
Assessment of Social Communication Deficits in School-Aged Children with Psychiatric Impairments


 Assessment of children with DS syndrome is often complicated due to the wide spectrum of presenting deficits (e.g., significant health issues in conjunction with communication impairment, lack of expressive language, etc) making accurate assessment of their communication a difficult task. In order to provide these children with appropriate therapy services via the design of targeted goals and objectives, we need to create comprehensive assessment procedures that focus on highlighting their communicative strengths and not just their deficits.
Assessment of children with DS syndrome is often complicated due to the wide spectrum of presenting deficits (e.g., significant health issues in conjunction with communication impairment, lack of expressive language, etc) making accurate assessment of their communication a difficult task. In order to provide these children with appropriate therapy services via the design of targeted goals and objectives, we need to create comprehensive assessment procedures that focus on highlighting their communicative strengths and not just their deficits.
Today I’d like to discuss assessment procedures for verbal monolingual and bilingual children with DS 4-9 years of age, since testing instruments as well as assessment procedures for younger as well as older verbal and nonverbal children with DS do differ.
When it comes to dual language use and genetic disorders and developmental disabilities many educational and health care professionals are still under the erroneous assumption that it is better to use one language (English) to communicate with these children at home and at school. However, studies have shown that not only can children with DS become functionally bilingual they can even become functionally trilingual (Vallar & Papagno, 1993; Woll & Grove, 1996). It is important to understand that “bilingualism does not change the general profile of language strengths and weaknesses characteristic of DS—most children with DS will have receptive vocabulary strengths and expressive language weaknesses, regardless of whether they are monolingual or bilingual.” (Kay-Raining Bird, 2009, p. 194)
Furthermore, advising a bilingual family to only speak English with a child will cause a number of negative linguistic and psychosocial implications, such as create social isolation from family members who may not speak English well as well as adversely affect parent-child relationships (Portes & Hao, 1998).
Consequently, when preparing to assess linguistic abilities of children with DS we need to first determine whether these children have single or dual language exposure and design assessment procedures accordingly.
It is very important to conduct a parental interview no matter the setting you are performing the assessment in. One of your goals during the interview will be to establish the functional goals the parents’ desire for the child which may not always coincide with the academic expectations of the program in question.
Begin with a detailed case history and review of current records and obtain information about the child’s prenatal, perinatal and postnatal development, medical history as well as the nature of previous assessments and provided related services. Next, obtain a detailed history of the child’s language use by inquiring what languages are spoken by household members and how much time do these people spend with the child?
A balanced assessment will include a variety of methods, including observations of the child as well as direct interactions in the form of standardized, informal and dynamic assessments. If you will be using standardized assessments (e.g., ROWPVT-4) YOU MUST use descriptive measures vs. standardized scores to describe the child’s functioning. The latter is especially applicable to bilingual children with DS. Consider using the following disclaimer: “The following test/s __________were normed on typically developing English speaking children. Testing materials are not available in standardized form for child’s unique developmental and bilingual/bicultural backgrounds. In accordance with IDEA 2004 (The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) [20 U.S.C.¤1414(3)],official use of standard scores for this child would be inaccurate and misleading so the results reported are presented in descriptive form. Raw scores are provided here only for comparison with future performance.”
Depending on the child’s age and level of abilities a variety of assessment measures may be applicable to test the child in the areas of Content (vocabulary), Form (grammar/syntax), and Use(pragmatic language).
For children over 3 years of age whose linguistic abilities are just emerging you may wish to use a vocabulary inventory such as the MacArthur-Bates (also available in other languages) as well as provide parents with the Developmental Scale for Children with Down Syndrome to fill out. This will allow you to compare where child with DS features in their development as compared to typically developing peers. For older, more verbal children who are using words, phrases, and/or sentences to express themselves, you may want to use or adapt (see above) one of the following standardized language tests:
Depending on your setting (hospital vs. school), you may not perform a detailed assessment of the child’s feeding and swallowing skills. However, it is still important to understand that due to low muscle tone, respiratory problems, gastrointestinal disorders and cardiac issues, children with DSoften present with feeding dysfunction which is further exacerbated by concomitant issues such as obesity, GERD, constipation, malnutrition (restricted food group intake lacking in vitamins and minerals), and fatigue. With respect to swallowing, they may experience abnormalities in both the oral and pharyngeal phases of swallow, as well as present with silent aspiration, due to which instrumental assessment (MBS) may be necessary (Frazer & Friedman, 2006).
In contrast to feeding and swallowing the oral-peripheral assessment can be performed in all settings. When performing oral-peripheral exam, you need to carefully describe all structural (anatomical) and functional (physiological) abnormalities (e.g., macroglossia, micrognathia, prognathism, etc). Note any issues with:
Take a careful look at the child’s speech. Perform dual speech sampling (if applicable) by considering the child’s phonetic inventory, syllable lengths and shapes as well as articulatory/phonological error patterns. Make sure to factor in the combined effect of the child’s craniofacial anomalies as well as system wide impairment (disturbances in respiration, voice, articulation, resonance, fluency, and prosody) on conversational intelligibility. Impaired intelligibility is a serious concern for individuals with DS, as it tends to persist throughout life for many of them and significantly interferes with social and vocational pursuits (Kent & Vorperian, 2013)
Don’t forget to assess the child’s voice, fluency, prosody, and resonance. Children with DS may have difficulty maintaining constant airstream for vocal production due to which they may occasionally speak with low vocal volume and breathiness (caused by air loss due to vocal fold hypotonicity). This may be directly targeted in treatment sessions and taught how to compensate for. When assessing resonance make sure to screen the child for hypernasality which may be due to velopharyngeal insufficiency secondary to hypotonicity as well as rule out hyponasality which may be due to enlarged adenoids (Kent & Vorperian, 2013). Furthermore, since stuttering and cluttering occur in children with DS at rates of 10 to 45%, compared to about 1% in the general population, a detailed analysis of disfluencies may be necessary(Kent & Vorperian, 2013). Finally, due to limitations with perception, imitation, and spontaneous production of prosodic features secondary to motor difficulties, motor coordination issues, and segmental errors that impede effective speech production across multisyllabic sequences, the prosody of individuals with DS will be impaired and might require a separate intervention. (Kent & Vorperian, 2013)
When it comes to auditory function, formal hearing testing and retesting is mandatory due to the fact that many children with DS have high prevalence of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss (Park et al, 2012). So if the child in question is not receiving regular follow-ups from the audiologist, it is very important to make the appropriate referral. Similarly, it is also very important that the child’s visual perception is assessed as well since children with DS frequently experience difficulties with vision acuity as well as visual processing, consequentially a consultation with developmental optometrist may be recommended/needed.
