Workshops, Lectures, Presentations and Webinars
- Elleseff, T (2021, Dec 3). Components of Comprehensive Preschool Evaluations. POWER UP Online Conference, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Dec 2). Targeted Pragmatic Assessments of School-Aged Children with Psychiatric Diagnoses. POWER UP Online Conference, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Nov 2). Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity in At-Risk Children: Differential Diagnosis of ADHD in Speech Language Pathology: Focus on Assessment and Treatment. Webinar for Garfield Public Schools. Garfield, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Oct 20) Reading Disorders 101: A Tutorial for Parents and Professionals. Webinar for the Apraxia Kids, Pittsburg, PA.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Sep 30) On the Value of Language Assessments for Children with Confirmed/Suspected Dyslexia. Webinar for the Kansas Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Wichita, KS.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Sep 30) Improving Critical Thinking Skills via Use of Picture Books in Children with Language Disorders. Webinar for the Kansas Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Wichita, KS.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Sep 2). Practical Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing and Treating Bilingual Children. Elmont Union Free School District Webinar, Elmont, NY.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Aug 25). A Reading Program is NOT Enough: A Deep Dive into the Dyslexia Diagnosis. International Dyslexia Association Georgia Branch Webinar. Atlanta, GA.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Aug 5). Clinical Assessment of Grade-Level Reading Abilities: Focus on Fluency and Comprehension. CEU SmartHub Recorded Webinar, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Aug 5). Teaching Emergent Readers via the Synthetic Phonics Approach. CEU SmartHub Recorded Webinar, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Jul 16). Improving Critical Thinking Skills via Use of Picture Books in Children with Language Disorders. The Ohio School Speech Pathology Educational Audiology Coalition Online Webinar
- Elleseff, T (2021, Jul 16). Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing and Treating Bilingual Children. The Ohio School Speech Pathology Educational Audiology Coalition Online Webinar
- Elleseff, T (2021, Jul 15). Assessing Social Skills in Children with Psychiatric Disturbances. The Ohio School Speech Pathology Educational Audiology Coalition Online Webinar
- Elleseff, T (2021, Jun 9). Auditory Processing Disorder Diagnosis: Science or Pseudoscience? International Dyslexia Association Georgia Branch Online Webinar.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Mar 5). Accurate Test Selection for Assessment Purposes. POWER UP Online Conference, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Mar 4). Behavior Management for SLPs. POWER UP Online Conference, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2021, Mar 4). Background History Matters: Conducting IEEs. POWER UP Online Conference, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2020, Dec 29). Neuropsychological or Language/Literacy Assessment: Which One is Right for the Student? International Dyslexia Association Georgia Branch Online Webinar.
- Elleseff, T (2020, Dec 2). Clinical Assessment of Narrative Skills. POWER UP Online Conference, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2020, Oct 20) How Language Affects Reading: What Parents and Professionals Need to Know. BUILD Tredyffrin-Easttown. Online Webinar.
- Elleseff, T (2020, Aug 27) Measurement and Interpretation of Standardized Reading Assessments for Professionals and Parents (Webinar) EBP REEL TALK, Smart Speech Therapy LLC
- Elleseff, T (2020, Aug 04) Components of Effective Reading Intervention. POWER UP Online Conference, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2020, Aug 03) Improving Critical Thinking Skills via Use of Picture Books in Children with Language Disorders. POWER UP, Online Conference, Lavi Institute.
