.S. Policy Makers and Test Developers” by Spaulding, Szulga, & Figueria (2012)
- Betz et al. (2013) Factors Influencing the Selection of Standardized Tests for the Diagnosis of Specific Language Impairment
Test Review: Test of Written Language-4 (TOWL-4)
Today due to popular demand I am reviewing The Test of Written Language-4 or TOWL-4. TOWL-4 assesses the basic writing readiness skills of students 9:00-17:11 years of age. The tests consist of two forms – A and B, (which contain different subtest content).
According to the manual, the entire test takes approximately 60-90 minutes to administer and examines 7 skill areas. Only the “Story Composition” subtest is officially timed (the student is given 15 minutes to write it and 5 minutes previous to that, to draft it). However, in my experience, each subtest administration, even with students presenting with mild-moderately impaired writing abilities, takes approximately 10 minutes to complete with average results (can you see where I am going with this yet?)
For detailed information regarding the TOWL-4 development and standardization, validity and reliability, please see HERE. However, please note that the psychometric properties of this test are weak.
Below are my impressions (to date) of using this assessment with students between 11-14 years of age with (known) mild-moderate writing impairments.
Subtests:
1. Vocabulary – The student is asked to write a sentence that incorporates a stimulus word. The student is not allowed to change the word in any way, such as write ‘running’ instead of run’. If this occurs, an automatic loss of points takes place. The ceiling is reached when the student makes 3 errors in a row. While some of the subtest vocabulary words are perfectly appropriate for younger children (~9), the majority are too simplistic to assess the written vocabulary of middle and high schoolers. These words may work well to test the knowledge of younger children but they do not take into the account the challenging academic standards set forth for older students. As a result, students 11+ years of age may pass this subtest with flying colors but still present with a fair amount of difficulty using sophisticated vocabulary words in written compositions.
2/3. Spelling and Punctuation (subtests 2 and 3). These two subtests are administered jointly but scored separately. Here, the student is asked to write sentences dictated by the examiner using appropriate rules for spelling and punctuation and capitalization. Ceiling for each subtest is reached separately. It occurs when the student makes 3 errors in a row in each of the subtests. In other words, if a student uses correct punctuation but incorrect spelling, his/her ceiling on the ‘Spelling’ subtest will be reached sooner then on the ‘Punctuation’ subtest and vise versa. Similar to the ‘Vocabulary‘ subtest I feel that the sentences the students are asked to write are far too simplistic to showcase their “true” grade level abilities.
The requirements of these subtests are also not too stringent. The spelling words are simple and the punctuation requirements are very basic: a question mark here, an exclamation mark there, with a few commas in between. But I was particularly disappointed with the ‘Spelling‘ subtest. Here’s why. I have a 6th-grade client on my caseload with significant well-documented spelling difficulties. When this subtest was administered to him he scored within the average range (Scaled Score of 8 and Percentile Rank of 25). However, an administration of Spelling Performance Evaluation for Language and Literacy – SPELL-2, yielded 3 assessment pages of spelling errors, as well as 7 pages of recommendations on how to remediate those errors. Had he received this assessment as part of an independent evaluation from a different examiner, nothing more would have been done regarding his spelling difficulties since the TOWL-4 revealed an average spelling performance due to its focus on overly simplistic vocabulary.
4. Logical Sentences – The student is asked to edit an illogical sentence so that it makes better sense. Ceiling is reached when the student makes 3 errors in a row. Again I’m not too thrilled with this subtest. Rather than truly attempting to ascertain the student’s grammatical and syntactic knowledge at sentence level a large portion of this subtest deals with easily recognizable semantic incongruities.
5. Sentence Combining – The student integrates the meaning of several short sentences into one grammatically correct written sentence. Ceiling is reached when the student makes 3 errors in a row. The first few items contain only two sentences which can be combined by adding the conjunction “and”. The remaining items are a bit more difficult due to the a. addition of more sentences and b. increase in the complexity of language needed to efficiently combine them. This is a nice subtest to administer to students who present with difficulty effectively and efficiently expressing their written thoughts on paper. It is particularly useful with students who write down a lot of extraneous information in their compositions/essays and frequently overuse run-on sentences.