Describe in detail the child’s adaptive behavior and learning style, including their social strengths and weaknesses. Observe the child’s eye contact, affect, attention to task, level of distractibility, and socialization patterns. Document the number of redirections and negotiations the child needed to participate as well as types and level of reinforcement used during testing.
Perform dual language sampling and look at functional vocabulary knowledge and use, grammar measures, sentence length, as well as the child’s pragmatic functions (what is the child using his/her language for: request, reject, comment, etc.) Perform a dynamic assessment to determine the child’s learnability (e.g., how quickly does the child learns and adapts to being taught new concepts?) since “even a minimal mediation in the form of ‘focusing’ improves the receptive language performance of children with DS” (Alony & Kozulin, 2007, p 323)
After all the above sections are completed, it is time to move on to the impressions section of the report. While it is important to document the weaknesses exposed by the assessment, it is even more important to document the child’s strengths or all the things the child did well, since this will help you to determine the starting treatment point and allow you to formulate relevant treatment goals.
When making recommendations for treatment, especially for bilingual children with DS, make sure to provide a strong rationale for the provision of services in both languages (if applicable) as well as specify the importance of continued support of the first language in the home.
Finally, make sure to provide targeted and measurable [suggested] treatment goals by breaking the targets into measurable parts:
Given ___time period (1 year, 1 progress reporting period, etc), the student will be able to (insert specific goal) with ___accuracy/trials, given ___ level of, given _____type of prompts.
Assessing communication abilities of children with developmental disabilities may not be easy; however, having the appropriate preparation and training will ensure that you will be well prepared to do the job right! Use multiple tasks and activities to create a balanced assessment, use descriptive measures instead of standard scores to report findings, and most importantly make your assessment functional by making sure that your testing yields relevant diagnostic information which could then be effectively used to provide effective quality treatments for clients with DS!
For comprehensive information on “Comprehensive Assessment of Monolingual and Bilingual Children with Down Syndrome” which discusses how to assess young (birth-early elementary age) verbal and nonverbal monolingual and bilingual children with Down Syndrome (DS) and offers comprehensive examples of write-ups based on real-life clients click HERE.
 Understanding the extent of speech and language delays in older internationally adopted children: Implications for School Based Speech and Language Intervention.
Understanding the extent of speech and language delays in older internationally adopted children: Implications for School Based Speech and Language Intervention.
Note: This article was first published in October 2011 Issue of Adoption Today Magazine (pp. 32-35) http://www.adoptinfo.net/catalog_g111.html?catId=55347
According to US State Department statistics, over 11,000 children were adopted internationally in the year 2010, with 2,803 of those children being school-aged (between 5-17 years old). Despite a staggering 50% decline in overall inter-country adoptions in the last 10 years, statistics on adoption of older children continue to remain steady (appropriately 3,000 older children were adopted each year, for the past decade). (Retrieved from http://adoption.state.gov/about_us/statistics.php Jul 29, 2011).
Subsequent to the school aged child’s arrival to US, one of the first considerations that arises, secondary to health concerns and transitional adjustments, is the issue of schooling and appropriate school based services provision. In contrast to children adopted at younger ages, who typically have an opportunity to acquire some English language skills before an academic placement takes place, older international adoptees lack this luxury. Unfortunately, due to their unique linguistic status, many school districts are at a loss regarding best services options for these children.
Despite the prevalence of available research on this subject, one myth that continues to persist is that older internationally adopted children are “bilingual” and as such should receive remedial services similar to those received by newly entering the country bilingual children (e.g., ESL classes).
It is very important to understand that most internationally adopted children rapidly lose their birth language, sometimes in as little as several months post arrival (Gindis, 2005), since they are often adopted by parents who do not speak the child’s first language and as such are unable/unwilling to maintain it. Not only are these children not bilingual, they are also not ‘truly’ monolingual, since their first language is lost rather rapidly, while their second language has been gained minimally at the time of loss. Moreover, even during the transition period during which international adoptees are rapidly losing their native language, their birth language is still of no use to them, since it’s not functional in their monolingual, English speaking only, home and school environments. As a result of the above constraints, select researchers have referred to this pattern of language gain, as “second, first language acquisition” (e.g., Roberts, et al., 2005), since the child is acquiring his/her new language literally from scratch.
This brings me to another myth, that given several years of immersion in a new language rich, home and school environments, most internationally adopted children with (mild) language delays will catch up to their non-adopted monolingual peers academically, without the benefit of any additional services.
This concept requires clarification, since the majority of parents adopting older children, often have difficulty understanding the extent of their child’s speech and language abilities in their native language at the time of adoption, and the implications for new language transference.