- Elleseff, T (2020, Feb 27) Assessing Preschool Children with Challenging Behaviors. American Speech Language and Hearing Association Online Conference. Rockville, MD
- Elleseff, T (2019, Oct 19) On the Value of Language Assessments for Children with Confirmed/Suspected Dyslexia. 41st Annual Conference of the Pennsylvania Branch, International Dyslexia Association (PBIDA). West Conshohocken, PA
- Elleseff, T (2019, Oct 18) Comorbidity of Language and Literacy Disorders in Children With Psychiatric Impairments: What Psychiatrists Need to Know. 66th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Chicago, IL
- Elleseff, T (2019, Oct 16) Assessing Preschool Children with Challenging Behaviors. American Speech Language and Hearing Association Online Conference. Rockville, MD
- Elleseff, T (2019, Jul 19-21) Behavior Management Strategies for SLPs. American Speech Language and Hearing Association Schools Connect Conference. Chicago, IL
- Elleseff, T (2019, Jul 19-21) Speech-Language Assessment and Treatment of Children with Alcohol-Related Disorders. American Speech Language and Hearing Association Schools Connect Conference. Chicago, IL
- Elleseff, T (2019, Jul 19-21) Language Difference vs. Disorder: Assessment Strategies for Children Who Are Bilingual. American Speech Language and Hearing Association Schools Connect Conference. Chicago, IL
- Elleseff, T (2019, Jun 5) From Wordless Picture Books to Reading Instruction: Effective Strategies for SLPs Working with Intellectually Impaired Students. Workshop for the New York City Board of Education – District 9, Brooklyn, NY
- Elleseff, T (2019, May 15) Assessing Social Communication from Toddlerhood through Adolescence: What SLPs need to Know. Workshop for the Hamilton County Educational Service Center, Cincinnati, OH.
- Elleseff, T & Caruso, C (2019, May 2) Research-Based Treatment Approaches for Childhood Apraxia of Speech Workshop for the New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Long Branch, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2019, May 1) Practical Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing Bilingual Children Workshop for the New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Long Branch, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2019, Feb 20) Assessing Preschool Children with Challenging Behaviors Presented for the American Speech Language and Hearing Association Online Conference. Rockville, MD
- Elleseff, T (2018, Nov 15) Practical Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing Bilingual Children Presented for the American Speech Language and Hearing Association Convention. Boston, MA
- Elleseff, T (2018, Oct 25) Behavior Management Strategies for Speech-Language Pathologists. Presented for the Milestone Therapeutic Services, Washington, DC.
- Elleseff, T (2018, Oct 19) Behavior Management Strategies for Speech-Language Pathologists. Scheduled presentation for the Clinical Connection Conference of the Maryland Speech Language and Hearing Association, Baltimore, MD
- Elleseff, T (2018, Sep 26) Red Flags for Undiagnosed Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders in Children and Adolescents Rutgers Health UBHC Monthly Child Division Lecture Series, Piscataway, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2018, May 22) Speech, Language, & Literacy Disorders in School Aged Children with Psychiatric Impairments Rutgers Health UBHC Monthly Child Division Lecture Series, Piscataway, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2018, Feb 16) Impact of Cultural and Linguistic Variables On Speech-Language Services presented for the Eatontown Board of Education, Eatontown, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2018, Jan 9) Normal Simultaneous Bilingual Language Development and Milestones Acquisition. Webinar presented for the New Jersey Speech Language and Hearing Association. Princeton, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2017, Nov 14) Best Practices in Bilingual Language and Literacy Interventions. Webinar presented for the Speech-Language & Audiology Canada.
- Elleseff, T (2017, Nov 11) Practical Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing Bilingual Children Presented for the American Speech Language and Hearing Association Convention. Los Angeles, CA.
- Elleseff, T (2017, Nov 7) Assessment and Treatment of Social-Communication Deficits in Children With/out Psychiatric Impairments. Workshop presented for the Butler County Educational Service Center, Hamilton, OH.
- Elleseff, T (2017, Oct 19 & 26) From First Words through Preschool: Recognizing the Warning Signs of Language Delay. Development through the Life Cycle Lecture Series. Presented for the Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Medical Residents Rutgers University/Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2017, Oct 19) Recognizing and Assessing Primary Language Impairment in Bilingual Learners. Webinar presented for the Speech-Language & Audiology Canada.