6. Contextual Conventions – The student is asked to write a story in response to a stimulus picture. S/he earn points for satisfying specific requirements relative to combined orthographic (E.g.: punctuation, spelling) and grammatical conventions (E.g.: sentence construction, noun-verb agreement). The student’s written composition needs to contain more than 40 words in order for the effective analysis to take place.
The scoring criteria ranges from no credit or a score of 0 ( based on 3 or more mistakes), to partial credit, a score of 1 (based on 1-2 mistakes) to full a credit – a score of 3 (no mistakes). There are 21 scoring parameters which are highly useful for younger elementary-aged students who may exhibit significant difficulties in the domain of writing. However, older middle school and high-school aged students as well as elementary aged students with moderate writing difficulties may attain average scoring on this subtest but still present with significant difficulties in this area as compared to typically developing grade level peers. As a result, in addition to this assessment, it is recommended that a functional assessment of grade-level writing also be performed in order to accurately identify the student’s writing needs.
7. Story Composition – The student’s story is evaluated relative to the quality of its composition (E.g.: vocabulary, plot, development of characters, etc.). The examiner first provides the student with an example of a good story by reading one written by another student. Then, the examiner provides the student with an appropriate picture card and tell them that they need to take time to plan their story and make an outline on the (also provided) scratch paper. The student has 5 minutes to plan before writing the actual story. After the 5 minutes, elapses they 15 minutes to write the story. It is important to note that story composition is the very first subtest administered to the student. Once they complete it they are ready to move on to the Vocabulary subtest. There are 11 scoring parameters that are significantly more useful for me to use with younger students as well as significantly impaired students vs. older students or students with mild-moderate writing difficulties. Again if your aim is to get an accurate picture of the older students writing abilities I definitely recommend the usage of clinical writing assessment rubrics based on the student’s grade level in order to have an accurate picture of their abilities.
OVERALL IMPRESSIONS:
Strengths:
- A thorough assessment of basic writing areas for very severely impaired students with writing deficits
- Flexible subtest administration (can be done on multiple occasions with students who fatigue easily)
Limitations:
- Untimed testing administration (with the exception of story composition subtests) is NOT functional with students who present with significant processing difficulties. One 12-year-old student actually took ~40 minutes to complete each subtest.
- Primarily useful for students with severe deficits in the area of written expression
- Not appropriate for students with mild-moderate needs (requires suplementation)
- Lack of remediation suggestions based on subtest deficits
- Weak psychometric properties
Overall, TOWL-4 can be a useful testing measure for ruling out weaknesses in the student’s basic writing abilities, with respect to simple vocabulary, sentence construction, writing mechanics, punctuation, etc. If I identify previously unidentified gaps in basic writing skills I can then readily intervene, where needed, if needed. However, it is important to understand that the TOWL-4 is only a starting point for most of our students with complex literacy needs whose writing abilities are above severe level of functioning. Most students with mild-moderate writing difficulties will pass this test with flying colors but still present with significant writing needs. As a result I highly recommend a functional grade-level writing assessment as a supplement to the above-standardized testing.
References:
Hammill, D. D., & Larson, S. C. (2009). Test of Written Language—Fourth Edition. (TOWL-4). Austin, TX: PRO-ED.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this post are the personal impressions of the author. This author is not affiliated with PRO-ED in any way and was NOT provided by them with any complimentary products or compensation for the review of this product.
Improving Emotional Intelligence of Children with Social Communication Disorders
 Our ability to recognize our own and other people’s emotions, distinguish between and correctly identify different feelings, as well as use that information to guide our thinking and behavior is called Emotional Intelligence (EI) (Salovey, et al, 2008).
Our ability to recognize our own and other people’s emotions, distinguish between and correctly identify different feelings, as well as use that information to guide our thinking and behavior is called Emotional Intelligence (EI) (Salovey, et al, 2008).
EI encompasses dual areas of: emotion understanding, which is an awareness and comprehension of one’s and others emotions (Harris, 2008) and emotion regulation, which are internal and external strategies people use to regulate emotions (Thompson, 1994).