Research on speech language abilities of older internationally adopted children is still rather limited, despite available studies to date. Some studies (e.g., Glennen & Masters, 2002; Krakow & Roberts, 2003, etc) suggest that age of adoption is strongly correlated with language outcomes. In other words, older internationally adopted children are at risk of having poorer language outcomes than children adopted at younger ages. That is because the longer the child stays in an institutional environment the greater is the risk of a birth language delay. Children in institutional care frequently experience neglect, lack of language stimulation, lack of appropriate play experiences, lack of enriched community activities, as well as inadequate learning settings all of which have long lasting negative impact on their language development. It is also important to understand that language delays in birth language transfer and become language delays in a new language. These delays will typically continue to persist unless appropriate intervention, in the form of speech language services, is provided.
So what are the options available to parents adopting older school age children with respect to determination of their child’s speech and language abilities?
For starters, at the time of adoption, it is very important to gain as much information regarding their child’s birth language abilities (and academic abilities, when applicable) as possible. In many older children (3+ years of age), speech and language delays in birth language (e.g., sound and word mispronunciations, limited vocabulary, grammatical errors, inability to answer simple or abstract questions, short sentence length) can be easily determined based on orphanage staff interviews, observations, and/or review of documentation included in the adoption record. In the Russian Federation, for example, speech language pathologists are assigned to orphanages, so when working with older international adoptees from the Russian Federation, one often finds a short statement in adoption records stating that the child presented with a speech and language delay for which he was receiving services.
If possible, prior to adoption, parents may wish to explore the option of obtaining an independent comprehensive speech language evaluation of the child’s birth language abilities, while the child is still located in the birth country. The above may be significant for a number of reasons. Firstly, it will allow the parents to understand the extent of the child’s language delay in their birth tongue. Secondly, it will increase the parents’ chances of obtaining school based remediation services for their child once they arrive to US.
In the absence of qualified speech pathologists attached to the orphanage or conclusive interviews with medical professionals, paraprofessionals, and teachers (lack of availability, language barrier, time constraints, etc) regarding the child’s speech and language development, it will be very helpful for parents to videotape the child during speaking tasks. Most parents who request pre-adoption consultations are well familiar with videotaping, requested by various pre-adoption professionals (pediatricians, psychologists, etc) in order to review the child’s presenting appearance, fine and gross motor skills, behavior and social skills as well as other areas of functioning. Language video samples should focus on child’s engagement in literacy tasks such as reading a book aloud (if sufficiently literate), and on speaking activities such as telling a story, recalling an episode from daily life or a conversation with familiar person. In the absence of all other data, these samples can later be analyzed and interpreted in order to determine if speech language deficits are present. (Glennen, 2009)
Parents need to understand that internationally adopted children can often be denied special education services in the absence of appropriate documentation. Such denials are often based on misinterpretation of the current IDEA 2004 law. Some denials may be based on the fact that once these children arrive to US, it is very difficult to find a qualified speech language pathologist who can assess the child in their birth language, especially if it’s a less commonly spoken language such as Amharic, Kazakh, or Ukrainian. Additionally, schools may refuse to test internationally adopted children for several years post arrival, on the grounds that these children have yet to attain “adequate language abilities in English” and as such, the testing results will be biased/inadequate, since testing was not standardized on children with similar linguistic abilities. Furthermore, even if the school administers appropriate testing protocols and finds the child’s abilities impaired, testing results may still be dismissed as inaccurate due to the child’s perceived limited English exposure.
Contrastingly, a speech and language report in the child’s birth language will outline the nature and severity of disorder, and state that given the extent of the child’s deficits in his/her birth language, similar pattern will be experienced in English unless intervention is provided. According to one of the leading speech-language researchers, Sharon Glennen, “Any child with a known history of speech and language delays in the sending country should be considered to have true delays or disorders and should receive speech and language services after adoption.” (Glennen, 2009, p.52)
To continue, some options in locating a speech pathologist in the child’s birth country include consulting with the adoption agency or the local pediatrician, who is providing medical clearance for the child. However, it is very important that the speech language pathologist be licensed and reputable, as unqualified professionals will not be able to make appropriate diagnostic interpretations and suggestions, and may provide erroneous information to the parent.
If the parents are unable to obtain the relevant report in the child’s birth country, the next viable option is to obtain a comprehensive speech language assessment upon arrival to US, from a qualified professional who is well versed in both: the child’s native language as well as speech and language issues unique to assessment of internationally adopted children. Please note that the window of opportunity to assess the school age child in his/her native language is very narrow, as birth language attrition occurs within literally a matter of several months post adoption and is more rapid in children with delayed and disordered speech and language abilities (Gindis, 1999, 2005, 2008).
If the presence of a speech language delay has been confirmed (e.g., documented in adoption paperwork, interpreted through video samples, supported by a psycho-educational assessment, etc) the next step is to request the relevant speech language services for your child through the school system. Typically school administration will ask you to produce such a request in writing. One such letter template is available through the Post Adoption Learning Center (see link below). This template, complete with relevant references, can be modified to each child’s unique circumstances, and submitted along with supporting paperwork (e.g., speech-language, psycho-educational reports) and available video samples. In cases of services denials, an educational attorney specializing in educational policy relevant to international adoptions may need be consulted.
Once the child is qualified for appropriate speech language services in the school system it is also important to understand that language acquisition occurs in a progression, with social language (CLF) preceding cognitive language (CLM) (Gindis, 1999). Communicative Language Fluency (CLF) is language used in social situations for day-to-day social interactions. These skills are used to interact at home, on the playground, in the lunch room, on the school bus, at parties, playing sports and talking on the telephone. Social interactions are usually context embedded. Because they occur in meaningful social contexts they are typically not very demanding cognitively and the language required is not specialized. These language skills usually emerge in internationally adopted children as early as several months post adoption. Once these abilities emerge and solidify it is very important for speech language pathologists not to dismiss the child from services but to continue the treatment and focus it in the realm of cognitive/ academic language.