- Elleseff, T (2017, June 15) Behavior Management for SLPs and Assessment of Social Communication in Children with Psychiatric Impairments Workshop presented for the Los Angeles Unified School District, Los Angeles, CA
- Elleseff, T; Caruso, C (2017, Apr 28) Bilingualism: Birth to Adulthood. Workshop presented at the New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Long Branch, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2017, Apr 24) From Wordless Picture Books to Reading Instruction: Effective Strategies for SLPs Working with Intellectually Impaired Students. Workshop presented for the New York City Board of Education – District 75, NY, NY
- Elleseff, T (2017, Mar 24) Best Practices in Bilingual Language and Literacy Interventions. Workshop presented for the Speech-Language & Audiology Canada, Montreal, Canada
- Elleseff, T (2016, Dec 7) Best Practices in Bilingual Language and Literacy Interventions. Workshop presented for the New York City Department of Education: Bilingual Providers Conference. Woodside, NY.
- Elleseff, T (2016, Nov 8) Narrative Assessments of Preschool and School Aged Children. Webinar presented for the Greenwich Public Schools, Greenwich CT
- Elleseff, T (2016, Nov 1). Recognizing the Warning Signs of Social Emotional Difficulties in Language Impaired Toddlers and Preschoolers Workshop presented for the Regional Professional Development Academy. Eatontown, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2016, Oct 13 & 20) From First Words through Preschool: Recognizing the Warning Signs of Language Delay. Development Through the Life Cycle Lecture Series. Presented for the Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Fellows Rutgers University/Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2016, Oct 11) Psychiatric Impairments and Language Disorders in School Aged Children. Presented for the Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Residents Rutgers University/Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2016, Oct 10) Introduction to Dyslexia and Learning Disabilities. Lecture presented at Rutgers University Behavioral Health Care: Rutgers Day School. Piscataway, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2016, Oct 5) Differential Assessment and Treatment of Processing Disorders in Speech Language Pathology. Workshop presented for the Wayne County Speech Language Hearing Association, Livonia, MI
- Elleseff, T (2016, July 13) Practical Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing and Treating Bilingual Children. Workshop presented for the Long Island Speech Language Hearing Association, Hauppauge, NY
- Elleseff, T (2016, May 25) Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Treating Bilingual Children New York City Department of Education: Monolingual Providers Conference. NY, NY.
- Wesler, J & Elleseff, T (2016, Apr 14) Overview of NJ Education Mandates: The Law and the SLP Workshop presented at the New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Long Branch, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2016, Mar 4) Assessment and Treatment of Non-Verbal Language Disorder (NVLD) in Speech Language Pathology Workshop presented at the Mississippi Speech Language Hearing Association, Jackson, MS.
- Elleseff, T (2016, Mar 3) Creating a Functional Therapy Plan and Selecting Clinical Materials for Pediatric Therapy Workshop presented at the Mississippi Speech Language Hearing Association, Jackson, MS.
- Elleseff, T (2016, Feb 15) Differential Diagnosis of ADHD (and C/APD) in Speech Language Pathology. Workshop presented for the Montville Public Schools. Montville, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2015, Dec 4) Translanguaging in the classroom: Tips for educators on enrichment multicultural activities. Session presented at the William Paterson University 35th Bilingual/ESL Conference. Wayne, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2015, Dec 3) Assessing and Treating Bilingual Children: Practical Strategies for SLPs. New York City Department of Education: Bilingual Providers Conference. Woodside, NY.
- Elleseff, T (2015, Nov 3) Assessing Social Communication Skills of School Aged Children Workshop presented for the Linden Public Schools, Linden, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2015, Oct 25) Assessment of Children With/Without Psychiatric and Emotional Disturbances from Preschool through Adolescence. Northeastern Speech-Language-Hearing Association of Pennsylvania Pocono Manor, PA.