Many students with social communication challenges experience problems with all aspects of EI, including the perception, comprehension, and regulation of emotions (Brinton & Fujiki, 2012).
A number of recent studies have found that children with language impairments also present with impaired emotional intelligence including impaired perception of facial expressions (Spackman, Fujiki, Brinton, Nelson, & Allen, 2005), prosodic emotions (Fujiki, Spackman, Brinton, & Illig, 2008) as well as abstract emotion comprehension (Ford & Milosky, 2003).

Children with impaired emotional intelligence will experience numerous difficulties during social interactions due to their difficulty interpreting emotional cues of others (Cloward, 2012). These may include but not be limited to active participation in cooperative activities, as well as full/competent interactions during group tasks (Brinton, Fujiki, & Powell, 1997)
Many students with social pragmatic deficits and language impairments are taught to recognize emotional states as part of their therapy goals. However, the provided experience frequently does not go beyond the recognition of the requisite “happy”, “mad”, “sad” emotions. At times, I even see written blurbs from others therapists, which state that “the student has mastered the goals of emotion recognition”. However, when probed further it appears that the student had merely mastered the basic spectrum of simple emotional states, which places the student at a distinct disadvantage as compared to typically developing peers who are capable of recognition and awareness of a myriad of complex emotional states.

That is why I developed a product to target abstract emotional states comprehension in children with language impairments and social communication disorders. “Gauging Moods and Interpreting Abstract Emotional States: A Perspective Taking Activity Packet” is a social pragmatic photo/question set, intended for children 7+ years of age, who present with difficulty recognizing abstract emotional states of others (beyond the “happy, mad, sad” option) as well as appropriately gauging their moods.
Many sets contain additional short stories with questions that focus on making inferencing, critical thinking as well as interpersonal negotiation skills. Select sets require the students to create their own stories with a focus on the reasons why the person in the photograph might be feeling what s/he are feeling.

There are on average 12-15 questions per each photo. Each page contains a photograph of a person feeling a particular emotion. After the student is presented with the photograph, they are asked a number of questions pertaining to the recognition of the person’s emotions, mood, the reason behind the emotion they are experiencing as well as what they could be potentially thinking at the moment. Students are also asked to act out the depicted emotion they use of mirror.
Activities also include naming or finding (in a thesaurus or online) the synonyms and antonyms of a particular word in order to increase students’ vocabulary knowledge. A comprehensive two page “emotions word bank” is included in the last two pages of the packet to assist the students with the synonym/antonym selection, in the absence of a thesaurus or online access.

Students are also asked to use a target word in a complex sentence containing an adverbial (pre-chosen for them) as well as to identify a particular word or phrase associated with the photo or the described story situation.
Since many students with social pragmatic language deficits present with difficulty determining a person’s age (and prefer to relate to either younger or older individuals who are perceived to be “less judgmental of their difficulties”), this concept is also explicitly targeted in the packet.
This activity is suitable for both individual therapy sessions as well as group work. In addition to its social pragmatic component is also intended to increase vocabulary knowledge and use as well as sentence length of children with language impairments.
Intended Audiences:
- Clients with Language Impairments
- Clients with Social Pragmatic Language Difficulties
- Clients with Executive Function Difficulties
- Clients with Psychiatric Impairments
- ODD, ADHD, MD, Anxiety, Depression, etc.
- Clients with Autism Spectrum Disorders
- Clients with Nonverbal Learning Disability
- Clients with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
- Adult and pediatric post-Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) clients
- Clients with right-side CVA Damage
Areas covered in this packet:
- Gauging Age (based on visual support and pre-existing knowledge)
- Gauging Moods (based on visual clues and context)
- Explaining Facial Expressions
- Making Social Predictions and Inferences (re: people’s emotions)
- Assuming First Person Perspectives
- Understanding Sympathy
- Vocabulary Knowledge and Use (pertaining to the concept of Emotional Intelligence)
- Semantic Flexibility (production of synonyms and antonyms)
- Complex Sentence Production
- Expression of Emotional Reactions
- Problem Solving Social Situations
- Friendship Management and Peer Relatedness
This activity is suitable for both individual therapy sessions as well as group work. In addition to its social pragmatic component is also intended to increase vocabulary knowledge and use as well as sentence length of children with language impairments. You can find it in my online store (HERE).