Cognitive Language Mastery (CLM) refers to language needed for formal academic learning. This includes listening, speaking, reading, and writing about subject area content material including analyzing, synthesizing, judging and evaluating presented information. This level of language learning is essential for a child to succeed in school. Language impaired children adopted at older ages need time and support to become develop cognitive language and become proficient in academic areas, an ability which usually takes a number of years to refine. Before discharging the child from therapy services it is very important that their cognitive/academic language abilities are assessed and are found within average limits.
Understanding the extent of speech language delay in internationally adopted older children AND factors pertaining to appropriate remediation are crucial for delivery of relevant (and meaningful to the child) speech language services as well as ensuring their continued academic success in school setting.
References:
• Gindis, B. (1999) Language-Related Issues for International Adoptees and Adoptive Families. In: T. Tepper, L. Hannon, D. Sandstrom, Eds. “International Adoption: Challenges and Opportunities.” PNPIC, Meadow Lands , PA. , pp. 98-108
• Gindis, B. (2005). Cognitive, language, and educational issues of children adopted from overseas orphanages. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 4 (3): 290-315.
• Gindis (2008) Abrupt Native Language Loss in International Adoptees Advance for Speech/Language Pathologists and Audiologists Dec 22.
• Glennen, S. & Masters, G. (2002). Typical and atypical language development in infants and toddlers adopted from Eastern Europe. American Journal of Speech-LanguagePathology, 44, 417-433
• Glennen, S., & Bright, B. J. (2005). Five years later: Language in school-age internationally adopted children. Seminars in Speech and Language, 26, 86-101.
• .Glennen, S (2009) Speech and Language Guidelines for Children Adopted from Abroad at Older Ages. Topics in language Disorders 29, 50-64.
• Intercountry Adoption Bureau of Consular Affairs US Department of State Retrieved on Jul 29, 2011 from http://adoption.state.gov/about_us/statistics.php
• Krakow, R. A., & Roberts, J. (2003). Acquisitions of English vocabulary by young Chinese adoptees. Journal of Multilingual Communication Disorders, 1, 169-176.
• Muchnik, M. How to request speech/language services for your child. Retrieved on Aug 2, 2011 from http://www.bgcenterschool.org/FreePresentations/P8-Speech-language-support.shtml
• Roberts, et al, (2005). Language development in preschool-aged children adopted from China. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research, 48, 93-107.
Bio: Tatyana Elleseff MA CCC-SLP is a bilingual speech language pathologist with a full-time affiliation with University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey and a private practice in Somerset, NJ. She received her Master’s Degree from New York University and her Bilingual Extension Certification from Columbia University. Currently she is licensed by the states of New Jersey and New York and holds a Certificate of Clinical Competence from American Speech Language and Hearing Association. She specializes in working with bilingual, multicultural, internationally and domestically adopted at risk children with complex medical, developmental, neurogenic, psychogenic, and acquired communication disorders. For more information about her services call 917-916-7487 or visit her website: www.smartspeechtherapy.com
Cite as: Elleseff, Tatyana (2011, October) Understanding the extent of speech and language delays in older internationally adopted children: Implications for School Based Speech and Language Intervention. Adoption Today.
 For bilingual and monolingual SLPs working with bilingual and multicultural children, the question of: “Is it a difference or a disorder?” arises on a daily basis as they attempt to navigate the myriad of difficulties they encounter in their attempts at appropriate diagnosis of speech, language, and literacy disorders.
For bilingual and monolingual SLPs working with bilingual and multicultural children, the question of: “Is it a difference or a disorder?” arises on a daily basis as they attempt to navigate the myriad of difficulties they encounter in their attempts at appropriate diagnosis of speech, language, and literacy disorders.
 For that purpose, I’ve recently created a Checklist for Identification of Speech-Language Disorders in Bilingual and Multicultural Children. Its aim is to assist Speech Language Pathologists (SLPs) and Teachers in the decision-making process of how to appropriately identify bilingual/multicultural children who present with speech-language delay/deficits (vs. a language difference), for the purpose of initiating a formal speech-language-literacy evaluation. The goal is to ensure that educational professionals are appropriately identifying bilingual children for assessment and service provision due to legitimate speech language deficits/concerns, and are not over-identifying students because they speak multiple languages or because they come from low socioeconomic backgrounds. It is very important to understand that true language impairment in bilingual children will be evident in both languages from early childhood onwards, and thus will adversely affect the learning of both languages.
For that purpose, I’ve recently created a Checklist for Identification of Speech-Language Disorders in Bilingual and Multicultural Children. Its aim is to assist Speech Language Pathologists (SLPs) and Teachers in the decision-making process of how to appropriately identify bilingual/multicultural children who present with speech-language delay/deficits (vs. a language difference), for the purpose of initiating a formal speech-language-literacy evaluation. The goal is to ensure that educational professionals are appropriately identifying bilingual children for assessment and service provision due to legitimate speech language deficits/concerns, and are not over-identifying students because they speak multiple languages or because they come from low socioeconomic backgrounds. It is very important to understand that true language impairment in bilingual children will be evident in both languages from early childhood onwards, and thus will adversely affect the learning of both languages.
However, today the aim of today’s post is not on the above product but rather on the FREE free bilingual and multicultural resources available to SLPs online in their quest of differentiating between a language difference from a language disorder in bilingual and multicultural children.