- Elleseff, T (2015, Oct 15) Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity in At-Risk Children: Differential Diagnosis of ADHD in Speech Language Pathology and Education. Regional Professional Development Academy. Eatontown, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2015, Sept 1) Assessment of Children With/Without Psychiatric and Emotional Disturbances from Preschool through Adolescence Workshop presented for the Rahway Public Schools, Rahway, NJ
- Caruso, C & Elleseff, T (2015, April 30) Working with CLD Populations: An Interactive Student Experience. Workshop presented at the New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Long Branch, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2015, Feb 13) Assessment and Treatment of Social Pragmatic Deficits in School Aged Children. Workshop presented at the 2015 Annual Illinois Speech Hearing Language Association, Chicago, IL
- Elleseff, T (2014, Dec 5) CLD Learners’ Pathway to Success: A Lexical Enhancement Approach. Session presented at the William Paterson University 34th Bilingual/ESL Conference. Wayne, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2014, Nov 10) Creating a Functional Therapy Plan: Therapy Goals & SOAP Note Documentation. Webinar presented for speechpathology.com, San Antonio, TX
- Elleseff, T (2014, Nov 6) Impact of Cultural and Linguistic Variables on Speech-Language Services. Guest lecture presented at Seton Hall University, South Orange, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2014, May 6) Narrative Assessments of Preschool and School Aged Children. Workshop presented at the Union County Speech and Hearing Association, New Providence, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2014, May 2). Speech Language Assessment of Older Internationally Adopted Children. Workshop presented at the New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Long Branch, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2014, Mar 21) Assessment and Treatment of Social Pragmatic Deficits in School Aged Children. Lecture presented at the 11th Annual Symposium for Speech Language Specialists. Rowan University, Glassboro, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2014, Jan 14) Executive Function Impairment and At-Risk Populations. Webinar presented for Advance for Speech Language Pathologists and Audiologists.
- Elleseff, T (2013, Oct 29) Assessing Social Functioning in Language Impaired Young Children. Webinar presented for Advance for Speech Language Pathologists and Audiologists.
- Elleseff, T (2013, Oct 17 & 24) From First Words through Preschool: Recognizing the Warning Signs of Language Delay. Development Through the Life Cycle Lecture Series scheduled for the Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Fellows Rutgers University/Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, NJ
- Gordina, A, Elleseff, T (2013, Aug 10) Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity in Adopted and Foster Children. Workshop presented at the 39th North American Council on Adoptable Children, Toronto, CA.
- Elleseff, T (2013, Jul 16) Impact of Cultural and Linguistic Variables on Speech-Language Services. Webinar presented for the New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association. Princeton, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2013, May 20) Language Difference vs. Language Disorder: An Overview of Assessment and Intervention Strategies for Speech Language Pathologists Working with Bilingual Children. Workshop presented for the Warren County Speech, Language, Hearing Association, Hackettstown, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2013, Mar 25) Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Part II: Assessment & Intervention. Webinar presented for speechpathology.com, San Antonio, TX
- Elleseff, T (2013, Feb 5) Selecting Clinical Materials for Pediatric Therapy. Guest lecture presented at Seton Hall University, South Orange, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2013, Jan 28) Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Part I: Overview of Deficits. Webinar presented for speechpathology.com, San Antonio, TX
- Elleseff, T (2013, Jan 22) Creating a Functional Therapy Plan: Therapy Goals & SOAP Note Documentation. Guest lecture presented at Seton Hall University, South Orange, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2013, Jan 17) Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity In At Risk Children: Differential Diagnosis of ADHD in Speech Language Pathology. Webinar presented for Advance for Speech Language Pathologists and Audiologists.
- Gordina, A, Elleseff, T. (2013, Jan 13). Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity in Adopted and Foster Children. Workshop presented at the New Jersey’s 31stAnnual “Let’s Talk Adoption”sm Conference Piscataway, NJ
- Gordina, A, Elleseff, T. (2013, Jan 13). Sobering Thoughts on Attitudes Towards the Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Workshop presented at the New Jersey’s 31st Annual “Let’s Talk Adoption”sm Conference Piscataway, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2013, Nov 15) Language Difference vs. Language Disorder: Assessment & Intervention Strategies for SLPs Working with Bilingual Children. Workshop presented for Educational Service Unit #3, Omaha, NE.