Helpful Smart Speech Resources:
- Vocabulary Intervention: Working with Disadvantaged Populations
- Creating a Functional Therapy Plan: Therapy Goals & SOAP Note Documentation
- Selecting Clinical Materials for Pediatric Therapy
- Pediatric Background History Questionnaire
- The Checklists Bundle
- Social Pragmatic Assessment and Treatment Bundle
- Assessment Checklist for Preschool Children
- Assessment Checklist for School Children
- General Assessment and Treatment Start Up Bundle
- Multicultural Assessment Bundle
- Narrative Assessment and Treatment Bundle
- Introduction to Prevalent Disorders Bundle
- Auditory Processing Deficits Checklist for School Aged Children
References:
- Brinton, B., Fujiki, M., & Powell, J. M. (1997). The ability of children with language impairment to manipulate topic in a structured task. Language, Speech and Hearing Services in Schools, 28, 3-11.
- Brinton B., & Fujiki, M. (2012). Social and affective factors in children with language impairment. Implications for literacy learning. In C. A. Stone, E. R. Silliman, B. J. Ehren, & K. Apel (Eds.), Handbook of language and literacy: Development and disorders (2nd Ed.). New York, NY: Guilford.
- Cloward, R. (2012). The milk jug project: Expression of emotion in children with language impairment and autism spectrum disorder (Unpublished honor’s thesis). Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah.
- Ford, J., & Milosky, L. (2003). Inferring emotional reactions in social situations: Differences in children with language impairment. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 46(1), 21-30.
- Fujiki, M., Spackman, M. P., Brinton, B., & Illig, T. (2008). Ability of children with language impairment to understand emotion conveyed by prosody in a narrative passage. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 43(3), 330-345
- Harris, P. L. (2008). Children’s understanding of emotion. In M. Lewis, J. M. Haviland-Jones, & L. Feldman Barrett, (Eds.), Handbook of emotions (3rd ed., pp. 320–331). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
- Salovey, P., Detweiler-Bedell, B. T., Detweiler-Bedell, J. B., & Mayer, J. D. (2008). Emotional intelligence. In M. Lewis, J. M. Haviland-Jones, & L. Feldman Barrett (Eds.), Handbook of Emotions (3rd ed., pp. 533-547). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
- Spackman, M. P., Fujiki, M., Brinton, B., Nelson, D., & Allen, J. (2005). The ability of children with language impairment to recognize emotion conveyed by facial expression and music. Communication Disorders Quarterly, 26(3), 131-143.
- Thompson, R. (1994). Emotion regulation: A theme in search of definition. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 59(2-3), 25-52
For the Love of Speech Blog Hop: February Edition
 Today I am very excited to participate along with 27 other talented SLPs in the For the Love of Speech Blog Hop. I love being an SLP, and to spread that love around from February 1-4 I am giving away a Valentine’s Day Product: “The Origins of Valentine’s Day: At thematic language activity packet for middle and high school students” .
Today I am very excited to participate along with 27 other talented SLPs in the For the Love of Speech Blog Hop. I love being an SLP, and to spread that love around from February 1-4 I am giving away a Valentine’s Day Product: “The Origins of Valentine’s Day: At thematic language activity packet for middle and high school students” .
This thematic packet was created to target listening and reading comprehension of middle and high school students diagnosed with language impairments and learning disabilities. The packet contains Response to Intervention (RTI) Tier 2 vocabulary words in story context. Expressive language activities for the packet include production of synonyms and antonyms, fill-in the blank, as well as sentence formulation using story vocabulary. Comprehension questions pertaining to story are provided in an open ended question format. It is great for teaching reading comprehension and sophisticated vocabulary in a thematic context related to familiar to the student events.
You can grab this product for free for a limited time only in my online store (HERE) and then head on over to Teach Speech 365 to grab her freebie as well. Collect all freebies by the time the blog hop ends on February 4th!
For more useful FREE and PAID products check out my online store by clicking HERE or on the picture below