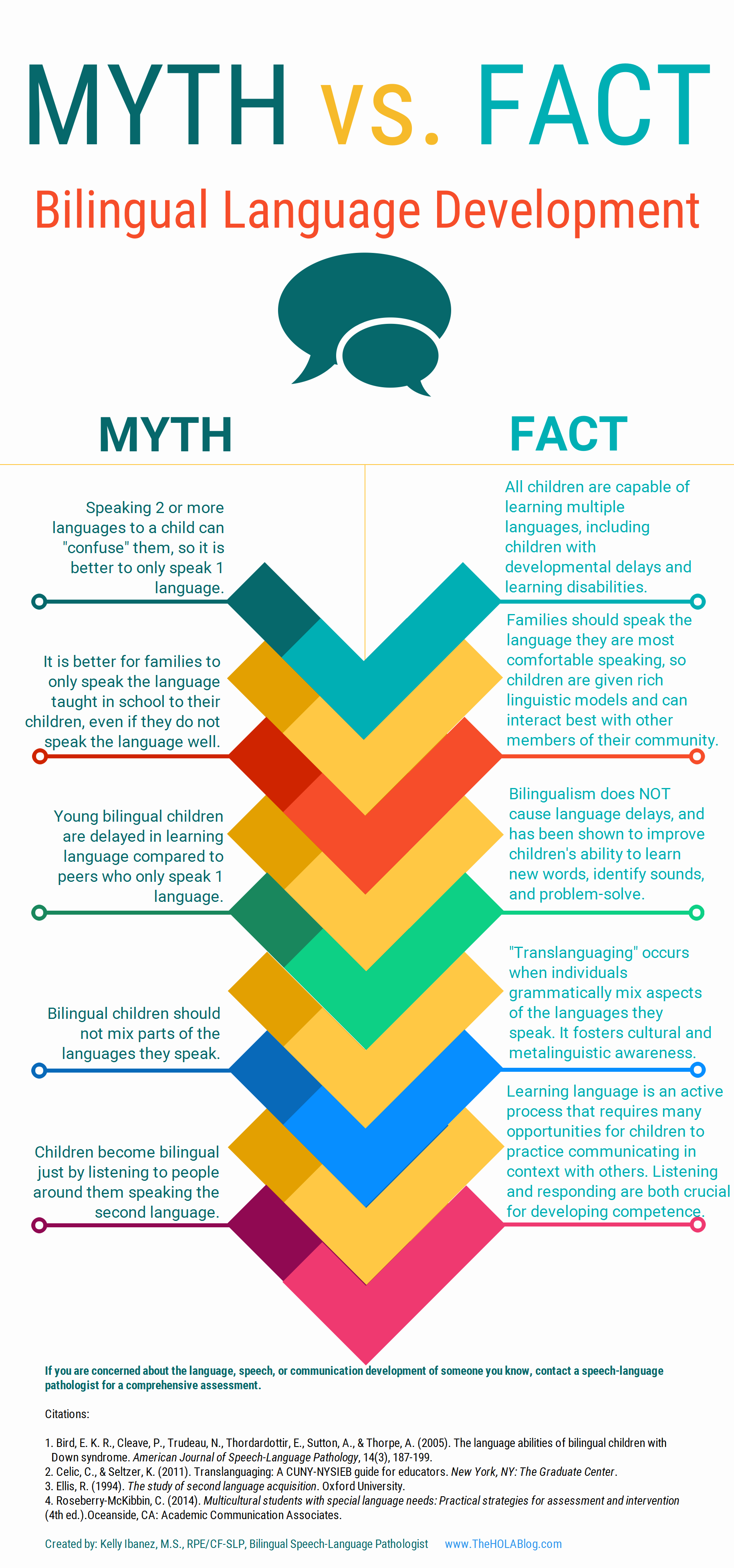 Let’s start with an excellent free infographic entitled from the Hola Blog “Myth vs. Fact: Bilingual Language Development” which was created by Kelly Ibanez, MS CCC-SLP to help dispel bilingual myths and encourage practices that promote multilingualism. Clinicians can download it and refer to it themselves, share it with other health and/or educational professionals as well as show it to parents of their clients.
Let’s start with an excellent free infographic entitled from the Hola Blog “Myth vs. Fact: Bilingual Language Development” which was created by Kelly Ibanez, MS CCC-SLP to help dispel bilingual myths and encourage practices that promote multilingualism. Clinicians can download it and refer to it themselves, share it with other health and/or educational professionals as well as show it to parents of their clients.
Let us now move on to the typical phonological development of English speaking children. After all, in order to compare other languages to English, SLPs need to be well versed in the acquisition of speech sounds in the English language. Children’s speech acquisition, developed by Sharynne McLeod, Ph.D., of Charles Sturt University, is one such resource. It contains a compilation of data on typical speech development for English speaking children, which is organized according to children’s ages to reflect a typical developmental sequence.
 Next up, is a great archive which contains phonetic inventories of the various language spoken around the world for contrastive analysis purposes. The same website also contains a speech accent archive. Native and non-native speakers of English were recorded reading the same English paragraph for teaching and research purposes. It is meant to be used by professionals who are interested in comparing the accents of different English speakers.
Next up, is a great archive which contains phonetic inventories of the various language spoken around the world for contrastive analysis purposes. The same website also contains a speech accent archive. Native and non-native speakers of English were recorded reading the same English paragraph for teaching and research purposes. It is meant to be used by professionals who are interested in comparing the accents of different English speakers.
![]() Now let’s talk about one of my favorite websites, MULTILINGUAL CHILDREN’S SPEECH, also developed by Dr. Mcleod of Charles Stuart University. It contains an AMAZING plethora of resources on bilingual speech development and assessment. To illustrate, its Speech Acquisition Data includes A list of over 200 speech acquisition studies. It also contains a HUGE archive on Speech Assessments in NUMEROUS LANGUAGES as well as select assessment reviews. Finally, the website also lists in detail how aspects of speech (e.g., consonants, vowels, syllables, tones) differ between languages.
Now let’s talk about one of my favorite websites, MULTILINGUAL CHILDREN’S SPEECH, also developed by Dr. Mcleod of Charles Stuart University. It contains an AMAZING plethora of resources on bilingual speech development and assessment. To illustrate, its Speech Acquisition Data includes A list of over 200 speech acquisition studies. It also contains a HUGE archive on Speech Assessments in NUMEROUS LANGUAGES as well as select assessment reviews. Finally, the website also lists in detail how aspects of speech (e.g., consonants, vowels, syllables, tones) differ between languages.