- Elleseff, T (2012, Oct 28) Behavior Management Strategies for Related Professionals. Session presented for the New Jersey Occupational Therapy Association, 38th Annual Convention. Seton Hall University, South Orange, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2012, Oct 24) Narrative Assessments of Preschool and School Aged Children. Session presented for the Morris County Speech and Hearing Association, Whippany, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2012, Oct 18) Psychiatric Impairments and Language Disorders in School Aged Children:
Why Psychiatrists and Speech Pathologists Should Collaborate More Together. Development Through the Life Cycle Lecture Series for the Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Fellows University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey/Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, NJ - Elleseff, T (2012, Oct 11) From First Words through Preschool: Recognizing the Warning Signs of Language Delay. Development Through the Life Cycle Lecture Series for the Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Fellows University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey/Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, NJ
- Gordina, A, Elleseff, T, & Shifrin, L (2012, Jul 27) Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity in Adopted and Foster Children. Workshop presented at the 38th North American Council on Adoptable Children, Crystal City, VA.
- Elleseff, T (2012, July) Improving Social Skills of Children with Psychiatric Disturbances. Webinar presented for speechpathology.com, San Antonio, TX
- Elleseff, T (2012, May) Assessing Social Skills of Children with Psychiatric Disturbances. Webinar presented for speechpathology.com, San Antonio, TX
- Elleseff, T (2012, April) Behavior Management Strategies for School Based Speech Language Pathologists Workshop presented at New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Long Branch, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2012, April) Social Pragmatic Assessment of Children Diagnosed with Emotional/Psychiatric Disturbances in the Schools. Workshop presented at New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association Convention, Long Branch, NJ
- Elleseff, T (2012, Jan) Special Considerations and Challenges in Assessment and Treatment of Bilingual Children with Developmental Disabilities. Workshop presented for Middlesex Regional Educational Services Commission, Metuchen NJ.
- Gordina, A & Elleseff, T (2011, Oct) A Case of Isolated Social Pragmatic Language Deficits and Sensory Integration Dysfunction in an Internationally Adopted Child: Implications for Medical Referral Workshop presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics: Council on Foster Care, Adoption and Kinship Care, Boston, MA.
- Gordina, A, Elleseff, T, & Shifrin, L (2011, Oct) Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity in At-Risk Children Workshop presented at the Opening Doors: Partnerships for Prevention and Healing, New Jersey Taskforce on Child Abuse and Neglect, East Brunswick, NJ.
- Elleseff, T (2011, June) The Role of Frontal Lobe in Speech and Language Functions. Lecture presented at the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey: Child Therapeutic Day Program. Piscataway, NJ.
Article Publications
- Elleseff, T (2016) Embracing ‘Translanguaging’ Practices: A Tutorial for SLPs New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association. VOICES, Summer, 9.
- Elleseff, T (2015, Aug). Assessing social communication of school-aged children Perspectives on School-Based Issues 16 (3): 79-86
- Caruso, C, Concepcion-Escano, Y & Elleseff, T (2015, Jan). Technical Manual: A guide for the appropriate assessment of culturally & linguistically diverse and internationally adopted individuals. New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association.
- Elleseff, T (2014). Creating Successful Team Collaboration: Behavior Management in the Schools. Perspectives on School-Based Issues, 15(1): 37-43.
- Elleseff, T (2014). ELL Spotlight on Russian: Considerations for Assessment and Treatment. New Jersey Speech Language Hearing Association: VOICES, Winter: 9-11.
- Elleseff, T (2013, Dec) Recognizing FASD-Related Speech and Language Deficits in Internationally Adopted Children. National Adoption Advocate. No. 66, pp 1-8.
- Elleseff, T(2013) Changing Trends in International Adoption: Implications for Speech-Language Pathologists. Perspectives on Global Issues in Communication Sciences and Related Disorders, 3: 45-53
- Elleseff, T (2013, Aug) FASD and Background History Collection: Asking the Right Questions Adoption Today, pp 32-35.
- Elleseff, T (2012, Dec 24) Understanding the risks of social pragmatic deficits in post institutionalized internationally adopted children. Published in Advance for Speech Language Pathologists and Audiologists. Pp 6-9.
- Elleseff, T (Jan 2, 2012) Speech-Language Strategies for Multisensory Stimulation of Internationally Adopted Children: Activity Suggestions for Parents and Professionals. Adoption Today Magazine. pp 40-43.
