November is Menkes Awareness month, so today Olga Z. Porterfield will be contributing a post on the Menkes Syndrome.
Menkes Syndrome (MNK), also known as Menkes disease, copper transport disease, steely hair disease, kinky hair disease, or Menkes kinky hair syndrome, is a disorder originally described by John Hans Menkes (1928–2008), which affects copper levels in the body, leading to copper deficiency. It is an x-linked recessive disorder, and is therefore considerably more common in males with females requiring two defective alleles to develop the disease. It is caused by a defective gene named ATP7A gene that regulates the metabolism of copper in the body. Continue reading Spotlight on Syndromes: An SLPs Perspective on Menkes Syndrome

 Today’s guest post on genetic syndromes comes from Rachel Nortz, who is contributing a post on the Down Syndrome.
Today’s guest post on genetic syndromes comes from Rachel Nortz, who is contributing a post on the Down Syndrome.
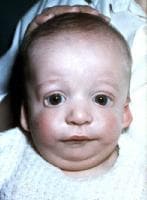 Today’s guest post on genetic syndromes comes from Amy Locy, who is contributing an informative piece on the Treacher Collins Syndrome (TCS). TSC occurs in 1 out of every 50,000 live births with 40% of children born with TCS having a family member with the syndrome. TCS is distributed equally across genders and races. It can often occur in conjunction with the Pierre Robin Sequence.
Today’s guest post on genetic syndromes comes from Amy Locy, who is contributing an informative piece on the Treacher Collins Syndrome (TCS). TSC occurs in 1 out of every 50,000 live births with 40% of children born with TCS having a family member with the syndrome. TCS is distributed equally across genders and races. It can often occur in conjunction with the Pierre Robin Sequence.  Today I am excited to introduce to you the new series which will be featured on my blog and will be written by myself as well as numerous knowledgeable contributing authors. It is an SLP’s perspective on genetic syndromes.
Today I am excited to introduce to you the new series which will be featured on my blog and will be written by myself as well as numerous knowledgeable contributing authors. It is an SLP’s perspective on genetic syndromes.
 Today I am reviewing a fun new app Apraxia RainbowBee developed by
Today I am reviewing a fun new app Apraxia RainbowBee developed by 
 My birthday month has been great! But all good things must come to an end! So take a look at the
My birthday month has been great! But all good things must come to an end! So take a look at the 