The Leader’s Project Website is another highly informative source of FREE information on bilingual assessments, intervention, and FREE CEUS.
Now, I’d like to list some resources regarding language transfer errors.
This chart from Cengage Learning contains a nice, concise Language Guide to Transfer Errors. While it is aimed at multilingual/ESL writers, the information contained on the site is highly applicable to multilingual speakers as well.
You can also find a bonus transfer chart HERE. It contains information on specific structures such as articles, nouns, verbs, pronouns, adverbs, adjectives, word order, questions, commands, and negatives on pages 1-6 and phonemes on pages 7-8.
A final bonus chart entitled: Teacher’s Resource Guide of Language Transfer Issues for English Language Learners containing information on grammar and phonics for 10 different languages can be found HERE.
Similarly, this 16-page handout: Language Transfers: The Interaction Between English and Students’ Primary Languages also contains information on phonics and grammar transfers for Spanish, Cantonese, Vietnamese, Hmong Korean, and Khmer languages.
 For SLPs working with Russian-speaking children the following links pertinent to assessment, intervention and language transference may be helpful:
For SLPs working with Russian-speaking children the following links pertinent to assessment, intervention and language transference may be helpful:
To determine information about the children’s language development and language environment, in both their first and second language, visit the CHESL Centre website for The Alberta Language Development Questionnaire and The Alberta Language Environment Questionnaire
There you have it! FREE bilingual/multicultural SLP resources compiled for you conveniently in one place. And since there are much more FREE GEMS online, I’d love it if you guys contributed to and expanded this modest list by posting links and title descriptions in the comments section below for others to benefit from!
Together we can deliver the most up to date evidence-based assessment and intervention to bilingual and multicultural students that we serve! Click HERE to check out the FREE Resources in the SLPs for Evidence-Based Practice Group
Helpful Bilingual Smart Speech Therapy Resources:
I frequently get emails, phone calls, and questions from parents and professionals regarding academic functioning of internationally adopted post institutionalized children. Unfortunately despite the fact that there is a fairly large body of research on this topic there still continue to be numerous misconceptions regarding how these children’s needs should be addressed in academic settings.
Perhaps one of the most serious and damaging misconceptions is that internationally adopted children are bilingual/multicultural children with Limited English Proficiency who need to be treated as ESL speakers. This erroneous belief often leads to denial or mismanagement of appropriate level of services for these children not only with respect to their language processing and verbal expression but also their social pragmatic language abilities.
Even after researchers published a number of articles on this topic, many psychologists, teachers and speech language pathologists still don’t know that internationally adopted children rapidly lose their little birth language literally months post their adoption by English-speaking parents/families. Gindis (2005) found that children adopted between 4-7 years of age lose expressive birth language abilities within 2-3 months and receptive abilities within 3-6 months post- adoption. This process is further expedited in children under 4, whose language is delayed or impaired at the time of adoption (Gindis, 2008). Even school-aged children of 10-12 years of age who were able to read and write in their birth language, rapidly lose their comprehension and expression of birth language within their first year post adoption, if adopted by English-speaking parents who are unable to support their birth language.
So how does this translate into appropriate provision of speech language services you may ask? To begin with, I often see posts on the ASHA forums or in Facebook speech pathology and special education groups seeking assistance with finding interpreters fluent in various exotic languages. However, unless the child is “fresh off the boat” (several months post arrival to US) schools shouldn’t be feverishly trying to locate interpreters to assist with testing in the child’s birth language. They will not be able to obtain any viable results especially if the child had been residing in the United States for several years.
So if the post-institutionalized, internationally adopted child is still struggling with academics several years post adoption, one should not immediately jump to the conclusion that this is an “ESL” issue, but get relevant professionals (e.g., speech pathologists, psychologists) to perform thorough testing in order to determine whether it’s the lack of foundational abilities due to institutionalization which is adversely impacting the child’s academic abilities.

Furthermore, ESL itself is often not applicable as an educational method to internationally adopted children. Here’s why:
Let’s literally take the first definition of ESL which pops-up on Google when you put in a query: “What is ESL?” “English as a Second Language (ESL) is an instructional program for students whose dominant language is not English. The purpose of the program is to increase the English language proficiency of eligible students so they can attain academic standards and achieve success in the classroom.”
Here is our first problem. These students don’t have a dominant language. They are typically adopted by parents who do not speak their birth language and that are unable to support them in their birth language. So upon arrival to US, IA children will typically acquire English via the subtractive model of language acquisition (birth language is replaced and eliminated by English), which is a direct contrast to bilingual children, many of whom learn via the additive model (adding English to the birth language (Gindis, 2005). As a result, of subtractive language acquisition IA children experience very rapid birth language attrition (loss) post-adoption (Gindis, 2003; Glennen, 2009). Thus they will literally undergo what some researchers have called: “second-first language acquisition” (Scott et al., 2011) and their first language will “become completely obsolete as English is learned” (Nelson, 2012, p. 2).
This brings us to our second problem: the question of “eligibility”. Historically, ESL programs have been designed to assist children of immigrant families acquire academic readiness skills. This methodology is based on the fact that skills from first language was ultimately transfer to the second language. However, since post-institutionalized children don’t technically have a “first language” and their home language is English, how could they technically be eligible for ESL services? Furthermore, because of frequent lack of basic foundational skills in the birth language internationally adopted post-institutionalized children will not benefit the same way from ESL instruction the same way bilingual children of immigrant families do. So instead of focusing on these children’s questionable eligibility for ESL services it is important to perform detailed review of their pre-adoption records in order to determine birth language deficits and consider eligibility for speech language services with the emphasis on improving these children’s foundational skills.