- Elleseff, T (Nov 16, 2011) The importance of pediatric orofacial assessments in speech pathology. Advance for Speech Language Pathologists and Audiologists
- Elleseff, T (Oct 1, 2011) Understanding the extent of speech and language delays in older internationally adopted children: Implications for School Based Speech and Language Intervention Adoption Today Magazine, pp 32-35
- Elleseff, T (June 6, 2011) Differential diagnosis of AD/HD and Auditory Processing Disorders in Internationally Adopted School Age Children Post Adoption Learning Center, International Adoptions Articles Directory
- Elleseff, T (Mar 14, 2011) What are social pragmatic language deficits and how do they impact international adoptees years post adoption? Post Adoption Learning Center, International Adoptions Articles Directory
- Elleseff, T (Feb 23, 2011) A case for early speech-language assessments of adopted children in the child’s birth language Post Adoption Learning Center, International Adoptions Articles Directory
- Elleseff, T (June 30, 2009) How to improve the feeding abilities of young adopted picky eaters Post Adoption Learning Center, International Adoptions Articles Directory
- Elleseff, T (May 27, 2009) Speech Language Services and Insurance Coverage: What Parents Need to Know Post Adoption Learning Center, International Adoptions Articles Directory
- Elleseff, T (May 11, 2009) How to select the right speech language pathologist for your adopted child? Post Adoption Learning Center, International Adoptions Articles Directory
- Elleseff, T (Feb 20, 2009) Functional Strategies for Improving the Language Abilities of Your Adopted School-Age Child Post Adoption Learning Center, International Adoptions Articles Directory
- Elleseff, T (Feb 15, 2009) Creating a learning rich environment to facilitate language development in adopted preschoolers. Post Adoption Learning Center, International Adoptions Articles Directory
ASHA Leader Blog Contributions:
- Elleseff, T (Jul 19, 2016) Assessing Students: Why Background History Matters
- Elleseff, T (Oct 15, 2015) Why the Phrase ‘It’s Not So Bad’ Causes Treatment Problems
- Elleseff, T (Feb 19, 2015) How to Evaluate Misbehavior
- Elleseff, T (Oct 1, 2013) A Tool to Help Children Ask for Help
- Elleseff, T (Sept 17, 2013) Why Suspected Childhood Apraxia of Speech Requires Careful Assessment
- Elleseff, T (Nov 28, 2012) “Appdapting” Flashcard Apps to Address Social Skills.
- Elleseff, T (Oct 29, 2012) Therapy Fun with Ready Made Fall and Halloween Bingo.
- Elleseff, T (Aug 14, 2012) Adventures in Word Finding or is Their Language Comprehension Really THAT Bad?
- Elleseff, T (Jul 3, 2012) Dinner with Friends or the Value of interdisciplinary Collaboration and Follow-Up
- Elleseff, T (Mar 6, 2012) Multicultural Considerations in Assessment of Play.
- Elleseff, T (Nov 3, 2011) Speech-Language Activity Suggestions for Multisensory Stimulation of At-Risk Children.
- Elleseff, T (Aug 4, 2011) Improving Pragmatic and Social Cognitive Abilities of Children with Psychiatric Disturbances.
 Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age.
Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age. Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age.
Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age. At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to
At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to  Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers.
Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers. High comorbidity between language and psychiatric disorders has been well documented (Beitchman, Cohen, Konstantaras, & Tannock, 1996; Cohen, Barwick, Horodezky, Vallence, & Im, 1998; Toppelberg & Shapiro, 2000). However, a lesser known fact is that there’s also a significant under-diagnosis of language impairments in children with psychiatric disorders.