Now that we have discussed the issue of ESL services, lets touch upon social pragmatic language abilities of internationally adopted children. Here’s how erroneous beliefs can contribute to mismanagement of appropriate services in this area.

Different cultures have different pragmatic conventions, therefore we are taught to be very careful when labeling certain behaviors of children from other cultures as atypical, just because they are not consistent with the conventions and behaviors of children from the mainstream culture. Here’s a recent example. A mainstream American parent consulted an SLP regarding the inappropriate social pragmatic skills of her teenaged daughter adopted almost a decade ago from Southeast Asia. The SLP was under the impression that some of the child’s deficits were due to multicultural differences and had to do with the customs and traditions of the child’s country of origin. She was considering advising the parent regarding requesting an evaluation by a SLP who spoke the child’s birth language.
Here are two problems with the above scenario. Firstly, any internationally adopted post-institutionalized child who was adopted by American parents who were not part of the culture from which the child was adopted, the child will quickly become acculturated and immersed in the American culture. These children “need functional English for survival”, and thus have a powerful incentive to acquire English (Gindis, 2005; p. 299). consequently, any unusual or atypical behaviors they exhibit in social interactions and in academic setting with other individuals cannot be attributed to customs and traditions of another culture.
Secondly, It is very important to understand that institutionalization and orphanage care have been closely linked to increase in mental health disorders and psychiatric impairments. As a result, internationally adopted children have a high incidence of social pragmatic deficits as compared to non-adopted peers as well as post-institutionalized children adopted at younger ages, (under 3). Given this, if parents present with concerns regarding their internationally adopted post-institutionalized children’s social pragmatic and behavioral functioning it is very important not to jump to erroneous conclusion pertaining to these children’s birth countries but rather preform comprehensive evaluations in order to determine whether these children can be assisted further in the realm of social pragmatic functioning in a variety of settings.
In order to develop a clear picture regarding appropriate service delivery for IA children, school based professionals need to educate themselves regarding the fundamental differences between development and learning trajectories of internationally adopted children and multicultural/bilingual children. Children, who struggle academically, after years of adequate schooling exposure, do not deserve a “wait and see” approach. They should start receiving appropriate intervention as soon as possible (Hough & Kaczmarek, 2011; Scott & Roberts, 2007).

Tatyana Elleseff, MA, CCC-SLP is a bilingual SLP who specializes in working with at-risk children with and without concomitant psychiatric impairments who present with complex language and literacy needs. She has been published in a variety of professional journals as well as presented for numerous national and international medical, academic, and non-profit organizations and speech-language-hearing associations. She is a clinical instructor at the RWJ Medical School Dept. of Psychiatry, a clinical supervisor at Rutgers Day School, and a co-founder of a CEU SmartHub a professional development organization that offers online high-caliber evidence-based conferences and continuing education training for speech-language pathologists and related professionals.
 Graduation time is rapidly approaching and many graduate speech language pathology students are getting ready to begin their first days in the workforce. When it comes to juggling caseloads and managing schedules, time is money and efficiency is the key to success. Consequently, a few years ago I created SLP Efficiency Bundles™, which are materials highly useful for Graduate SLPs working with pediatric clients. These materials are organized by areas of focus for efficient and effective screening, assessment, and treatment of speech and language disorders. Continue reading SLP Efficiency Bundles™ for Graduating Speech Language Pathologists
Graduation time is rapidly approaching and many graduate speech language pathology students are getting ready to begin their first days in the workforce. When it comes to juggling caseloads and managing schedules, time is money and efficiency is the key to success. Consequently, a few years ago I created SLP Efficiency Bundles™, which are materials highly useful for Graduate SLPs working with pediatric clients. These materials are organized by areas of focus for efficient and effective screening, assessment, and treatment of speech and language disorders. Continue reading SLP Efficiency Bundles™ for Graduating Speech Language Pathologists
 Many young children develop speech skills within a wide range of time and with different capabilities. However, by a certain point, most children have begun to learn how to speak and communicate effectively. Of course, when parents notice that their child isn’t keeping up with other children, they worry. While most children develop appropriately given enough time, some children do experience issues with speech-language development.
Many young children develop speech skills within a wide range of time and with different capabilities. However, by a certain point, most children have begun to learn how to speak and communicate effectively. Of course, when parents notice that their child isn’t keeping up with other children, they worry. While most children develop appropriately given enough time, some children do experience issues with speech-language development.
Delays in speech development are caused by a variety of reasons, so it is important to understand what these potential causes are, as well as why a thorough, professional evaluation may be needed for some children. Too often parents, relatives, neighbors, and school officials believe they know for sure that something is off, but in fact, their guesses may be dead wrong. Instead, accurate diagnosis of speech-language problems requires a thorough evaluation by trained professionals and includes testing of both speech-language and hearing to determine the root cause of any potential problems. Continue reading Guest Post: 10 Common Causes of Pediatric Speech and Language Problems
Boston MA- First conference of the Fall 2011 season:
October 17, 2011: Got to co-present with my favorite pediatrician (Alla Gordina, MD, FAAP) an interesting clinical case in front of American Academy Of Pediatrics: Council on Foster Care, Adoption and Kinship Care. Granted my part was via phone and connection wasn’t great but it so nice to see medical professionals being interested in ancillary professionals’ perspective on issues of internationally adopted children.