High comorbidity between language and psychiatric disorders has been well documented (Beitchman, Cohen, Konstantaras, & Tannock, 1996; Cohen, Barwick, Horodezky, Vallence, & Im, 1998; Toppelberg & Shapiro, 2000). However, a lesser known fact is that there’s also a significant under-diagnosis of language impairments in children with psychiatric disorders.  In this post, I am continuing my series of articles on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first installment in this series offered suggestions regarding what information to include in
In this post, I am continuing my series of articles on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first installment in this series offered suggestions regarding what information to include in  As mentioned in my previous post on
As mentioned in my previous post on  Developmental Milestones expected of a 16-18 months old toddler:
Developmental Milestones expected of a 16-18 months old toddler:  Play Skills/Routines:
Play Skills/Routines: Materials to use with the child to promote language and play:
Materials to use with the child to promote language and play:  Core vocabulary categories for listening and speaking:
Core vocabulary categories for listening and speaking: The end of the school year is almost near. Soon many of our clients with language and literacy difficulties will be going on summer vacation and enjoying their time outside of school. However, summer is not all fun and games. For children with learning needs, this is also a time of “
The end of the school year is almost near. Soon many of our clients with language and literacy difficulties will be going on summer vacation and enjoying their time outside of school. However, summer is not all fun and games. For children with learning needs, this is also a time of “ It’s early August, and that means that the start of a new school year is just around the corner. It also means that many newly graduated clinical fellows (as well as SLPs switching their settings) will begin their exciting yet slightly terrifying new jobs working for various school systems around the country. Since I was recently interviewing clinical fellows myself in my setting (an outpatient school located in a psychiatric hospital, run by a university), I decided to write this post in order to assist new graduates, and setting-switching professionals by describing what knowledge and skills are desirable to possess when working in the schools.
It’s early August, and that means that the start of a new school year is just around the corner. It also means that many newly graduated clinical fellows (as well as SLPs switching their settings) will begin their exciting yet slightly terrifying new jobs working for various school systems around the country. Since I was recently interviewing clinical fellows myself in my setting (an outpatient school located in a psychiatric hospital, run by a university), I decided to write this post in order to assist new graduates, and setting-switching professionals by describing what knowledge and skills are desirable to possess when working in the schools. 


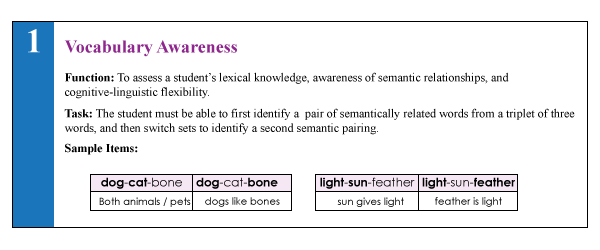




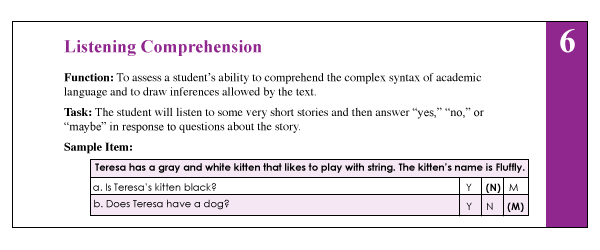



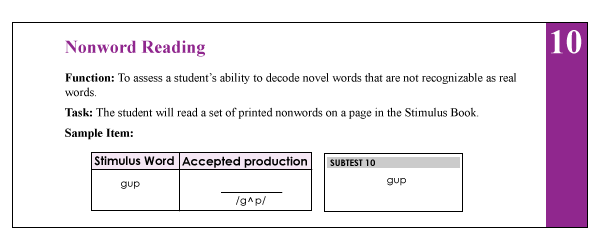



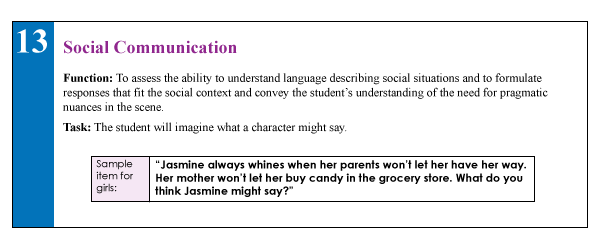



 Lately, I’ve been seeing more and more posts on social media asking for testing suggestions for students who exhibit
Lately, I’ve been seeing more and more posts on social media asking for testing suggestions for students who exhibit 