Presentation Title: A Case of Isolated Social Pragmatic Language Deficits in an Internationally Adopted Child
Presentation Highlights:
Language based deficits may affect internationally adopted children many years post adoption
Even children adopted at very young ages can present with subtle BUT significant delays in select areas of functioning (see below)
One such delay may be in the area of social pragmatic functioning or the use of language
Select examples of social pragmatic deficits include:
Implications for Professionals:
Very easy to misdiagnose a child with social pragmatic deficits as someone with psychiatric disturbances (e.g., ADHD or Autism) without multidisciplinary differential diagnosis
“Low risk referrals” do carry a significant risk of deprivation-related issues, which can surface years after adoption
Internationally adopted children with behavioral, listening, sensory, and any unusual deficits need a differential diagnosis (including assessment of language abilities before a conclusive diagnosis is made)

You have decided to consult a private speech language pathologist because of concerns over your adopted child’s developing speech and language. But how do you choose the right one? There are many speech therapists out there and not all of them are alike in experience and skills. On top of it all, you are also looking for a bilingual therapist, one who is not only proficient in your child’s native language but is also knowledgeable regarding the speech and language issues of international adoptees. That is not an easy decision to make, especially for many parents who until now have not had any direct contact with a speech language pathologist.
Not to worry, below is a list of simple guidelines designed to assist you in the right therapist selection.
Let’s begin with something basic: educational and professional credentials. A speech language pathologist must possess a Master’s Degree (or its equivalent) from a reputable academic institution of higher learning. They must also have a Certificate of Clinical Competence from the American Speech Language Hearing Association as well as an appropriate licensure from the state in which they maintain their practice. Additionally, it is highly recommended that they have Bilingual Certification as it indicates that they have completed the necessary academic coursework and are proficient in the issues surrounding normal and disordered speech-language acquisition of bilingual children in dual languages.
Now we are ready to proceed to experience. Here its gets a little tricky. The traditional approach: “I want the therapist with a gazillion years of experience” is just not going to be all that useful. It can’t be just any experience; it has to be the right experience! After all do you really want a therapist with 30 years of experience in exclusively treating articulation deficits when your child needs help with feeding and swallowing or with developing augmentative/alternative communication?
It is important to choose a therapist who has a rich and varied experience from multiple settings, total years of experience may not be as important as the qualitative value of that experience. A good therapist has probably spent a considerable portion of his/her time in a variety of settings from schools and early intervention agencies to hospitals and rehabilitation clinics. As the result of working in these diverse environments that therapist is much more likely to come up with innovative ideas and solutions to your child’s problems as opposed to just using the same old remediation strategies that they have learned way back then. It is also a good idea to inquire regarding the areas of specialization of the therapist in order to find out whether he/she has successfully treated children with similar problems to your child’s.
Typically, private speech language pathologists who maintain some type of pediatric hospital affiliation (e.g. per diem or part-time employees) are up to date regarding the current methodologies, which they apply to practice on daily basis. The reasons for that are twofold:
Speech departments in hospitals deal with diverse caseloads, with patients ranging in ages, diagnoses (some of which can be quite unusual), and levels of severity. In an average inpatient department staff SLP’s are expected to carry caseloads of 12-16 patients per day.
In order to keep up with the caseload diversity and with the latest treatment trends, hospitals require these SLP’s to actively take professional development courses in order to provide their patients with the best quality of care.
This brings us to another important consideration: professional development. To maintain their state licensure and national certification all therapists are required to take professional education courses in order to stay up to date with all the relevant research and new treatments developed in our field. The minimum requirement is to accumulate 30 professional education hours every 3 years whether by attending courses in person, taking them online through qualified providers, or by conducting workshops and presenting at conferences. Professional development provides the speech therapists with an opportunity to use evidence based techniques supported and tested by research to treat a variety of communication disorders. Consequently, when selecting your therapist it is important to find out just how up to date are they on the current treatment methods and methodologies pertaining to your child speech and language deficits. You can always find out this information by politely questioning the therapist regarding their background and “resume highlights.”
It is also important to find out whether you understand and agree with the therapist’s methods and approaches. For example, if your child is a toddler, it probably does not make sense for him/her to spend most sessions doing worksheets and drills when he/she needs to be engaged in play based, child centered therapy. Don’t be intimidated by the therapist’s credentials and your lack of knowledge, if something they said doesn’t make sense, ask follow up questions and/or look up pertinent information online. While you should not use the internet to diagnose your child’s problems, it can be used as a valuable learning tool to look up information and to share ideas with other parents who experience similar difficulties.
Now that we have specified general selection criteria, let’s talk about how to initiate your search for the right SLP. The best way is again to go online. Start your search by going to the ASHA website and clicking on the ‘Find Professional Button’ located in the top of the page and then follow the instructions on the screen. Fill out your search criteria carefully but don’t be too specific. For example, don’t look for a Russian speaking SLP in Blue Creek, California as you will probably not find one. Instead try typing in the first 3 digits of your zipcode or your state of residence (if it’s small enough) and don’t forget to specify the language of the practitioner. That will get you the optimum results.
Once you have located several candidates, you can narrow down the search by trying to learn something about them online. Google the clinician’s name (or the name of their practice) to see whether they have their own website, have written any articles or have been profiled by any organizations. To make sure that your practitioner’s licensure is up to date, visit your state’s speech language accreditation website and type in the last name of the professional. Typically, a window will pop up listing the therapists’ names alphabetically, find the one you are looking for and check if their license is active. Finally, armed with your research, create a list of questions that you might have for the practitioners and start making phone calls. Find out all the pertinent information and don’t forget to ask about rates which may differ depending on what services the practitioner is providing.
Please note that many private practitioners refuse to deal with insurance companies directly due to the hassle of multiclient billing as well as extended wait for reimbursement. They will instead provide you with a letter for your insurance company, containing the necessary diagnosis and treatment codes, incurred fees as well as a brief description of services provided, and will expect you to apply for reimbursement on your own.
Now that we have gone over the selection process in some detail, please keep in mind that you can always learn more information on this and any other speech pathology related topic by visiting the ASHA website and clicking on the ‘Public’ tab located at the top of the screen.
Best of luck in your search and happy hunting!
Useful websites:
Find a Professional SLP on the ASHA website: http://www.asha.org/proserv/
State Contacts & Licensure Requirements: http://www.asha.org/about/legislation-advocacy/state/